Introduction . 9
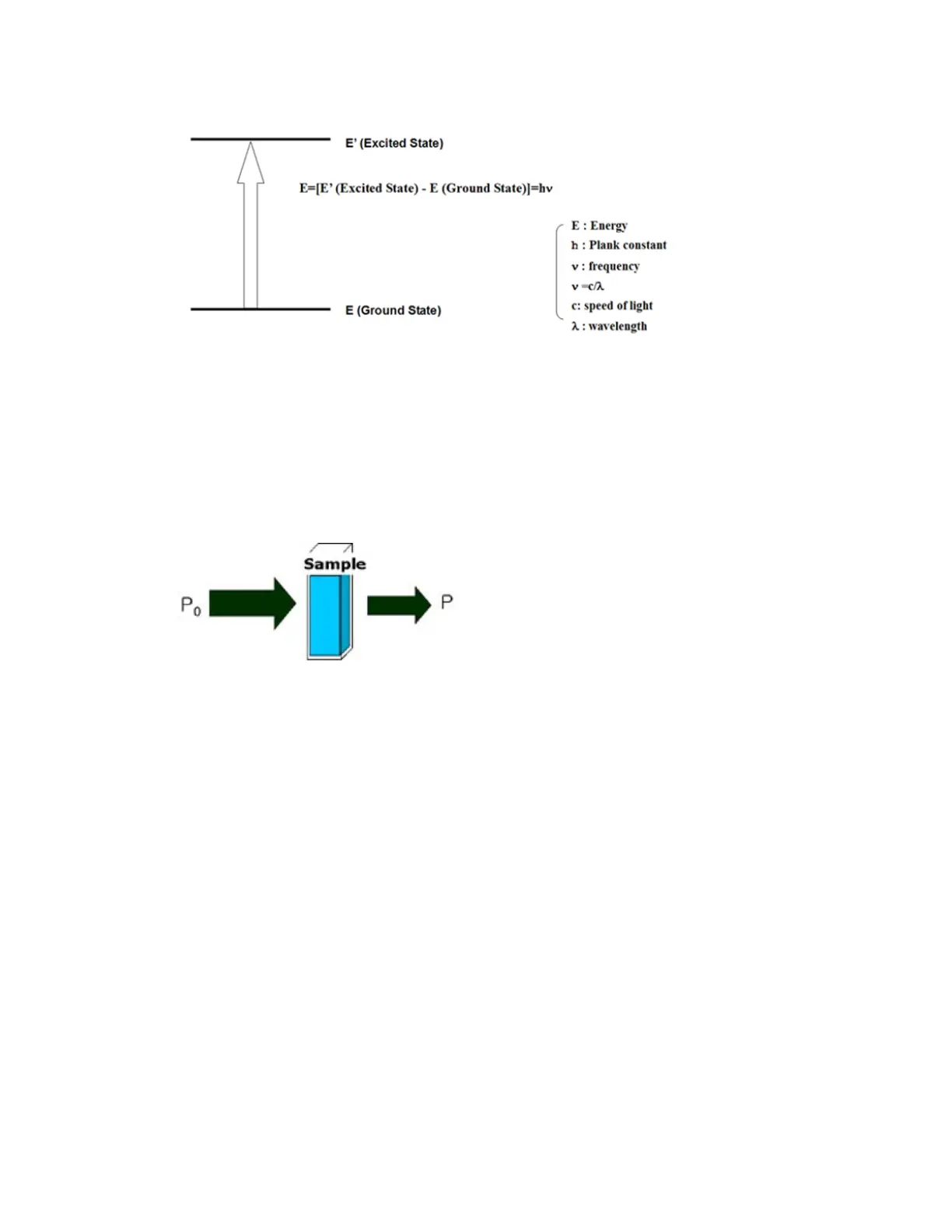
Figure 2. Energy Absorption
Once a sample absorbs light energy, the intensity of incoming light P
0
(the energy from the
light source) reduces to P by losing some of its energy;
therefore, we define the transmittance of a sample as follows:
Figure 3. Sample Absorption
As a result of absorption by a sample, transmittance is defined as;
T = P / P
0
And Absorbance is defined as:
A = -log T = log( P
0
/ P )
Absorbance is related to c (concentration) and b (pathlength of
light) according to the Lambert-Beer law and the equation;
A=εbc
Where,
ε
, the molar absorption coefficient of a particular molecule, varies with the
wavelength.
Although Beer's law has several limitations, it is widely applied to quantitative analysis.

 Loading...
Loading...