10327203;a4
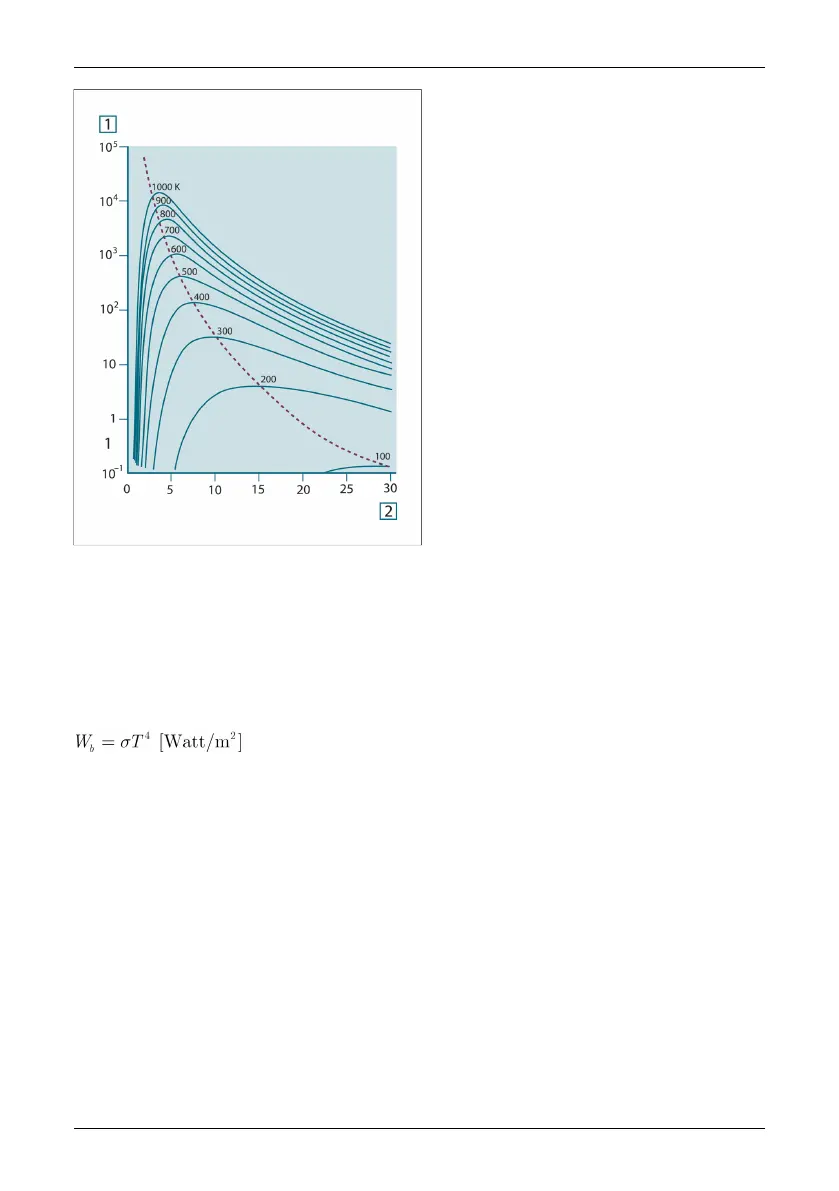
Figure 21.6 Planckian curves plotted on semi-log scales from 100 K to 1000 K. The dotted line represents
the locus of maximum radiant emittance at each temperature as described by Wien's displacement law.
1: Spectral radiant emittance (W/cm
2
(μm)); 2: Wavelength (μm).
21.3.3 Stefan-Boltzmann's law
By integrating Planck’s formula from λ = 0 to λ = ∞, we obtain the total radiant
emittance (W
b
) of a blackbody:
This is the Stefan-Boltzmann formula (after Josef Stefan, 1835–1893, and Ludwig
Boltzmann, 1844–1906), which states that the total emissive power of a blackbody is
proportional to the fourth power of its absolute temperature. Graphically, W
b
represents
the area below the Planck curve for a particular temperature. It can be shown that the
radiant emittance in the interval λ = 0 to λ
max
is only 25% of the total, which represents
about the amount of the sun’s radiation which lies inside the visible light spectrum.
Publ. No. T559498 Rev. a461 – ENGLISH (EN) – August 19, 2010 73
21 – Theory of thermography

 Loading...
Loading...