Chapter 7 Counters
© National Instruments Corporation 7-37 M Series User Manual
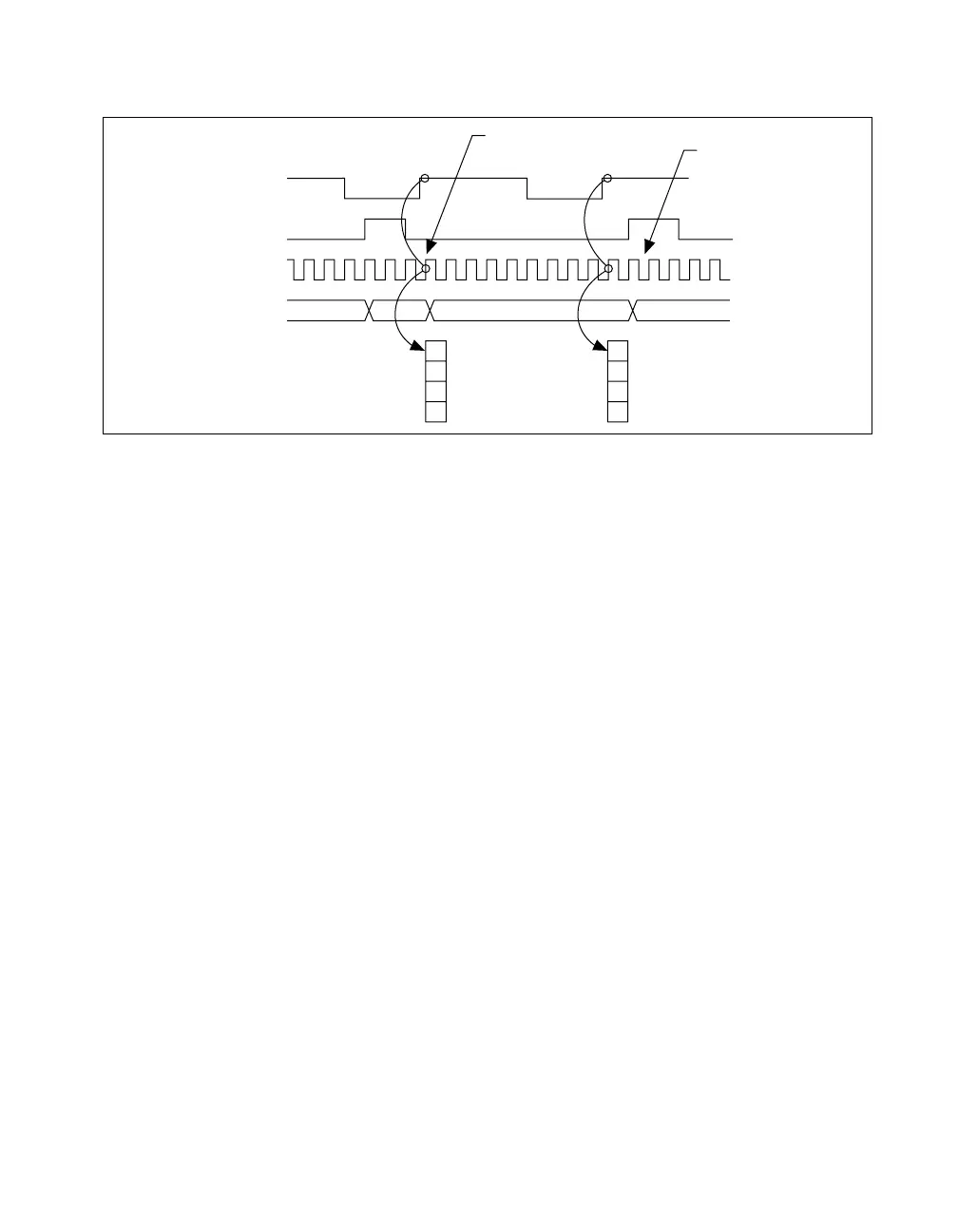
Figure 7-32. Duplicate Count Prevention Example
Even if the Source pulses are long, the counter increments only once for
each Source pulse.
Normally, the counter value and Counter n Internal Output signals change
synchronously to the Source signal. With duplicate count prevention, the
counter value and Counter n Internal Output signals change synchronously
to the 80 MHz Timebase.
Note that duplicate count prevention should only be used if the frequency
of the Source signal is 20 MHz or less.
When To Use Duplicate Count Prevention
You should use duplicate count prevention if the following conditions are
true:
• You are making a counter measurement.
• You are using an external signal (such as PFI x) as the counter Source.
• The frequency of the external source is 20 MHz or less.
• You can have the counter value and output to change synchronously
with the 80 MHz Timebase.
In all other cases, you should not use duplicate count prevention.
Gate
Source
80 MHz Timebase
Counter Value
Buffer
0
7
7
670 1
Counter detects
rising Gate edge.
Counter value
increments only
one time for each
Source pulse.

 Loading...
Loading...