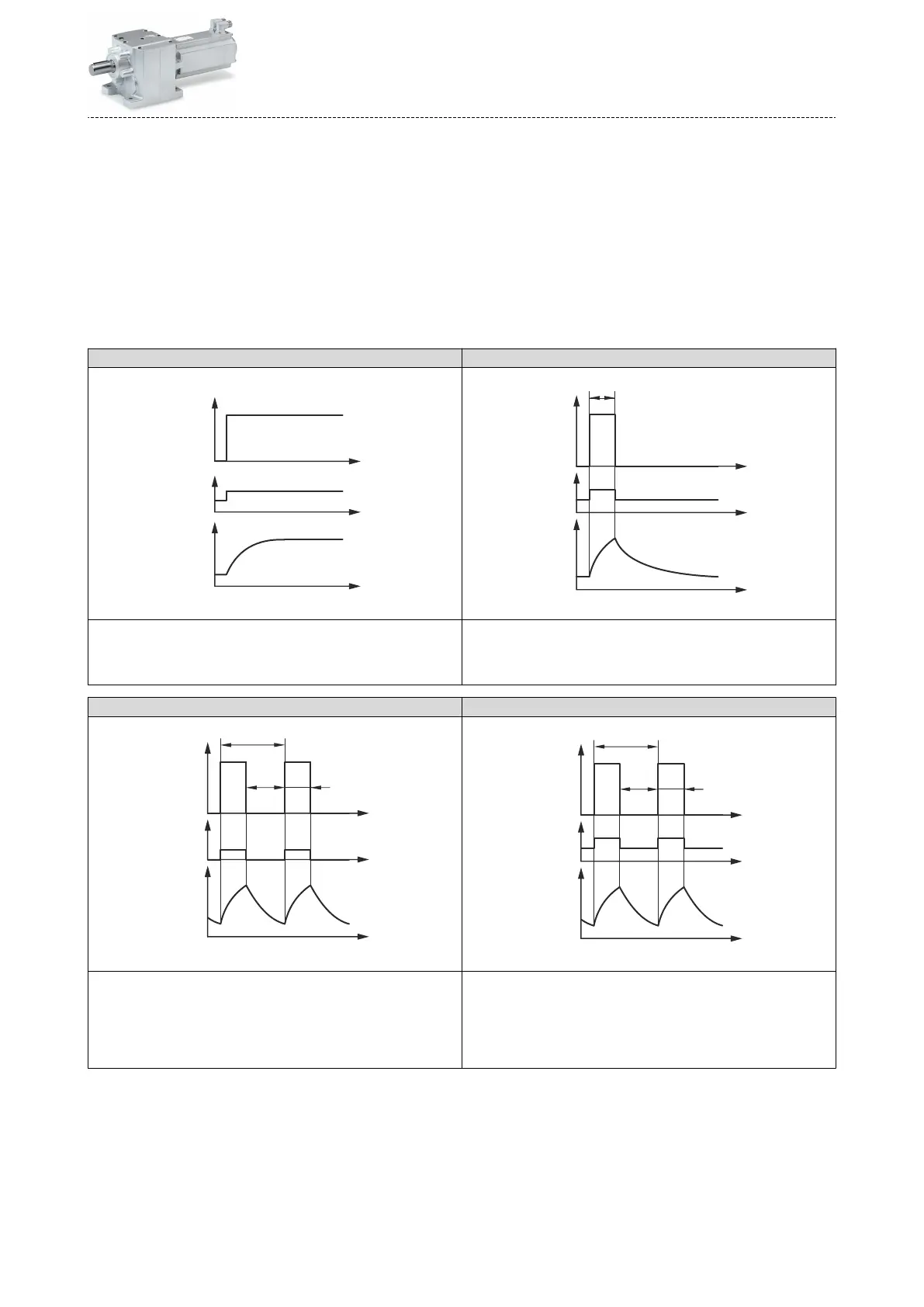
Operang modes of the motor
In connuous operaon a motor reaches its permissible temperature limit if it outputs the
rated power dimensioned for connuous operaon. However, if the motor is only subjected to
load for a short me, the power output by the motor may be greater without the motor
reaching its permissible temperature limit. This behaviour is referred to as overload capacity.
Depending on the duraon of the load and the resulng temperature rise, the required motor
can be selected reduced by the overload capacity.
Operang modes S1 ... S10 as specied by EN 60034-1 describe the basic stress of an electrical
machine.
The most important operang modes
Connuous operaon S1 Short-me operaon S2
Operaon with a constant load unl the motor reaches the thermal
steady state. The motor may be actuated connuously with its rated
power.
Operaon with constant load; however, the motor does not reach the
thermal steady state. During the following standsll, the motor winding
cools down to the ambient temperature again. The increase in power
depends on the load duraon.
Intermient operaon S3 Non-intermient periodic operaon S6
Sequence of idencal duty cycles comprising operaon with a constant
load and subsequent standsll. Start-up and braking processes do not
have an impact on the winding temperature. The steady-state is not
reached. The guide values apply to a cycle duraon of 10 minutes. The
power increase depends on the cycle duraon and on the load period/
downme rao.
Sequence of idencal duty cycles comprising operaon with a constant
load and subsequent no-load operaon. The motor cools down during
the no-load phase. Start-up and braking processes do not have an
impact on the winding temperature. The steady-state is not reached. The
guide values apply to a cycle duraon of 10 minutes. The power increase
depends on the cycle duraon and on the load period/idle me rao.
P Power P
V
Power loss
t Time t
B
Load period
t
L
Idle me t
S
Cycle duraon
ϑ Temperature
Appendix
Good to know
Operang modes of the motor
153

 Loading...
Loading...