Access Log
The
ACCESS LOG command allows
the
Initiator
to
read
the
entries contained in
the
disk
drive's maintenance log. This information is available for maintenance purposes.
The
log
information is maintained in a RAM table which is initialized from
the
disk log on power-on,
reset, or Format Unit.
It
is only posted
to
the
disk when an error entry is added.
The
ACCESS LOG command will
alwa.ys
return
this information from
the
RAM log;
there
is no
disk access.
,-
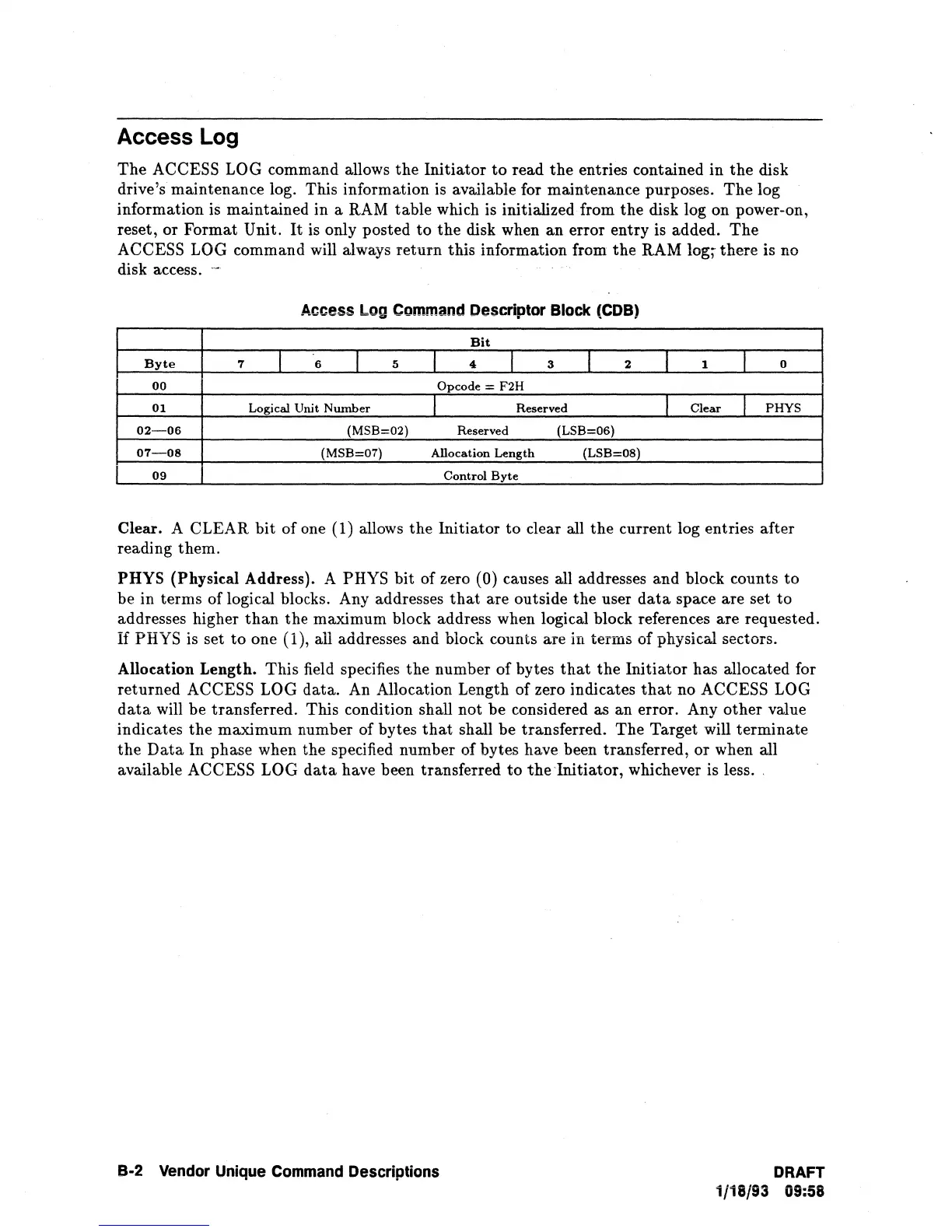
Access Log
Command
Descriptor
Block
(COB)
Bit
Byte
7
1
6
J
5
l
4
I
3
I
2
J
1
1
0
00
Opcode
=
F2H
01
Logical
Unit
Number
I
Reserved
I
Clear
I
PHYS
02-06
(MSB=02)
Reserved
(LSB=06)
07-08
(MSB=07)
Allocation
Length
(LSB=08)
09
Control
Byte
Clear. A CLEAR
bit
of one (1) allows
the
Initiator
to
clear all
the
current log entries after
reading them.
PHYS (Physical Address). A PHYS
bit
of zero (0) causes all addresses and block counts
to
be
in
terms of logical blocks. Any addresses
that
are outside the user
data
space are set
to
addresses higher
than
the maximum block address when logical block references are requested.
If
PHYS is set
to
one (1), all addresses
and
block counts are in terms of physical sectors.
Allocation Length.
This
field specifies
the
number of bytes
that
the
Initiator has allocated for
returned
ACCESS LOG data. An Allocation Length of zero indicates
that
no ACCESS LOG
data
will
be
transferred. This condition shall
not
be
considered as an error. Any
other
value
indicates
the
maximum
number of bytes
that
shall
be
transferred.
The
Target will
terminate
the
Data
In phase when
the
specified number of bytes have been transferred, or when all
available
ACCESS LOG
data
have been transferred
to
the
Initiator, whichever is less
..
8-2
Vendor
Unique
Command
Descriptions
DRAFT
1/18/93 09:58
 Loading...
Loading...