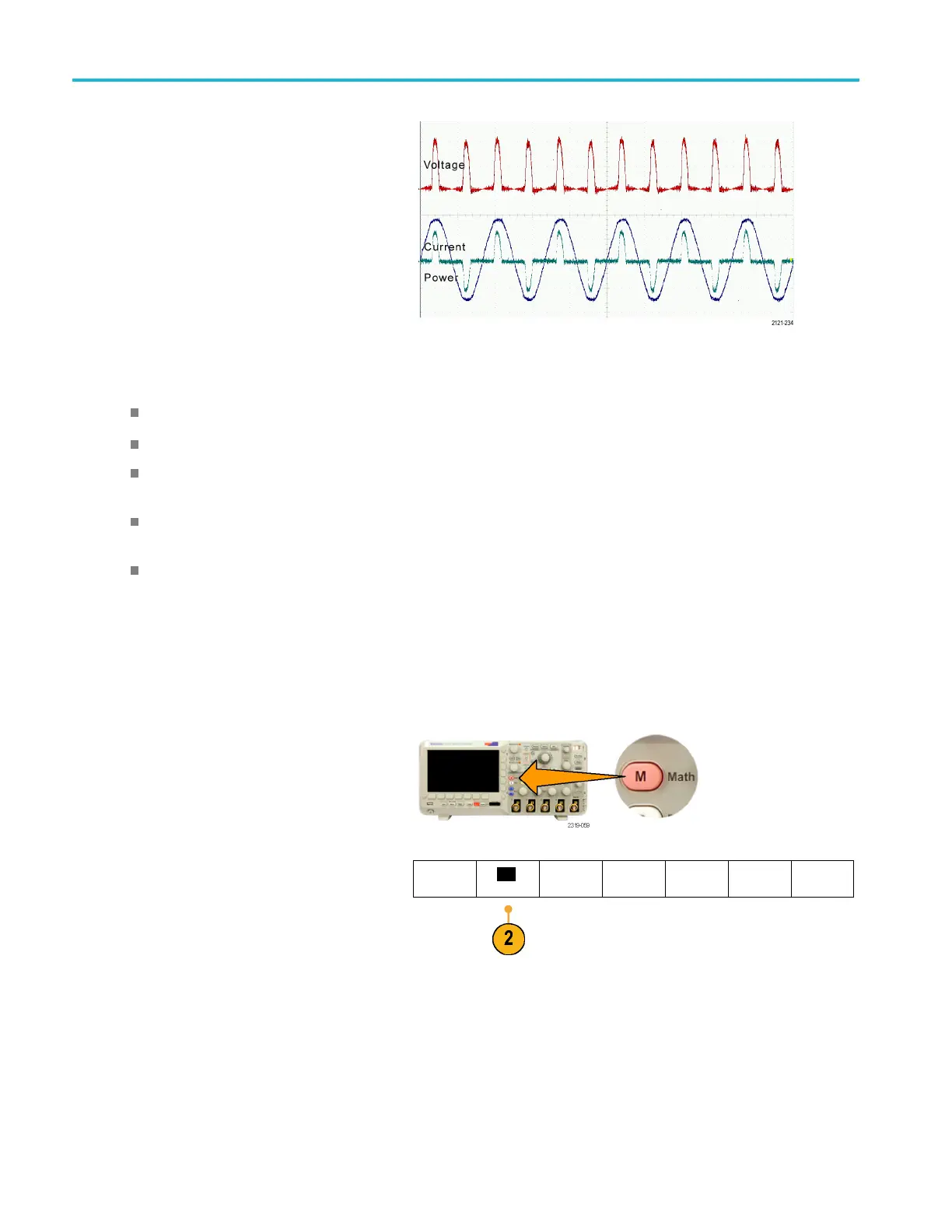
Analyze Wavefor
mData
For example, yo
u might calculate power
by multiplying a voltage waveform and a
current waveform.
Quick Tips
Math waveforms can be created from channel or reference waveforms or a combination of them.
Measurements can be taken on m ath waveforms in the same w ay as on channel waveforms.
Math waveforms derive their horizontal scale and position from the sources in their m ath expressions. Adjusting these
controls
for the source waveforms also adjusts the math waveform.
You can zo
om in on math waveforms using the inner knob of the Pan-Zoom control. Use the outer knob for positioning
the zoomed area. (See page 105, Using Wave Inspector to Manage Long Record Length Waveforms.)
Both math sources must have the same record length.
Using FFT
An FFT breaks down signals i nto component frequencies, whic h the oscilloscope uses to display a graph of the frequency
domain of a signal, as opposed to the oscilloscope's standard t ime domain graph. You can match these frequencies with
known system frequencies, such as system clocks, oscillators, or power supplies.
1. Push Math.
2. Push FFT.
Dual Wfm
Math
FFT About FFT
(M) Label
100 MSO2000B and DPO2000B Series Oscilloscopes User Manual

 Loading...
Loading...