Mechanical installation
Preparation
Maximum permissible load at the motor adapter
4
26
Lenze ¯ MA 12.0014 ¯ 5.1
4.3.5 Maximum permissible load at the motor adapter
( Stop!
¯ The loads generated by the motor mounted must be checked!
¯ The forces F
M
mentioned (see following tables) at the adapter must
not be exceeded!
For the effective force F
M
, static forces (e.g. weight) and dynamic forces (e.g.
acceleration forces, for example caused by vibrations or start−up processes) have to be
taken into consideration.
Furthermore the loading case of the force F
M
has to be taken into consideration:
Loading case k
loading
case
Static 1
Dynamic−pulsating 0.8
Dynamic−alternating 0.6
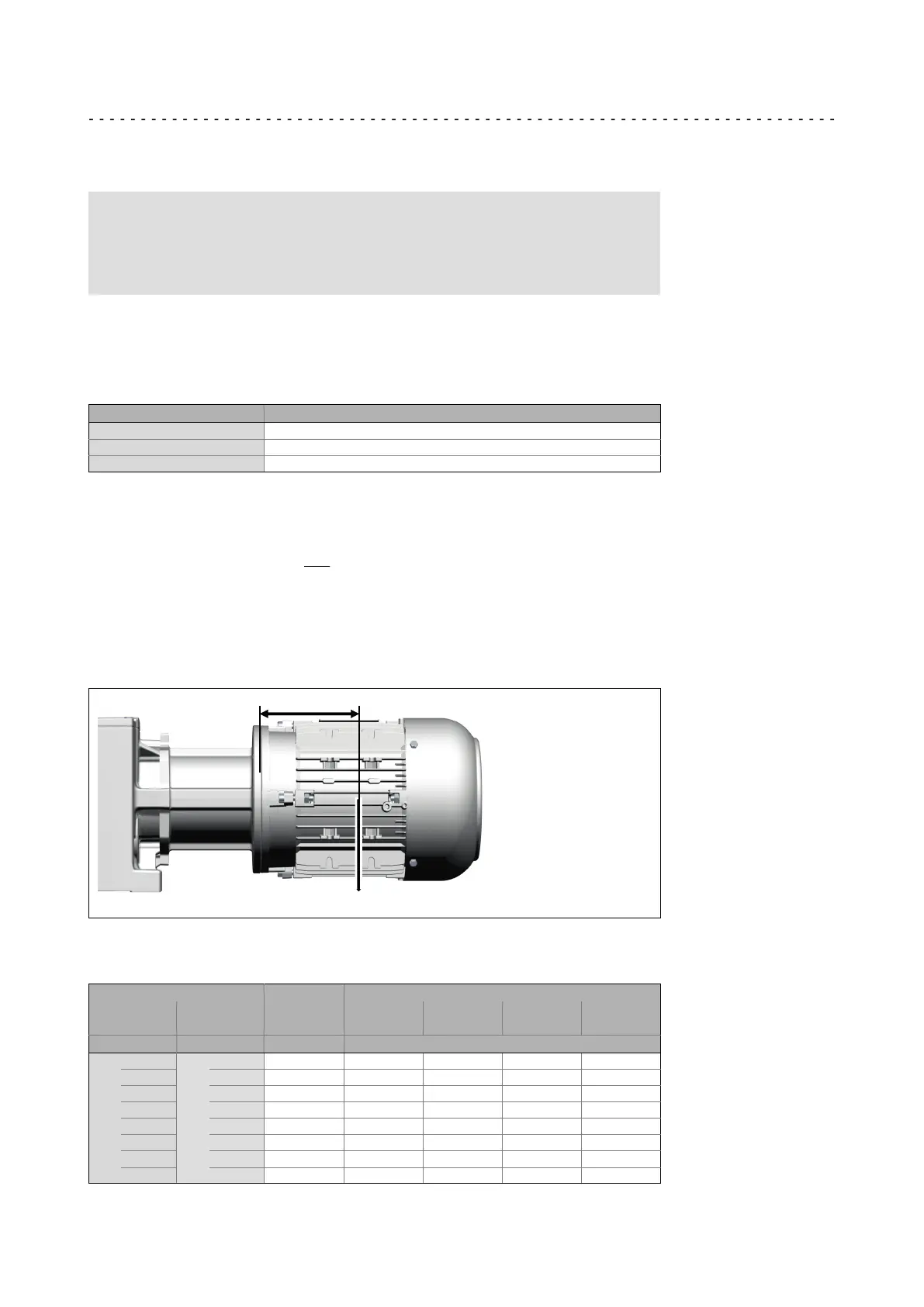
The position of the motor‘s centre of gravity, including all motor options, must be
calculated. If the distance of the centre of gravity L
Tab
is greater, the permissible force
must be reduced as follows.
F
Mperm
+ k
loading_case
@ F
MTab
@
L
Tab
L
v k
loading_case
@ F
MTab
If forces act from several directions, e.g. in the case of a moving horizontal travelling
drive, the acting forces have to be added vectorially (e.g. vertical force due to weight plus
horizontal acceleration force).
F
Mperm
corresponds to the maximum value of the forces added vectorially!
L
F
M
If the permissible force F
Mperm
is exceeded, the motor has to be supported in a suitable,
distortion−free fashion!
Drive size
Distance L
Tab
of the motor
Gearbox type
IEC NEMA
B110
G50BB111
B240
G50BB124
B450
G50BB145
B600
G50BB160
[mm] Maximum permissible force F
M
Tab
[N]
N
xA/2B
A
A 80 350 350 350 350
1B − 80 450 600 800 800
xC 5C 115 450 600 800 800
xD 5D 115 450 660 1000 1500
xE 5E 145 −−−−− 660 1000 1500
xF − 145 −−−−− −−−−− −−−−− 1500
xG 5G 190 −−−−− −−−−− −−−−− −−−−−
xH xH 250 −−−−− −−−−− −−−−− −−−−−

 Loading...
Loading...