ENGLISH
27
According to our experience, the damping rate of the compression stage
can remain unchanged. The damping rate of the rebound stage can be
reduced by a few clicks for a softer spring or increased by a few clicks for a
harder spring.
Checking the basic setup of the telescopic fork
The precise riding sag of the telescopic fork cannot be determined for
various reasons. Similar to the shock absorber, smaller deviations in your
weight can be compensated by adjusting the spring preload. However, if
your telescopic fork bumps frequently (hard end stop during compression),
you should install harder fork springs to avoid damaging the telescopic fork
and frame.
Changing the spring preload on the telescopic fork (SX
models)
The telescopic forks of the SX models come with a preload adjuster for easy
adjustment of the spring preload. You can adjust the spring preload ± 9 mm
by turning the adjusting screws (basic position = middle position).
NOTE:
Always turn the adjusting screws the same distance on both fork legs.
Different spring preloads on the fork legs will reduce the telescopic fork's
response.
Changing the spring preload on the telescopic fork
(MXC/EXC models)
The telescopic forks for these models must be partly disassembled to adjust
the spring preload (see WP manual). Pretension spacers are available in
heights of 1.5, 2.5 and 5 mm (see spare parts catalog). The fork springs
may not be pretensioned by more than 20 mm.
The preload adjuster used in the SX models can easily be retrofitted for the
telescopic forks of the MXC/EXC models.
NOTE:
WP precisely adjusts the spring pressure by inserting pretension spacers.
Fluctuations in production are compensated with pretension spacers in
various heights. This can cause the fork springs in the fork legs to have
different degrees of pretension. Fork springs and pretension spacers should
always stay together.
Replacing fork springs
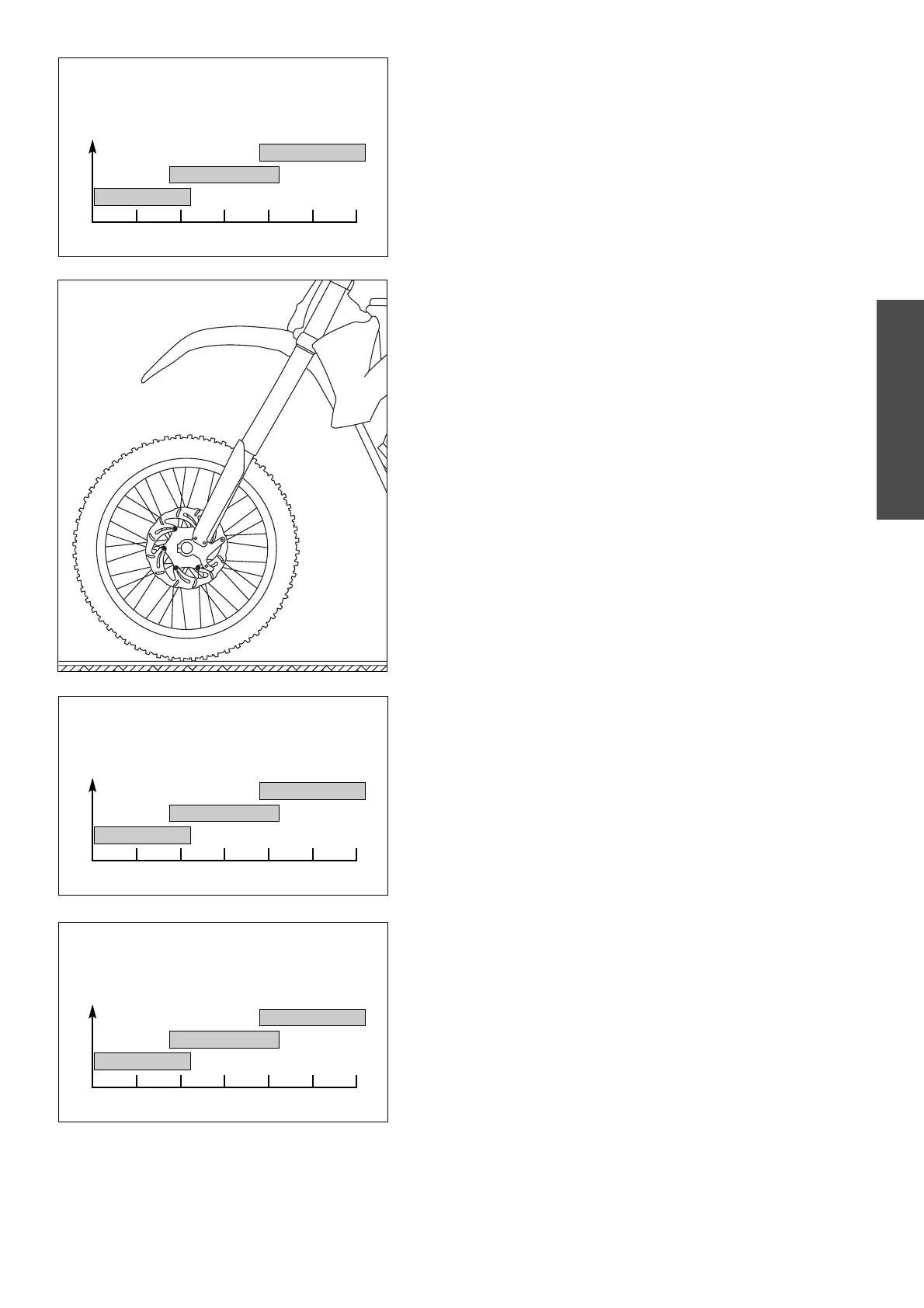
If you weigh less than 70 kg or more than 80 kg, you should install the
respective fork springs. The correct spring rate is shown in the illustrations.
The standard spring is shown in bold print. The type number of the
telescopic fork is embossed on the caps on the top of the telescopic fork.
If you are uncertain which spring to use, contact your KTM workshop.
According to our experience, the damping rate of the compression stage
can remain unchanged. The damping rate of the rebound stage can be
reduced by a few clicks for a softer spring or increased by a few clicks for a
harder spring.
60
SPRING RATE
65 70 75 80 85 90
RIDERS WEIGHT INCLUSIVE GEARS IN KILOGRAM
88/250
88/250
88/250
PDS 1218Y772 250/400/450/525
MXC/MXC-Desert/EXC/EXC-G
60
SPRING RATE
65 70 75 80 85 90
RIDERS WEIGHT INCLUSIVE GEARS IN KILOGRAM
4,6 N/mm
4,8 N/mm
4,2 N/mm
1418Y747 450/525 SX
60
SPRING RATE
65 70 75 80 85 90
RIDERS WEIGHT INCLUSIVE GEARS IN KILOGRAM
4,2 N/mm
4,4 N/mm
4,0 N/mm
1418Y748 250/400/450/525
MXC/MXC-Desert/EXC/EXC-G

 Loading...
Loading...











