User Guide 46
Configuring VLAN Overview
1
Overview
VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) is a network technique that solves broadcasting issues
in local area networks. It is usually applied in the following occasions:
To restrict broadcast domain: VLAN technique divides a big local area network into
several VLANs, and all VLAN traffic remains within its VLAN. It reduces the influence of
broadcast traffic in Layer 2 network to the whole network.
To enhance network security: Devices from different VLANs cannot achieve Layer 2
communication, and thus users can group and isolate devices to enhance network
security.
For easier management: VLANs group devices logically instead of physically, so devices
in the same VLAN need not be located in the same place. It eases the management of
devices in the same work group but located in different places.
There are 3 types of VLAN modes supported on the switch:
MTU VLAN
MTU VLAN (Multi-Tenant Unit VLAN) defines an uplink port which will build up several
VLANs with each of the other ports. Each VLAN contains two ports, the uplink port and
one of the other ports in the switch, so the device connected to the uplink port can
communicate with the device connected to any other port, but devices connected to other
ports cannot communicate with each other.
Port Based VLAN
VLANs are divided based on ports. In port based VLAN mode, each port can only be added
to one VLAN.
802.1Q VLAN
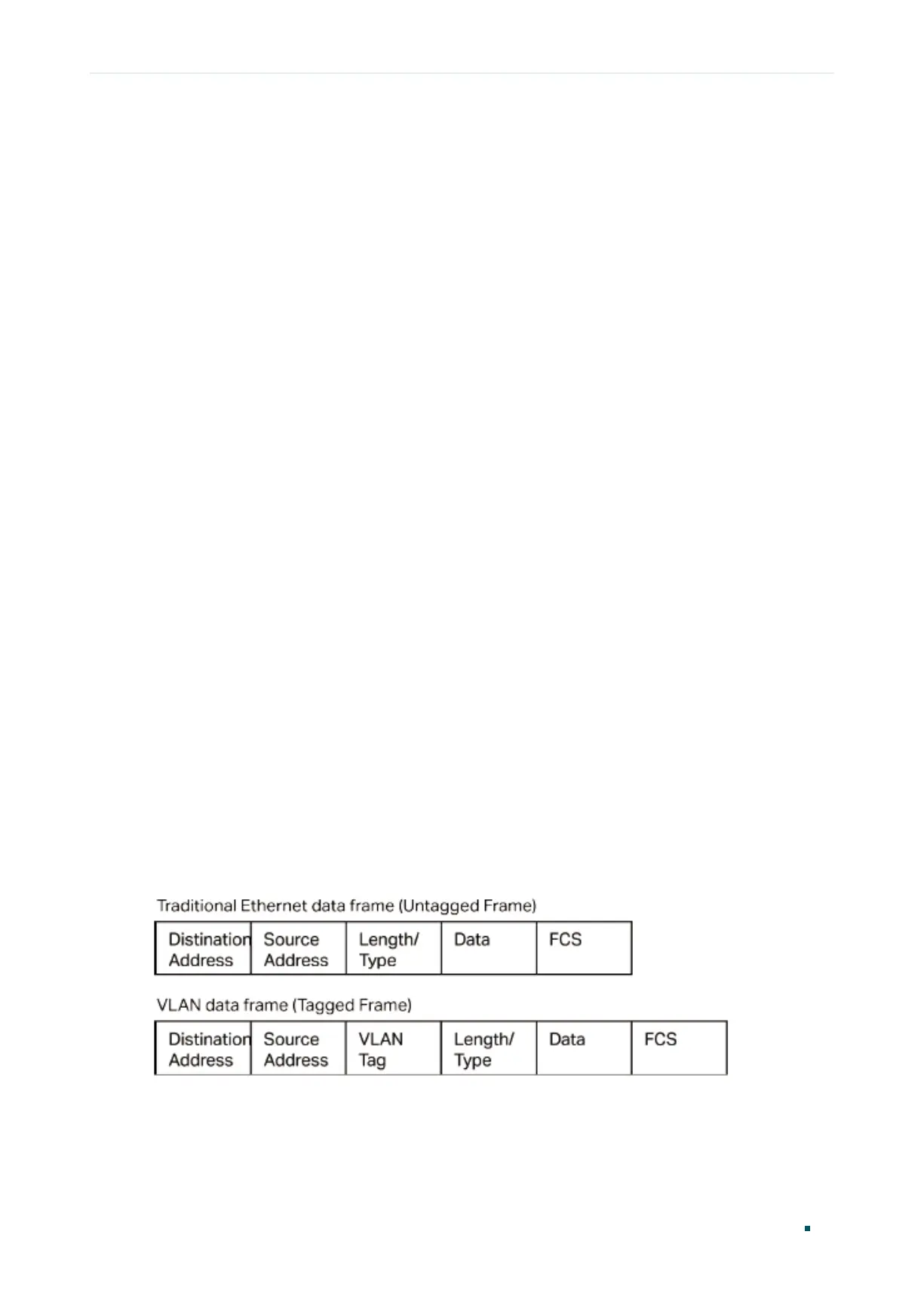
The IEEE 802.1Q protocol defines a new format of VLAN data frame (Tagged Frame). As the
following figure shows, compared to the traditional Ethernet data frame (Untagged Frame),
the VLAN data frame (Tagged Frame) adds a VLAN tag.
On receiving a tagged frame, the switch checks the VID (VLAN ID) contained in the VLAN
tag to determine which VLAN the frame belongs to. On receiving an untagged frame, the
switch will first insert a VLAN tag to the frame, using the PVID (Port VLAN ID) of the port as
its VID, and then forward it as a tagged frame.

 Loading...
Loading...











