ZED-F9R-Integration manual
• The recommended configuration when using the UBX-TIM-TP message is to set both the
measurement rate (CFG-RATE-MEAS) and the time pulse frequency (CFG-TP-*) to 1 Hz.
Since the rate of UBX-TIM-TP is bound to 1 Hz, more than one UBX-TIM-TP message can
appear between two pulses if the time pulse frequency is set larger than 1 Hz. In this case
all UBX-TIM-TP messages in between time pulses T1 and T2 belong to T2 and the last UBX-
TIM-TP before T2 reports the most accurate quantization error. In general, if the time pulse
rate is not configured to 1 Hz, there will not be a single UBX-TIM-TP message for each time
pulse.
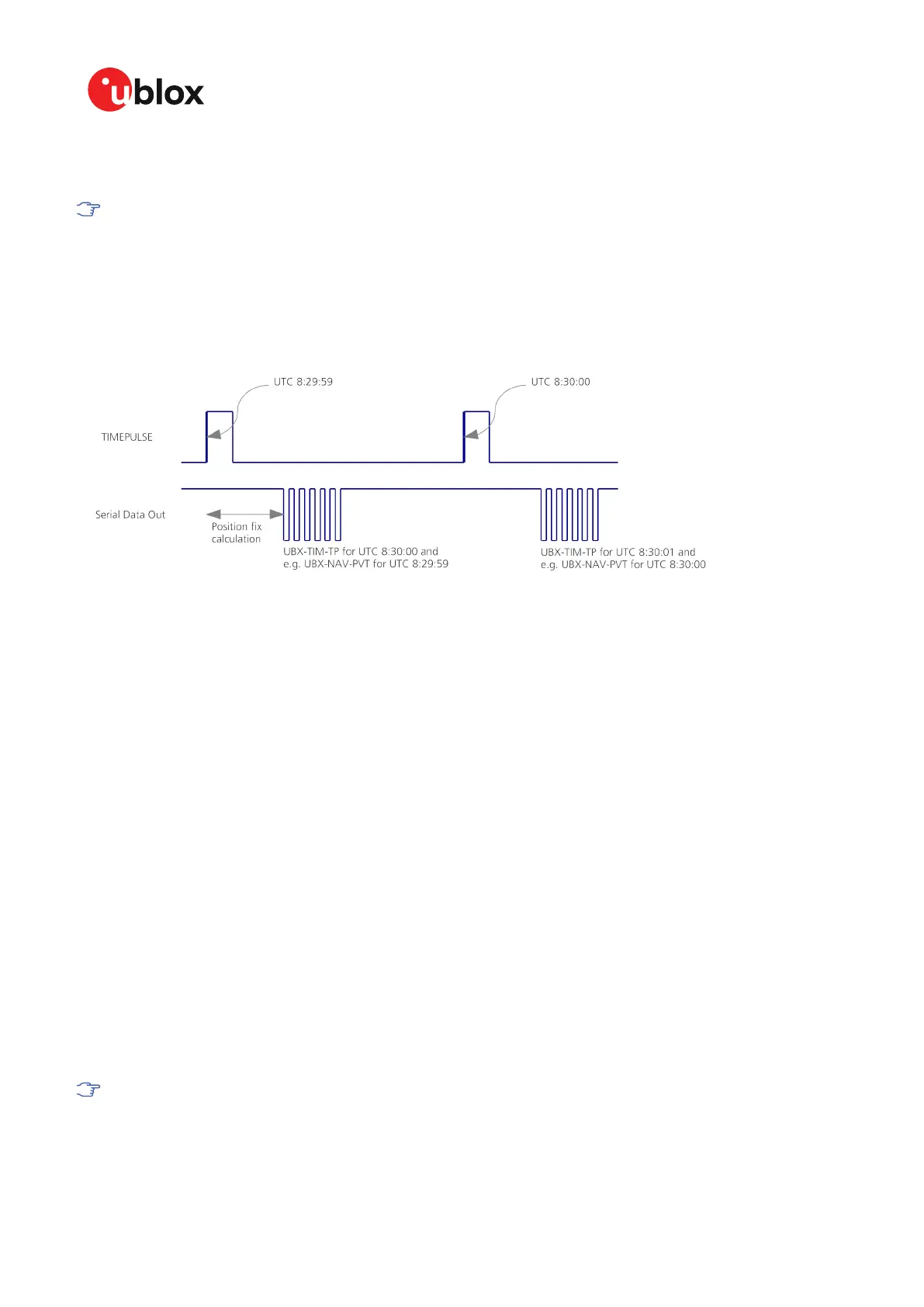
The sequential order of the signal present at the TIMEPULSE pin and the respective output message
for the simple case of 1 pulse per second (1PPS) is shown in the following figure.
Figure 24: Time pulse and TIM-TP
3.10.10.3 GNSS time bases
GNSS receivers must handle a variety of different time bases as each GNSS has its own reference
system time. What is more, although each GNSS provides a model for converting their system time
into UTC, they all support a slightly different variant of UTC. So, for example, GPS supports a variant
of UTC as defined by the US National Observatory, while BeiDou uses UTC from the National Time
Service Center, China (NTSC). While the different UTC variants are normally closely aligned, they
can differ by as much as a few hundreds of nanoseconds.
Although u-blox receivers can combine a variety of different GNSS times internally, the user must
choose a single type of GNSS time and, separately, a single type of UTC for input (on EXTINT pins)
and output (via the TIMEPULSE pin) and the parameters reported in corresponding messages.
The CFG-TP-TIMEGRID_TP* configuration item allows the user to choose between any of the
supported GNSS (GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou, etc.) time bases and UTC. Also, the CFG-NAVSPG-
UTCSTANDARD configuration item allows the user to select which variant of UTC the receiver
should use. This includes an "automatic" option which causes the receiver to select an appropriate
UTC version itself, based on the GNSS configuration, using, in order of preference, USNO if GPS is
enabled, SU if GLONASS is enabled, NTSC if BeiDou is enabled and, finally, European if Galileo is
enabled.
The receiver will assume that an input time pulse uses the same GNSS time base as specified for the
time pulse output. So if the user selects GLONASS time for time pulse output, any time pulse input
must also be aligned to GLONASS time (or to the separately chosen variant of UTC). Where UTC is
selected for time pulse output, any GNSS time pulse input will be assumed to be aligned to GPS time.
u-blox receivers allow users to independently choose GNSS signals used in the receiver
(using CFG-SIGNAL-*) and the input/output time base (using CFG-TP-*). For example it
is possible to instruct the receiver to use GPS and GLONASS satellite signals to generate
BeiDou time. This practice will compromise time pulse accuracy if the receiver cannot
UBX-20039643 - R06
3 Receiver functionality Page 71 of 119
C1-Public
 Loading...
Loading...