Chapter 7 Optional AccessoriesME300
7-25
Installation
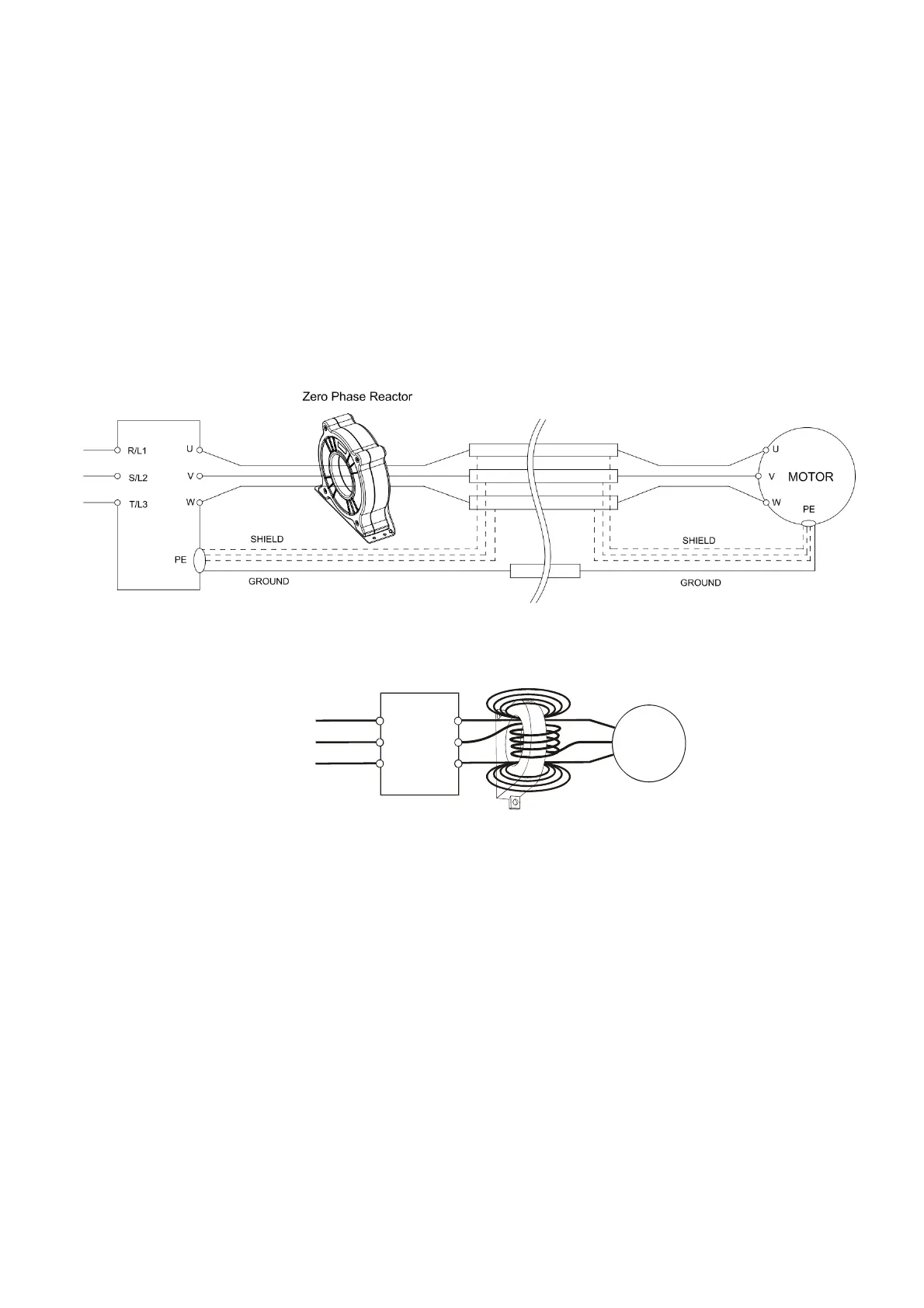
During installation, pass the cable through at least one zero phase reactor.
Use a suitable cable type (insulation class and wire section) so that the cable passes easily through the
zero phase reactor. Do not pass the grounding cable through the zero phase reactor; only pass the motor
wire through the zero phase reactor.
With longer motor cables the zero phase reactor can effectively reduce interference at the motor
output. Install the zero phase reactor as close to the output of the drive as possible. Figure A shows the
installation diagram for a single turn zero phase reactor. If the wire diameter allows several turns, Figure
B shows the installation of a multi-turn zero phase reactor. The more turns, the better the noise suppression
effect.
Figure A: Single turn wiring diagram for a shielding wire with a zero phase reactor
Power
Supply
Zero Phase Reactor
MOTOR
U/T1
V/T2
W/T3
R/L1
S/L2
T/L3
Figure B: Multi-turn zero phase reactor
Installation notes
Install the zero phase reactor at the output terminal of the frequency converter (U.V.W.). After the zero
phase reactor is installed, it reduces the electromagnetic radiation and load stress emitted by the wiring of
the frequency converter. The number of zero phase reactors required for the drive depends on the wiring
length and the drive voltage.
The normal operating temperature of the zero phase reactor should be lower than 85°C (176°F).
However, when the zero phase reactor is saturated, its temperature may exceed 85°C (176°F). In this
case, increase the number of zero phase reactors to avoid saturation. The following are reasons that might
cause saturation of the zero phase reactors: the drive wiring is too long, the drive has several sets of loads,
the wiring is in parallel, or the drive uses high capacitance wiring. If the temperature of the zero phase
reactor exceeds 85°C (176°F) during the operation of the drive, increase the number of zero phase
reactors.
 Loading...
Loading...











