Chapter 7 Counters
M Series User Manual 7-36 ni.com
The counter synchronizes or samples the Gate signal with the Source
signal, so the counter does not detect a rising edge in the Gate until the next
Source pulse. In this example, the counter stores the values in the buffer on
the first rising Source edge after the rising edge of Gate. The details of
when exactly the counter synchronizes the Gate signal vary depending on
the synchronization mode. Synchronization modes are described in the
Synchronization Modes section.
Example Application That Works Incorrectly
(Duplicate Counting)
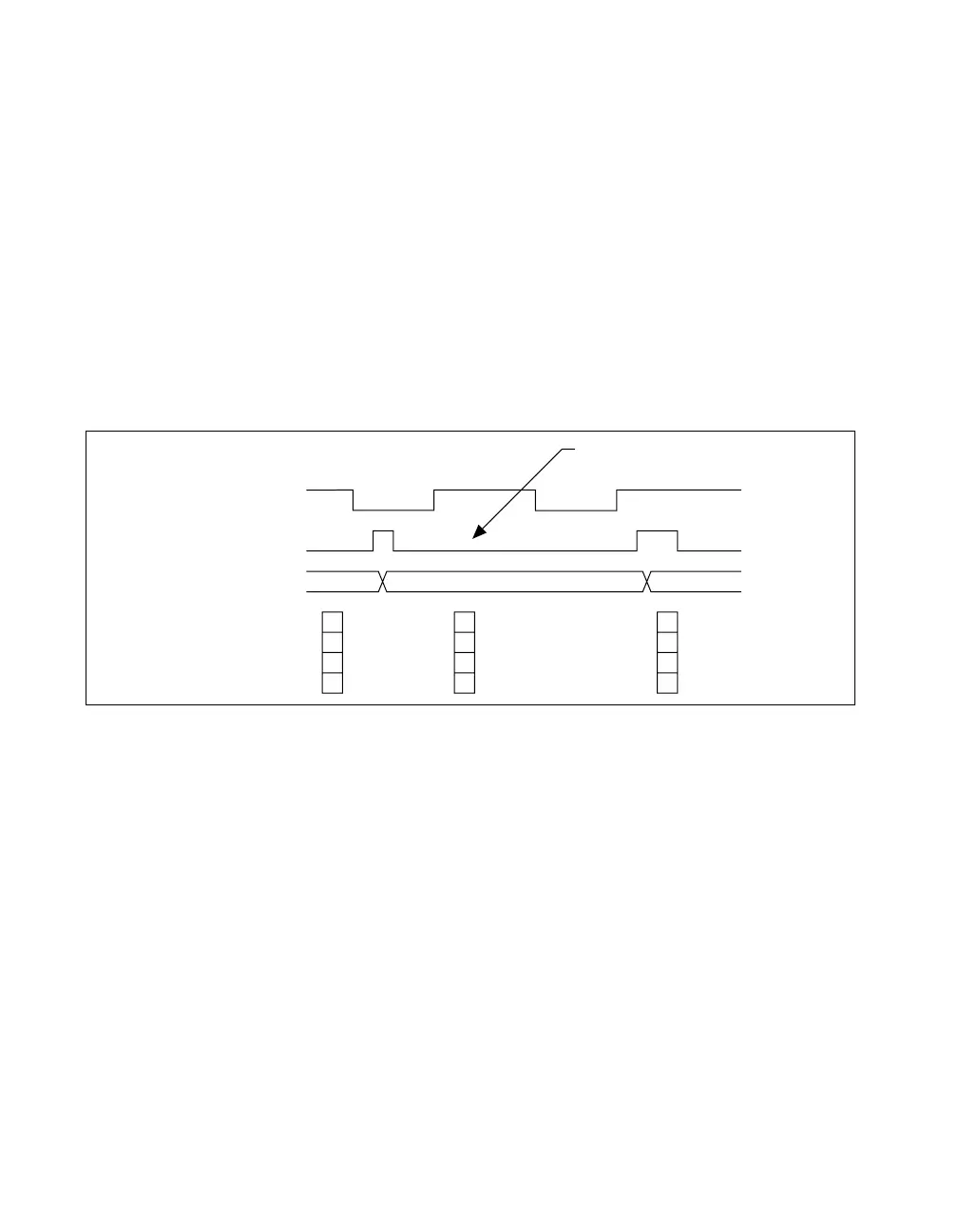
In Figure 7-31, after the first rising edge of Gate, no Source pulses occur,
so the counter does not write the correct data to the buffer.
Figure 7-31. Duplicate Count Example
Example Application That Prevents Duplicate Count
With duplicate count prevention enabled, the counter synchronizes both the
Source and Gate signals to the 80 MHz Timebase. By synchronizing to the
timebase, the counter detects edges on the Gate even if the Source does not
pulse. This enables the correct current count to be stored in the buffer even
if no Source edges occur between Gate signals, as shown in Figure 7-32.
Gate
Source
Counter Value
Buffer
7
67 1
No Source edge, so no
value written to buffer.

 Loading...
Loading...