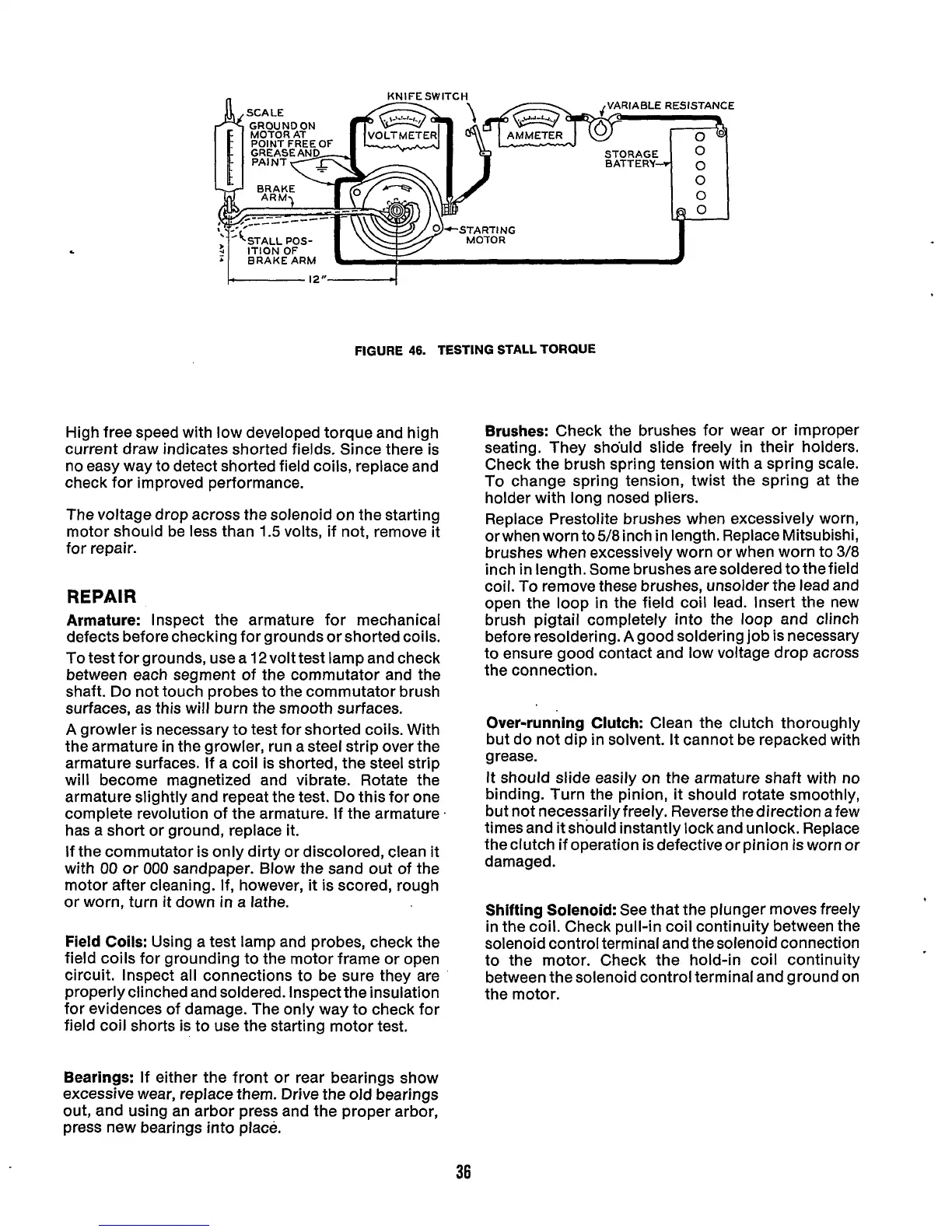
VARIABLE RESISTANCE
STALL
POS-
BRAKE
ARM
I----
12"-4
FIGURE
46.
TESTING
STALL
TORQUE
High free speed with low developed torque and high
current draw indicates shorted fields. Since there is
no easy way to detect shorted field coils, replace and
check for improved performance.
The voltage drop across the solenoid on the starting
motor should be less than
1.5
volts, if not, remove it
for repair.
REPAIR
Armature:
Inspect the armature for mechanical
defects before checking for grounds or shorted coils.
To
test for grounds, use a l2volt test lamp and check
between each segment of the commutator and the
shaft.
Do
not touch probes to the commutator brush
surfaces, as this will burn the smooth surfaces.
A
growler is necessary to test for shorted coils. With
the armature in the growler, run a steel strip over the
armature surfaces.
If
a coil is shorted, the steel strip
will become magnetized and vibrate. Rotate the
armature slightly and repeat the test.
Do
this for one
complete revolution of the armature. If the armature
has a short or ground, replace it.
If the commutator is only dirty or discolored, clean
it
with
00
or
000
sandpaper. Blow the sand out of the
motor after cleaning.
If,
however,
it
is scored, rough
or worn, turn it down in a lathe.
Field Coils:
Using a test lamp and probes, check the
field coils for grounding to the motor frame or open
circuit. Inspect all connections to be sure they are
properly clinched and soldered. Inspect the insulation
for evidences of damage. The only way to check for
field coil shorts is to use the starting motor test.
Brushes:
Check the brushes for wear or improper
seating. They should slide freely in their holders.
Check the brush spring tension with a spring scale.
To change spring tension, twist the spring at the
holder with long nosed pliers.
Replace Prestolite brushes when excessively worn,
orwhen worn to 5/8inch in length. Replace Mitsubishi,
brushes when excessively worn or when worn to 3/8
inch in length. Some brushes aresoldered to the field
coil. To remove these brushes, unsolder the lead and
open the loop in the field coil lead. Insert the new
brush pigtail completely into the loop and clinch
before resoldering.
A
good soldering job is necessary
to ensure good contact and low voltage drop across
the connection.
Over-running Clutch:
Clean the clutch thoroughly
but do not dip in solvent.
It
cannot be repacked with
grease.
It should slide easily on the armature shaft with no
binding. Turn the pinion,
it
should rotate smoothly,
but not necessarily freely. Reverse the direction a few
times and
it
should instantly lock and unlock. Replace
the clutch if operation is defective or pinion is worn
or
damaged.
Shifting Solenoid:
See that the plunger moves freely
in the coil. Check pull-in coil continuity between the
solenoid control terminal and the solenoid connection
to the motor. Check the hold-in coil continuity
between thesolenoid control terminal and ground on
the motor.
Bearings:
If either the front or rear bearings show
excessive wear, replace them. Drive the
old
bearings
out, and using an arbor press and the proper arbor,
press new bearings into place.
36
 Loading...
Loading...