9
DEVICE EXPLANATION
9.7 File Register (R)
9
- 62
9
Device Explanation
10
CPU Module Processing
Time
11
Procedure for Writing
Program to CPU Module
AppendicesIndex
9.7 File Register (R)
(1) Definition
File registers are expansion devices for data registers.
The file registers can be used at the same processing speed as the data registers.
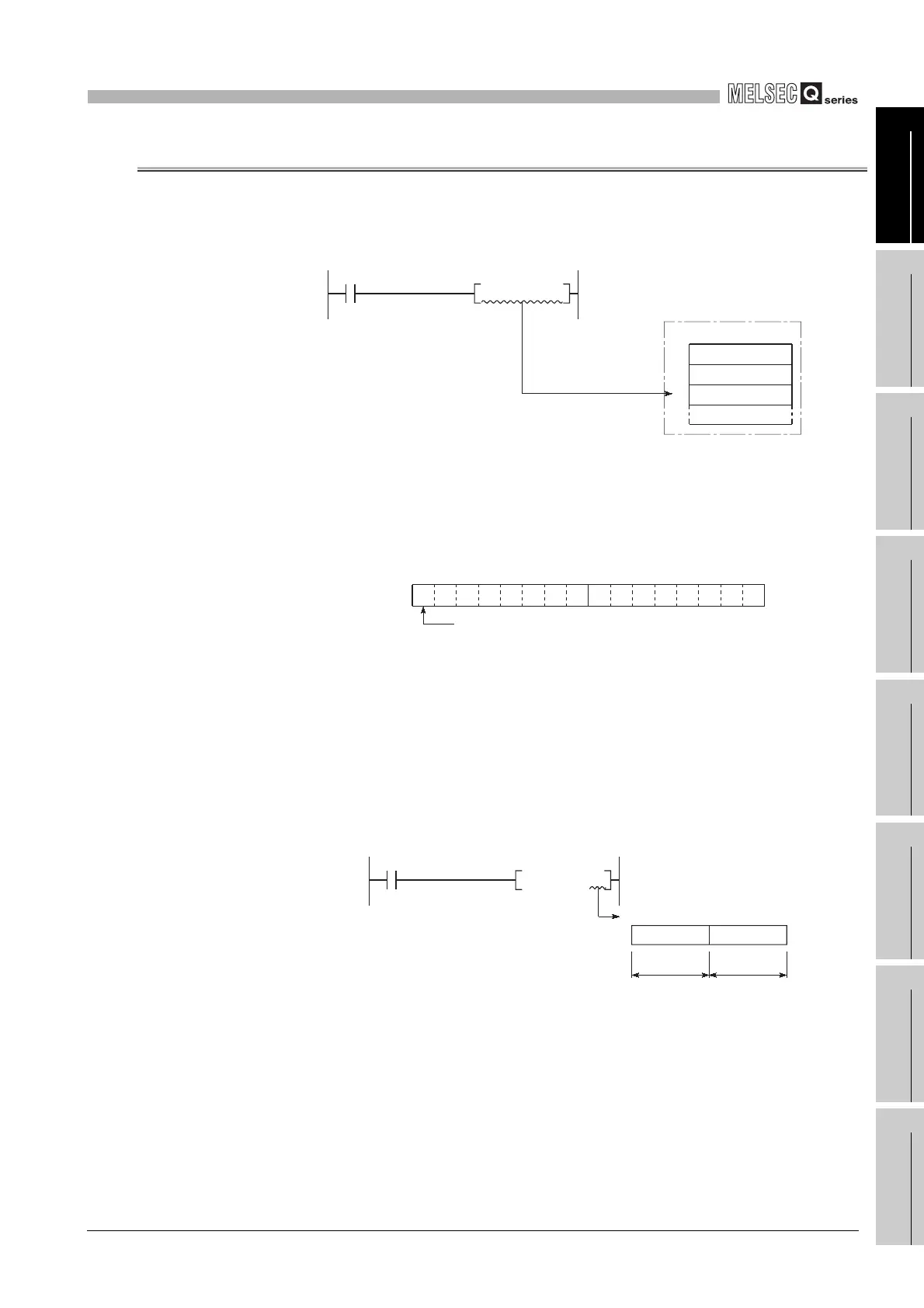
(2) Bit configuration of file register
(a) Bit configuration and read and write units
File registers, which consist of 16 bits per point, read and write data in 16bit units.
(b) When file register is used for 32-bit instruction
If the file registers are used for 32-bit instructions, the data will be stored in
registers Rn and Rn + 1.
The lower 16 bits of data are stored in the file register No. (Rn) designated in the
sequence program, and the upper 16 bits of data are stored in the designated file
register No.+ 1.
For example, if file register R2 is designated in the DMOV instruction, the lower 16
bits are stored in R2, and the upper 16 bits are stored in R3.
Two file registers can store a range of numeric data from -2147483648 to
2147483647 or from 0
H
to FFFFFFFF
H
. (The most significant bit in a 32-bit
configuration is a sign bit.)
Diagram 9.65 Write to file register
Diagram 9.66 Bit configuration of file register
Diagram 9.67 Data transfer by 32-bit instruction and storage destination
K100 R2MOV
"100" is written to R2.
File register
R0
R1
R2
Rn
b15
to
b0
The most significant bit is sign bit.
D0 R2DMOV
R3
Upper 16 bits Lower 16 bits
R2
Processing object: R2, R3
 Loading...
Loading...











