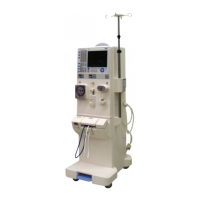
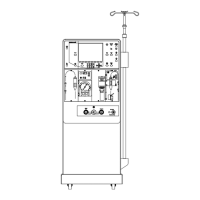
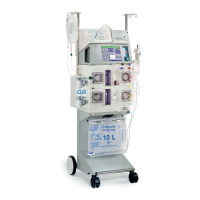
Fresenius Medical Care 4008 4/09.03 (TM) 8-19
8.7 P.C.B. LP 450-2 Level detector control (LD)
8.7.1 Description
● Audible section (transmitter)
The self-capacitance of the transmitting converter is charged up to +12 V via R78 and discharged
periodically via T9. The discharging current incites the oscillator to a dampened ultrasonic
oscillation. With bridge BR1 being inserted in the calibration position (1-2), the converter is
charged up to +6 V only, owing to the voltage division via R78 and R46. This reduces the
transmitting amplitude to half its size. With transistor T8 being activated by the LDSA signal, the
transmitting amplitude is reduced to a third of its size (test) due to the voltage division via R78 and
R79.
● Audible section (receiver)
Up to the outputs of the monostable alarm circuits IC 3 and IC 7 respectively, the two receiver
channels are identical. This is the reason why only the upper channel will be described. The
voltage emitted by the receiving converter is amplified by T2 in the amplifier stage and delivered
to OP IC 1, which is connected as precision rectifier. The amplified positive half waves, which are
emitted to pin 3 of comparator IC 2 via the RC element R6 and C6, appear at the cathode of DI3.
As soon as the peaks of the signal envelope pending there exceed the reference voltage at pin 2,
output 1 emits H pulses at 90-ms intervals, which, inverted via T3, are applied to the trigger input
pin 5 of the first monostable circuit IC 3. The two monostable circuits of IC 3 can be retriggered.
Due to their loading, the first one has a time constant of 60 ms and the second of 470 ms. The first
60-ms time constant has been selected such that, after each trigger pulse on the input side, the
output can return to its initial position, until the next trigger pulse arrives. If this is the case, the
second monostable circuit is retriggered at 90-ms intervals, while its output LDA1 remains at H
level (alarm-free). Should comparator IC 2 not emit trigger pulses due to too small an input signal,
the second monostable circuit returns to its initial position after 470 ms, while inducing L level at
pin 14 of plug X351. The monitor interprets this L level as level detector alarm, which stops the
blood systems.
The working method of the second receiver channel is the same with the exception of the longer
time constant of 700 ms of the second monostable circuit IC 7. Here, however, the output pin 7
sets the storage flip-flop IC 8 by means of H level in case of an alarm. The output pin 2 of IC 8 then
inhibits FET T14 by means of L level so that the venous line clamp located in the drain branch
becomes dead and closes. Upon T14 being inhibited, DI11 is inhibited as well, so that a 24-V level
is applied to pin 6 of plug X351 via R55. During the test, this voltage is sampled in order to
determine whether the venous line clamp has been turned off by the second receiver channel. If
the alarm condition has been eliminated meanwhile, the flip-flop IC 8 can be reset by means of
the positive edge of the dialysis start pulse from pin 12 of plug X351. In this case, the H level at pin
2 of IC 8 turns FET T14 on again, and the venous line clamp is opened.

 Loading...
Loading...