Instruction Manual Easygraph
Page 29
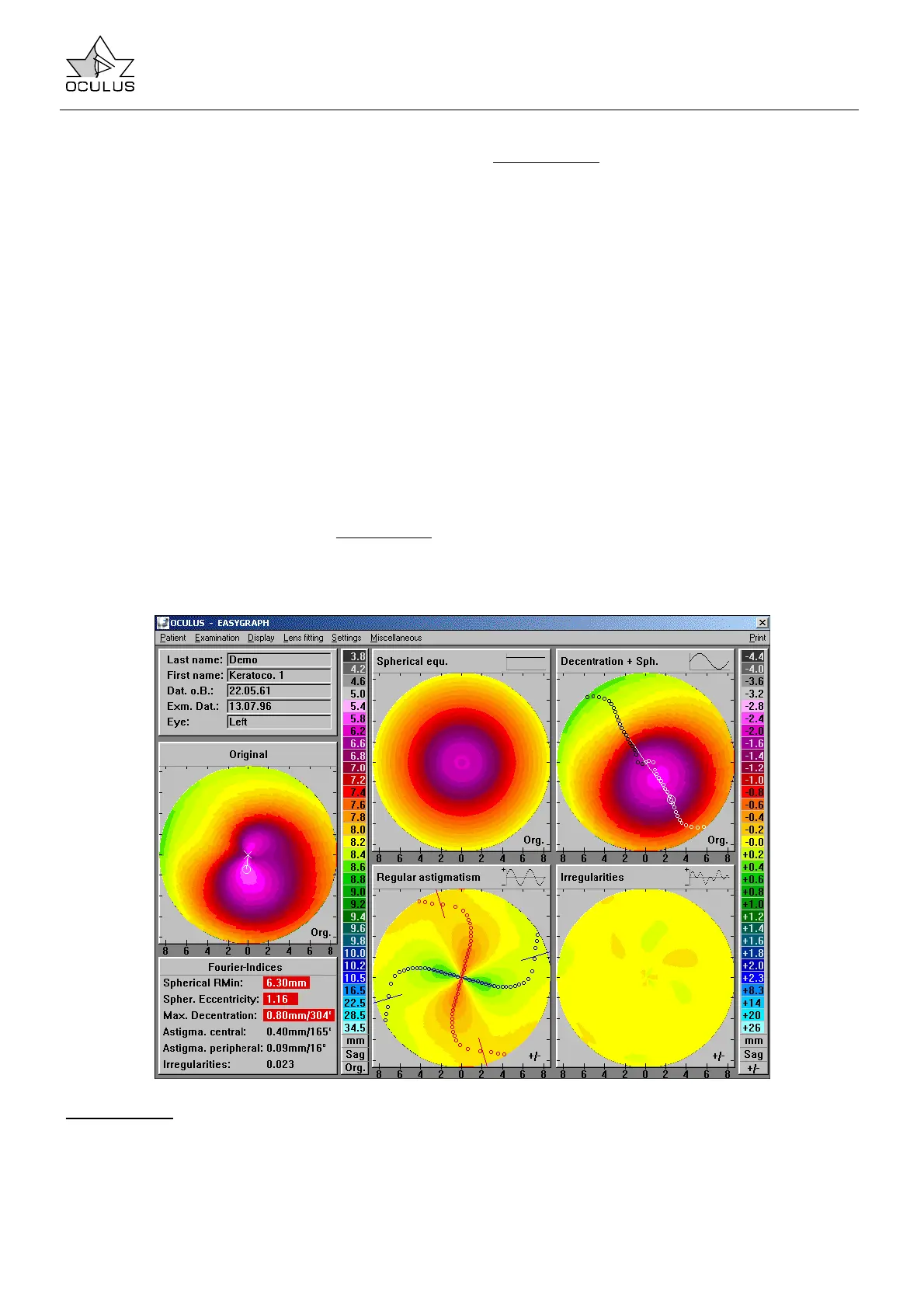
• Spherical RMin: minimal radius of curvature of
the spherical component
• Spher. Eccentricity: corneal eccentricity
calculated from the spherical component. This
must not be confused with the eccentricity at
30°, which is determined according to the
sagittal radii method.
• Max. Decentration: maximum value and
position of decentration in the “Decentration”
diagram
• Astigma. central: curvature difference and axis
position of regular, central astigmatism
• Astigma. peripheral: curvature difference and
axis position of regular, peripheral astigmatism
• Irregularities: mean of all deviations in the
“Irregularities” diagram
Note Ö Pathological values are highlighted in red
as a matter of course.
Color bars:
The “Fourier Analysis“ display uses two color bars
with identical color increments. The left color bar
(Org.) corresponds to the overview display, while the
right color bar
has a relative (+/-) scale. At the
bottom right of every topographic map is an
indication of the color bar being used.
The original color bar (left) is only used in the
“Original” and the “Spherical equivalent" maps. The
“Decentration", “Regular astigmatism” and
“Irregularities" maps can only be represented
using the relative color bar (+/-) because they
represent additive components of the original image.
However, if “Spherical equivalent” is added to either
“Irregularities” or “Decentration”, then the resulting
maps will refer to the left color bar (Org.) (see also
7.5.4 page 62).
Curvature values can be queried in any topographic
image by clicking onto the location of interest (left
mouse button). This causes the curvature value at
that location to be displayed above the mouse
pointer.
7.5.2.4.1 Applications of the Fourier Display Mode in Keratokonus
In keratoconus one finds the following deviations
from the image generated by a normal eye, each of
which may be more or less pronounced depending
on the stage of the disease.
“Spherical equ.”
The minimal radius of curvature is steeper and
normally less than 6.93 mm for sagittal curvature
(6.87 for tangential curvature), while eccentricity
may exceed 0.85. However, both parameters are
subject to considerable variation and may not be
used as indices in isolation from each other.

 Loading...
Loading...