The CM737 controls the indoor temperature as a
function of the measured outside air temperature.
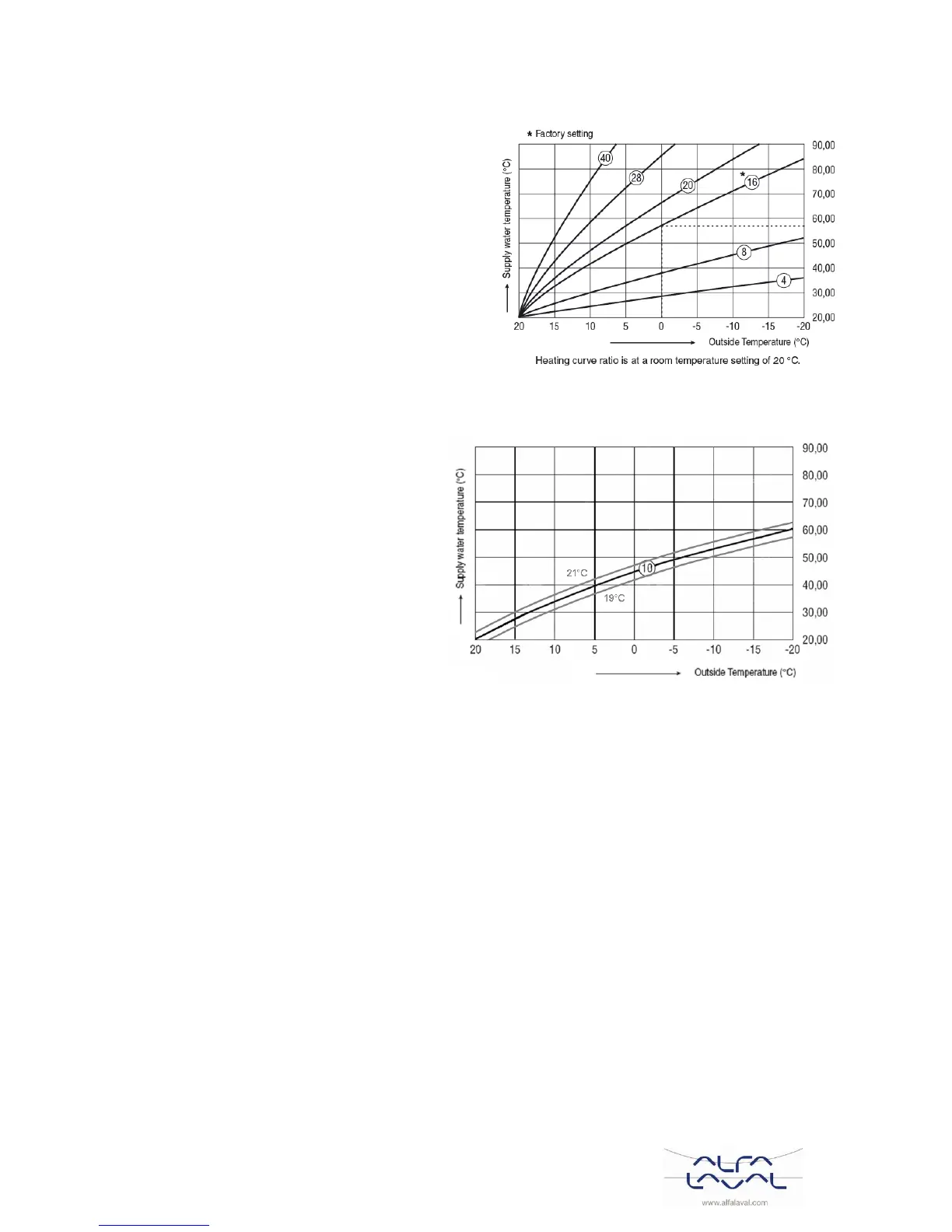
The heating curve is the ratio between the measured
outside air temperature and the calculated supply
water temperature.
The ideal heating curve is dependent on the type of
installation (radiators, convectors, etc.), the thermal
properties and the location of the property. A heating
curve ratio of 1 to 40 can be set.
The figure shows several heating curve ratios for a
room temperature setting of 20°C without room
temperature compensation.
If any other room temperature set point
than 20
o
C is used the selected curve will
be parallel compensated. Every change
of the room temperature set point from
20
o
C will change the supply temperature
with approximately 3
o
C. If the room
temperature set point is increased from
20
o
C to 21
o
C, the supply temperature will
increase with approximately 3
o
C.
This example shows parallels of curve 10
by 19
o
C and 21
o
C.

 Loading...
Loading...











