11 - 25
TROUBLESHOOTING11.
11.4.2 Faults in the output circuit
Faults concerning output circuits and the corrective actions are explained.
Table 11.3 Faults with the output circuit and the corrective actions
Situation Cause Countermeasure
Example
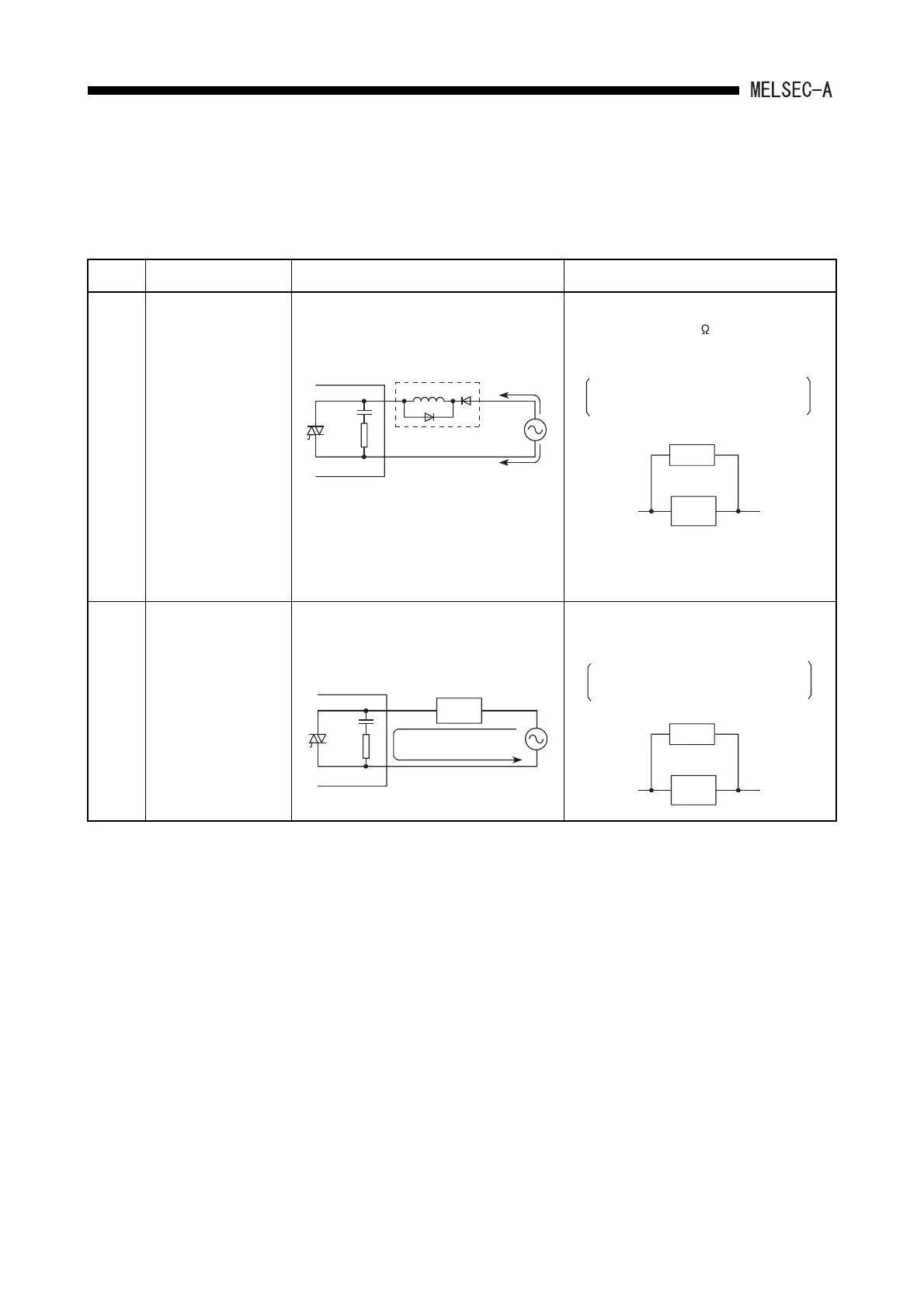
1
An excessive voltage is
applied to the load when
output is off.
• When the load is subjected to half wave
rectification inside
(Solenoids have these types.)
• When the polarity of the power supply is [1], C
is charged, and when the polarity is [2], the
voltage charged in C + voltage of the power
supply are applied to the both ends of D1.
The maximum value of the voltage is about
2.2E.
• Connect a resistor with several tens to
several hundreds of k to the both ends of
the load.
With this kind of usage, there is no problem
with the output element, but the diode built-
in to the load may deteriorate and burn-out.
Example
2
Load does not turn OFF.
(Triac output)
• Leak current caused by built-in noise
supressor
• Connect a resistor to the both ends of the
load.
When the wiring distance from the output
card to the load is long, be aware of the risk
of a leak current due to line capacity.
Output module
A1SY22
D1
[1]
[2]
Load
Resister
Load
Load
Leakage current
A1SY22
Output module
Resister
Load

 Loading...
Loading...