1 - 3
1 Introduction to Instructions for Safety Control Units and Interpreting Instruction Descriptions
NX-series Safety Control Unit Instructions Reference Manual (Z931)
1-2 Interpreting Instruction
Descriptions
1
1-2-1 Items
1-2 Interpreting Instruction Descriptions
The notation that is used to describe instructions is explained in this section.
The following items are provided. The order of the items is not the same for all instructions. If there are
items that are specific to one type of instruction, they are explained in the section for each instruction
type.
1-2-1 Items
Item Description
Instruction The instruction word is given.
Name The name of the instruction is given.
FB/FUN Whether the instruction is a function block (FB) instruction or a function (FUN) instruction
is given.
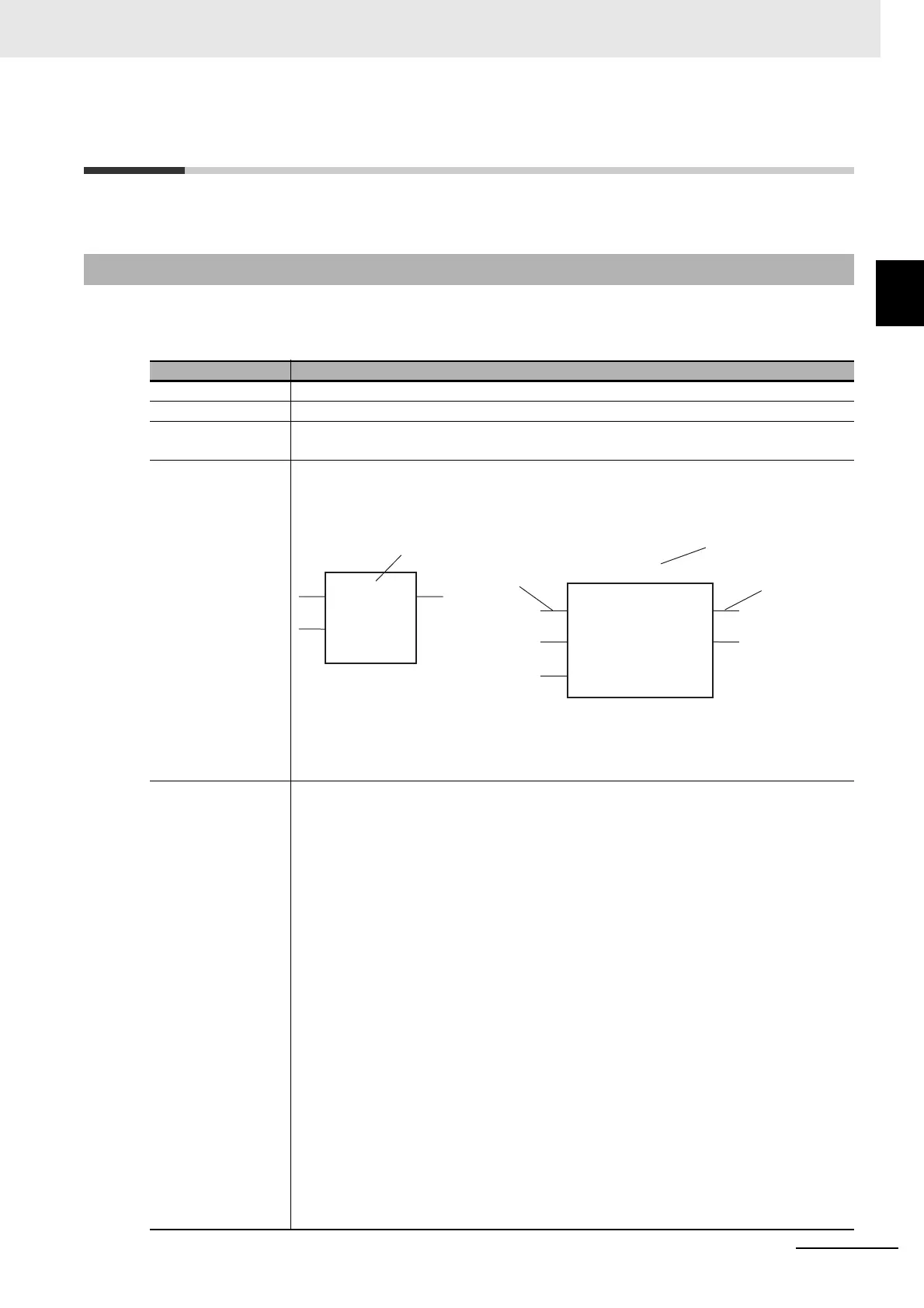
Graphic expression The figure that represents the instruction in a function block diagram is given.
Instance specification: An instance of an instruction is indicated by “XX_instance” above a
FB instruction. You must assign an instance name to any instance of an instruction that
you specify.
Variables • Variable
The input variable or output variable is given.
•Name
The name of the variable is given.
Example: Up-counter
• I/O
Whether the variable is an input variable or output variable is given.
• Description
The meaning of the variable and any restrictions are given.
• Valid range
The range that the variable can take is given. “Depends on data type” indicates that the
valid range of the variable depends on the data type that you use. The valid ranges of
the data types are given later in this section.
•Default
The specified default value is automatically used for the variable if you do not assign a
parameter to the instruction before it is executed. “---” indicates the following:
Input variables: The default value of the data type of the input variable is assigned. The
default values of the data types are given later in this section.
Output variables: Default values are not set.
• Data type
The data type of the variable is given. Broadly speaking, there are two classifications of
data types: safety signals and non-safety signals. These two classifications of data
types are described later.
Instance specification
Input variable
name
Output variable
name
ADD
Instruction word
SF_CTU
CU
SF_CTU_instance
RESET
PV
Q
CV
Example for a FUN
Instruction
Example for a FB
Instruction

 Loading...
Loading...