4-1
4. Preparing for Service
TROUBLESHOOTING
Refer to Section 11. Troubleshooting before starting
work on the genset. Note that some problems have
several possible causes.
SAFETY
There are hazards in servicing gensets. Study Safe-
ty Precautions and become familiar with the haz-
ards listed in Table 4-1. Note the following safe-
guards and ways of avoiding hazards:
• Use personal protection: Wear appropriate
protective safety equipment, such as safety
shoes and safety glasses.
• Do not wear rings or jewelry and do not wear
loose or damp clothing that might get caught in
equipment or conduct electricity.
• Reduce the hazard: A safe, orderly workshop
area and well-maintained equipment reduce
the hazard potential. Keep guards and shields
in place on machinery and maintain equipment
in good working condition. Store flammable liq-
uids in approved containers; away from fire,
flame, spark, pilot light, switches, arc-produc-
ing equipment and other ignition sources. Keep
the workshop clean and well-lighted and pro-
vide adequate ventilation.
• Develop safe work habits: Unsafe actions
cause accidents with tools and machines. Be
familiar with the equipment and know how to
use it safely. Use the correct tool for the job and
check its condition before starting. Comply with
the warnings in this manual and take special
precautions when working around electrical
equipment. Do not work alone if possible and
take no risks.
• Be prepared for an accident: Keep fire extin-
guishers and safety equipment nearby. Agen-
cies such as the Red Cross and public safety
departments offer courses in first aid, CPR and
fire control. Take advantage of this information
to be ready to respond to an accident. Learn to
be safety-conscious and make safety proce-
dures part of the work routine.
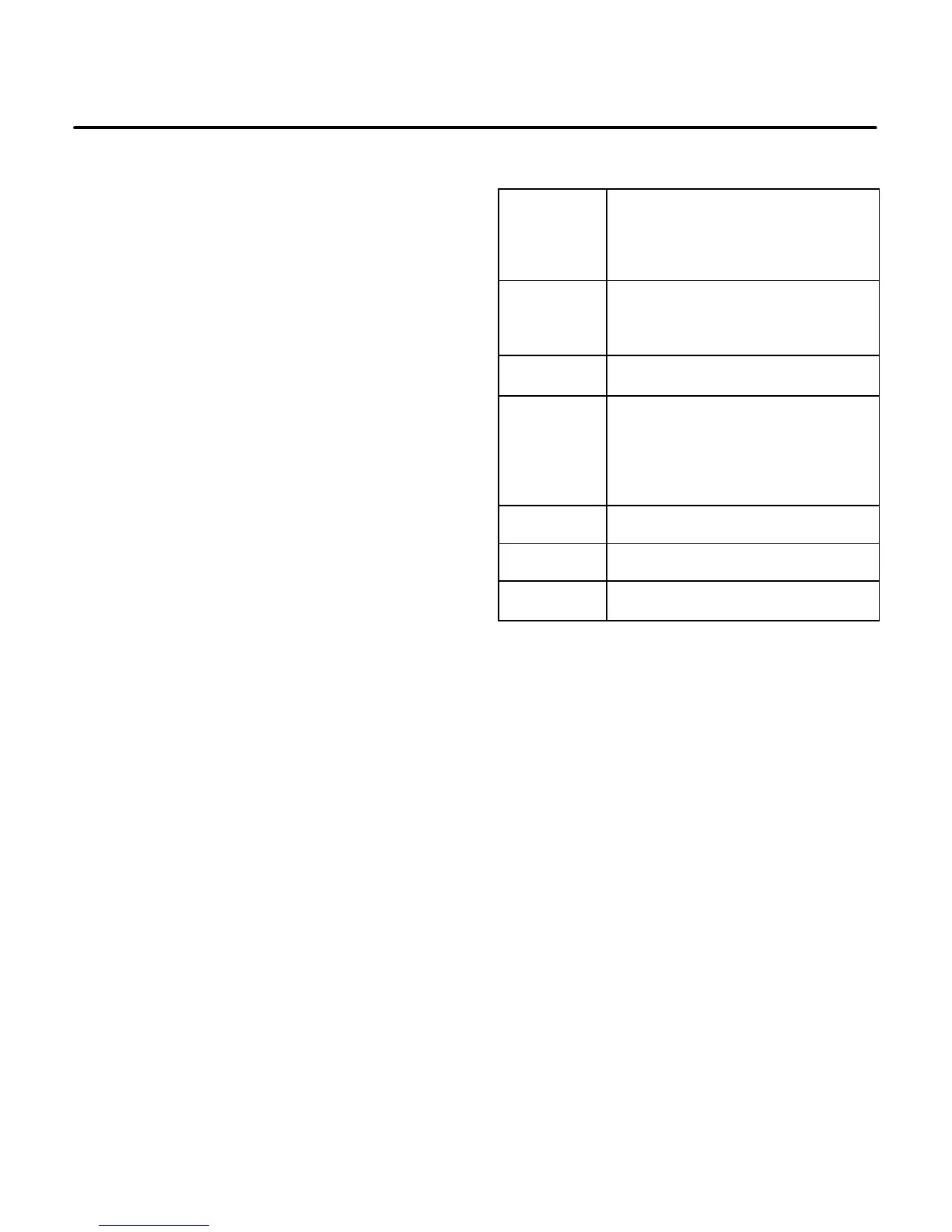
TABLE 4-1. HAZARDS AND THEIR SOURCES
Fire and
Explosion
• Leaking or spilled fuel
• Hydrogen gas from battery
• Oily rags improperly stored
• Flammable liquids improperly
stored
Burns
• Hot exhaust pipes
• Hot engine and generator sur-
faces
• Electrical shorts
Poisonous
Gas
• Operating genset where ex-
haust gases can accumulate
Electrical
Shock (AC)
• Improper generator connec-
tions
• Faulty wiring
• Working in damp conditions
• Jewelry touching electrical
components
Rotating
Machinery
• Fan guards not in place
Slippery
Surfaces
• Leaking or spilled oil
Heavy
Objects
• Removing genset from vehicle
• Removing heavy components
SPECIAL TOOLS
The following special tools are required to service
the genset. See the Onan Tool Catalog.
Engine Tools
Torque wrench (0-75 lbs-ft or 0-100 N-m)
Feeler gauge
Leak down tester
Spark plug gap gauge
Cylinder compression tester
Flywheel puller
Snap ring pliers
Cylinder ridge reamer
Piston ring compressor
Piston ring spreader
Cylinder hone
Valve seat cutter
Valve spring compressor
Piston groove cleaner
Outside micrometer set (1-4 in.)
Telescoping gauge set (0.500-4.000 in.)
Hole gauge (0.300-0.400 in.)
Plasti-Gage bearing clearance guide

 Loading...
Loading...