GNSS Module Series
L76&L76-L_Hardware_Design 42 / 59
In a complex communication environment, interference signals can come from in-band and out-of-band
signals. Therefore, interference can be divided into two types: in-band interference and out-of-band
interference, which are both described in this chapter.
In this chapter, you can also find suggestions for decreasing the impact of interference signals that will
ensure the interference immunity of a GNSS receiver.
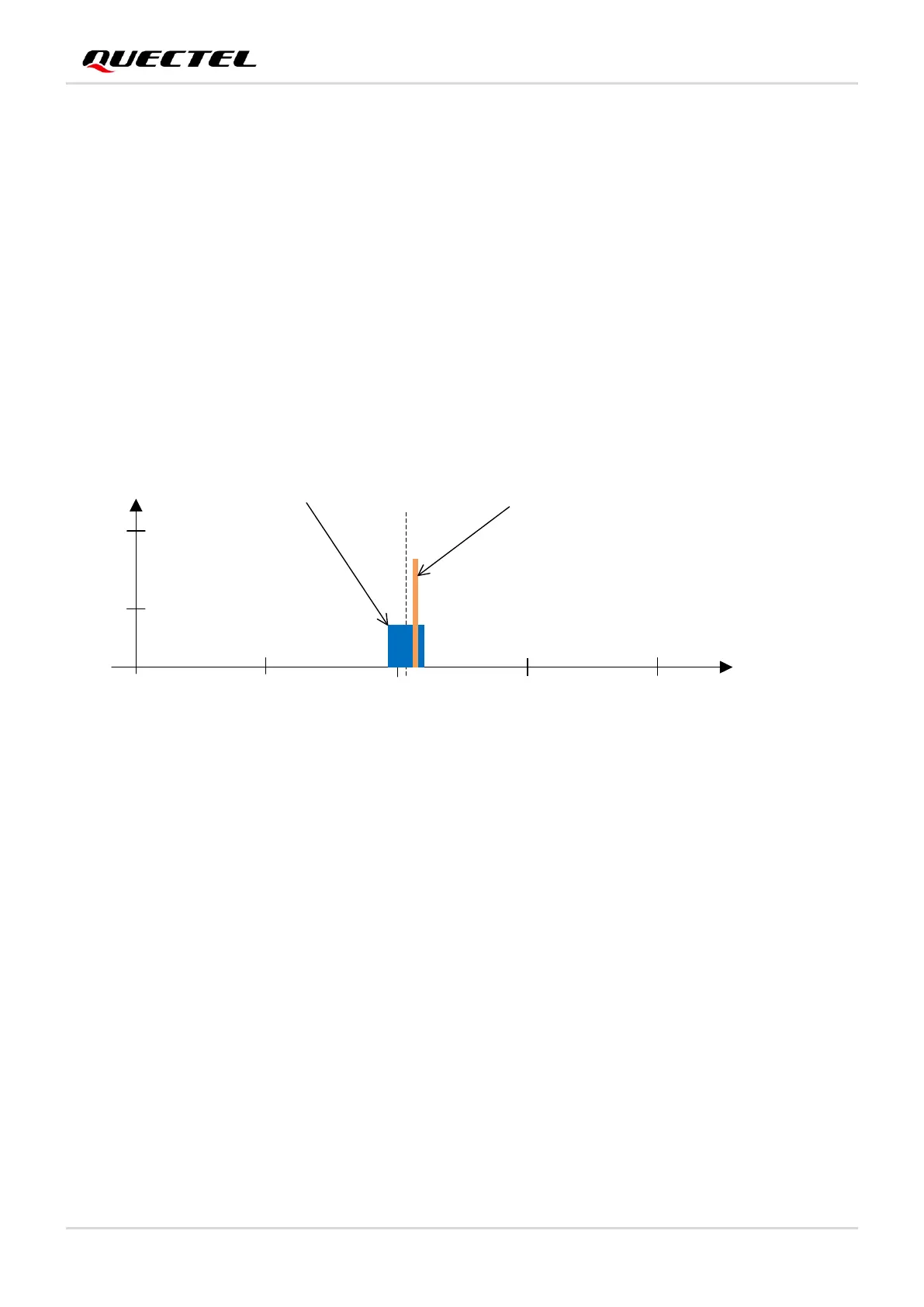
5.3.1. In-Band Interference
In-band interference refers to the signal whose frequency is within or near the operating frequency range
of a GNSS signal.
See the following figure for more details.
Figure 23: In-Band Interference on GPS L1
The most common in-band interferences usually come from:
⚫ Harmonics, caused by crystals, high-speed signal lines, MCUs, switch-mode power supply etc., or
⚫ Intermodulation from different communication systems.
Common frequency combinations are presented in the table below. The table lists some probable in-band
interferences generated by two kinds of out-of-band signal intermodulation, or the second harmonic of
LTE B13.

 Loading...
Loading...











