Using a graphic display calculator
© Oxford University Press 2012: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute
Casio fx-9860GII
The required value of
μ
is 0.309 (to 3 sf).
Calculating normal probabilities
5.14 Calculating normal probabilities from X-values
Example 57
A random variable X is normally distributed with a mean of 195 and a standard
deviation of 20 or x ~ N(195, 20)
2
. Calculate
a
the probability that X is less than 190.
b
the probability that X is greater than 194.
c
the probability that X lies between 187 and 196.
Press
MENU
and choose 2: STAT and press
Press
F5
DIST
F1
NORM
F2
Ncd to use the Normal Cumulative
Distribution function.
Press
F2
Var.
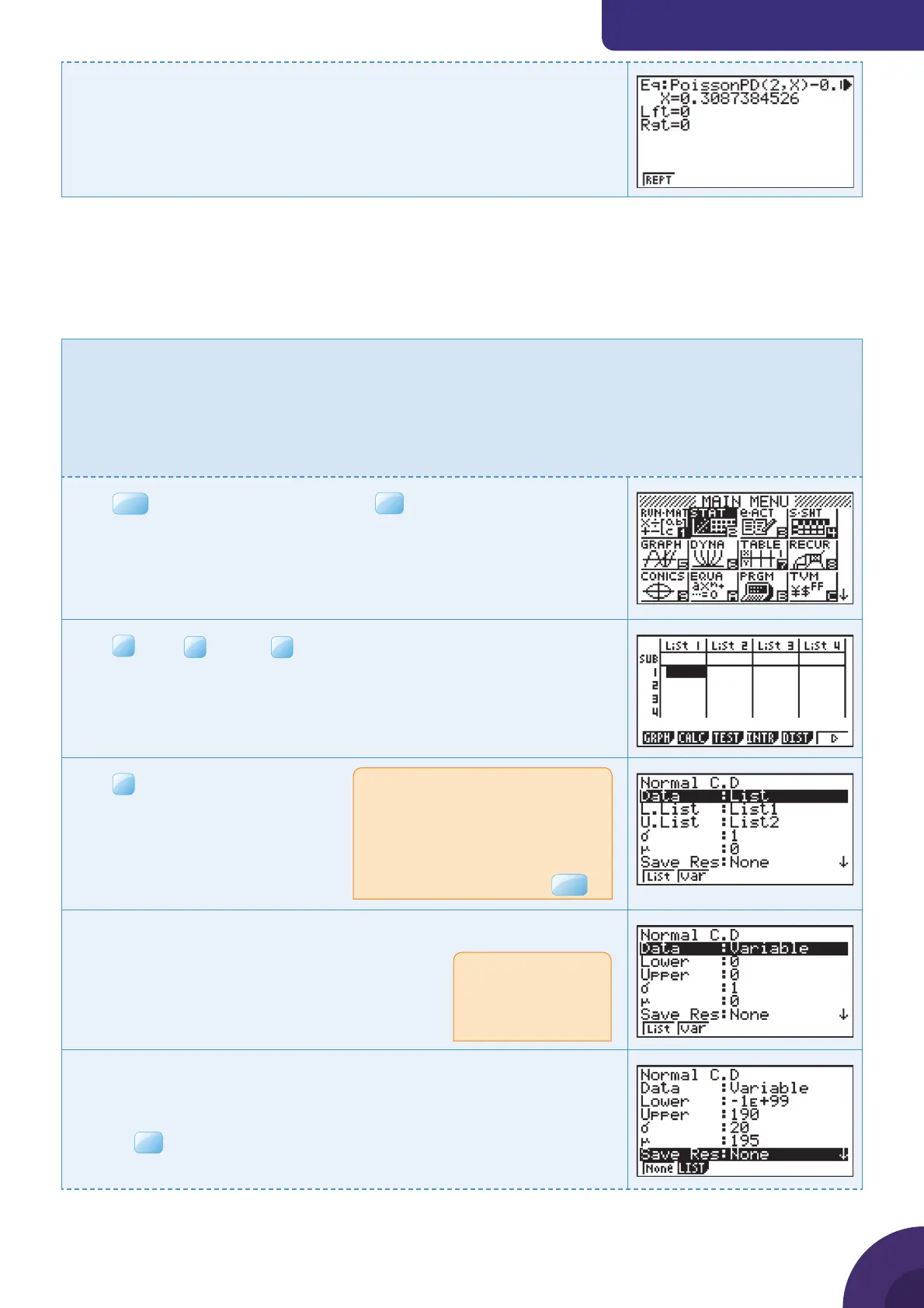
This dialogue box is used to calculate normal probabilities.
a
P(x < 190)
Enter Lower Bound as −1E99, Upper Bound as 190,
σ
as 20
and
μ
as 195.
Press
The value 1E99 is the largest value
that can be entered in the GDC and is
used in the place of ∞. It stands for
1 × 10
99
( –1E99 is the smallest value
and is used in the place of –∞). To
enter the E, you need to press
EXP
.
You should enter the
values, Lower Bound,
Upper Bound,
σ
and
μ
,
in order.
{ Continued on next page
52

 Loading...
Loading...
















