MOCA
Version 1.0, 04/2015. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
42
Version 1.0, 04/2015. Copyright 2015 Hitron Technologies
42
Hitron HT-EMN2 User’s Guide
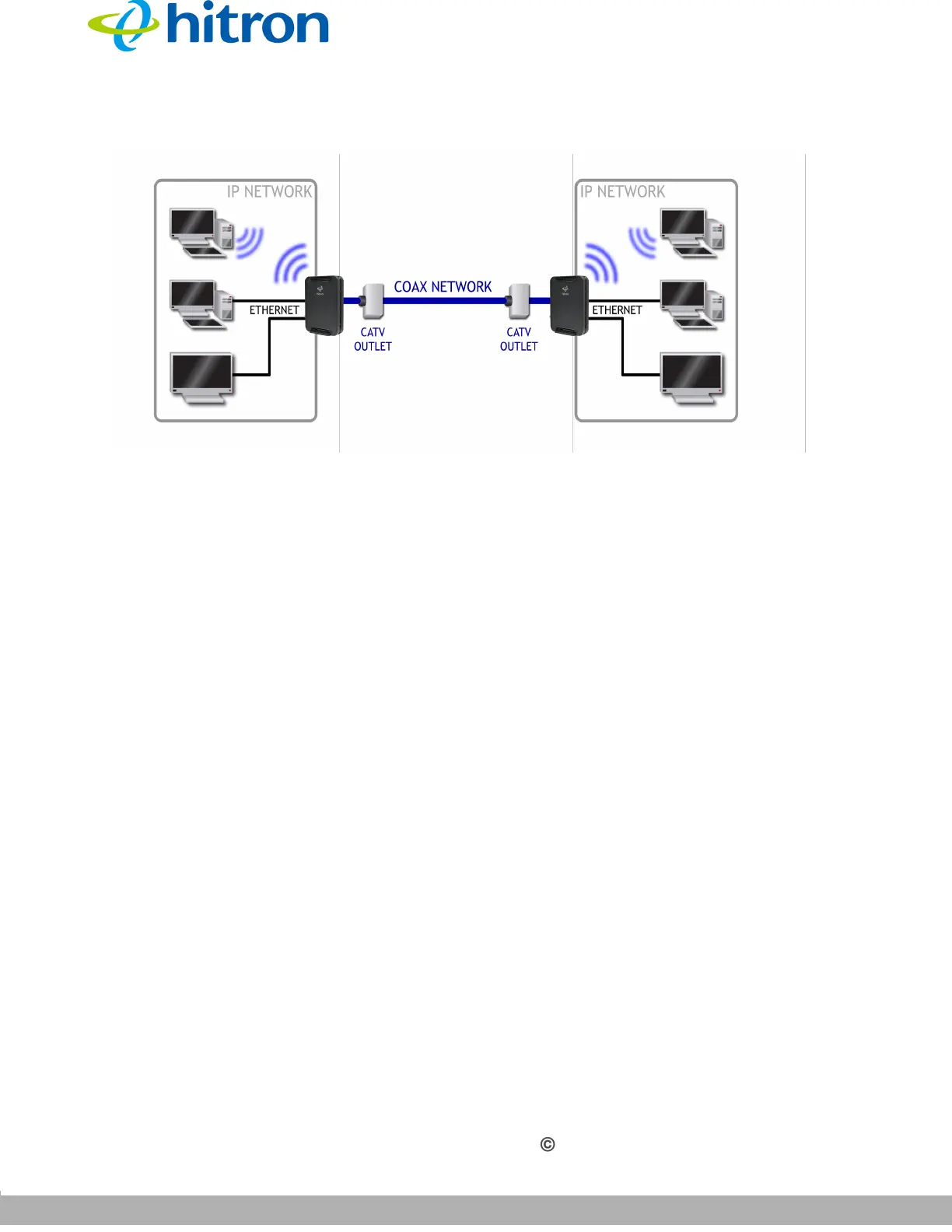
Figure 14: Bridging the Gap Between IP and Coaxial Networks
MoCA traffic on the coax network does not interfere with existing broadcasts from
cable, telco, IPTV or satellite service providers, as it makes use of a previously-
unused segment of the RF spectrum. The medium is ideal for real-time applications,
providing high data throughput (100Mbps~1Gbps) with low latency, jitter or data loss.
Also, coax cabling is generally better-shielded than IP networking media, especially
wireless.
Applications to which MoCA networking is well-suited include:
Video on Demand (VoD)
Multi-room, multi-camera Digital Video Recording (DVR)
Gaming (LAN or online multiplayer)
Internet video
Home automation
Video conferencing
5.1.1.1 Horizontal vs. Vertical Communications
Unlike traditional coax networking (TV, satellite, IPTV, etc.) MoCA devices do not
need to receive data from a single source. It is “outlet-to-outlet”. Each MoCA network
uses a Network Controller (NC) to manage the network’s communications, but any
ECB on the network is capable of acting as the NC. By default, the NC is chosen by
negotiation between all ECBs on the network, based on factors such as signal
strength.
 Loading...
Loading...