2007.03.07Flow2 stairliftTab 06: Systematic fault finding
www.ThyssenKruppAccessibility.nl4
Systematic fault finding
Review the history
Consult the logbook to find out whether the stairlift was serviced recently, or whether any similar
notifications of faults have been made in the past.
The example of the lamp switching
The desk lamp’s bulb blows repeatedly. The bulb has already been replaced twice in the past month,
whilst normally these bulbs last for years. It’s time for a thorough inspection of the lamp.
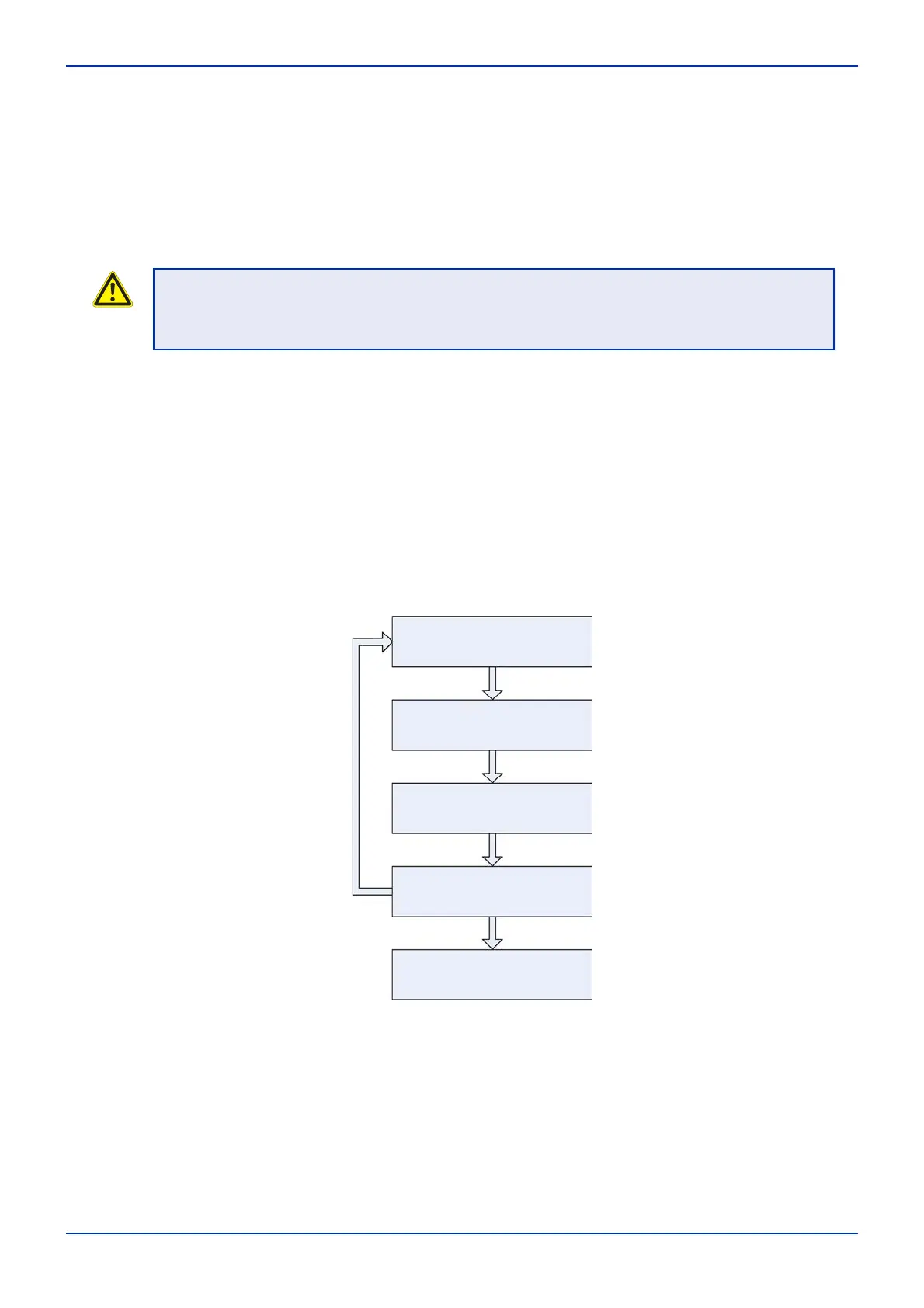
2.3 Fault analysis
During the fault analysis you repeatedly work through the following steps, whereby you continually
go into further depth until you examine the smallest replaceable components!
Define the area of the fault
You can define the area of the fault on the basis of the problem definition and your knowledge of the
system. The problem area is the collection of all those parts of the system that could contribute to the
problem.
CAUTION
In the event of the repeated occurrence of a fault do not simply repeat the corrective
action. The cause of the problem could be at a lower level.
Define the area of the fault
Distinguish possible causes
Determine the sequence of your
work
Eliminate causes
Find the real cause
Fig. 2-2 Fault finding steps

 Loading...
Loading...