Section 3 – Web Configuration
DNS
DNS
Domain Name System (DNS) is an Internet service that translates the domain
name into IP address. Because the domain name is alphabetic, it is easier to
remember. The Internet, however, is based on IP addresses. Every time you use a
domain name, DNS translates the name into the corresponding IP address. For
example, the domain name www.example.com might be translated to
198.105.232.4. The DNS has its own network. If one DNS server does not know
how to translate a particular domain name, it asks another one, and so on, until
the correct IP address is returned.
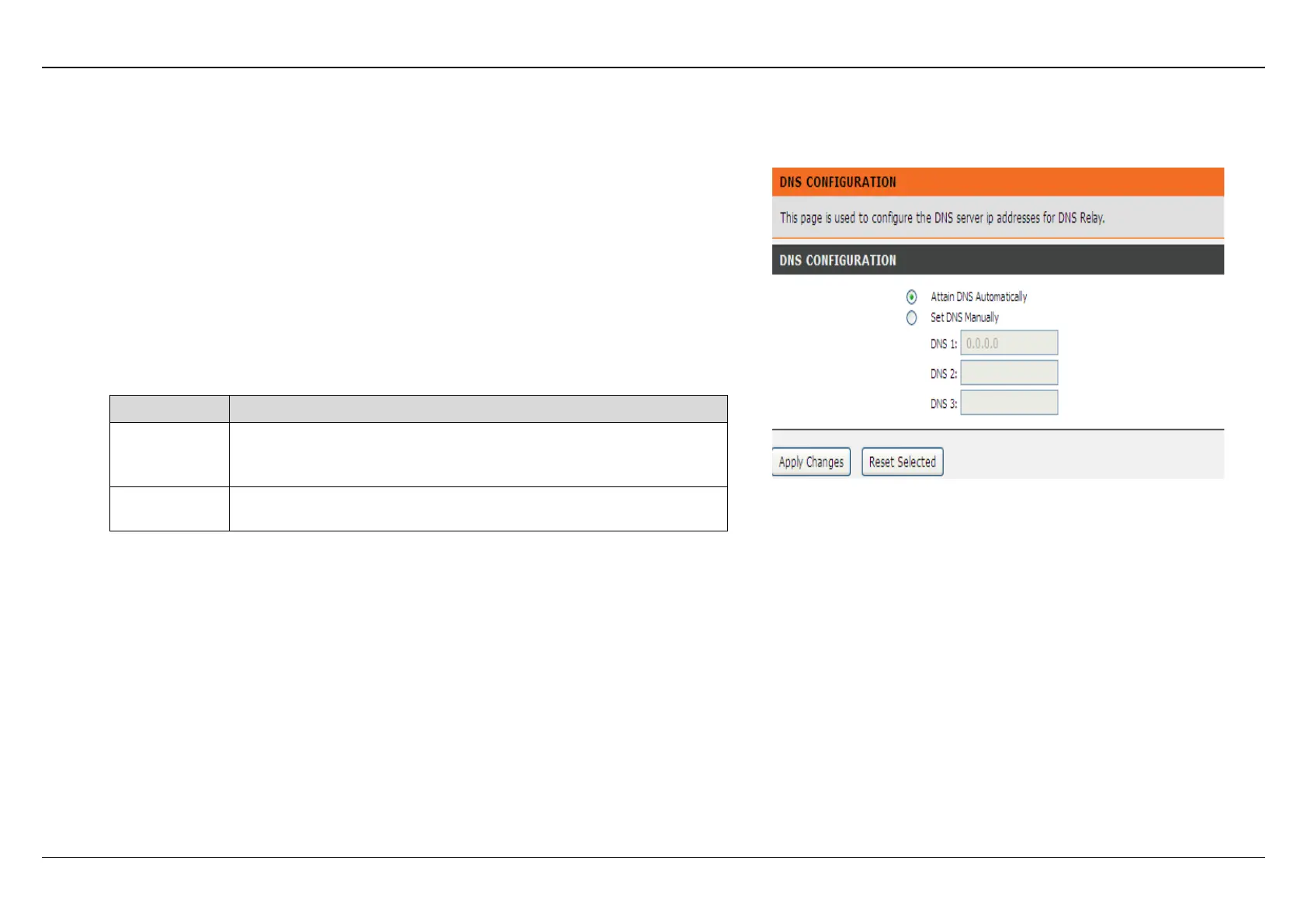
Choose ADVANCED > DNS > DNS. The page shown in the figure appears on the
right. The DNS in this page is based on IPv4 protocol.
The following table describes the parameters and buttons of this page:
Automaticall
Select it, the router accepts the first received DNS
assignment from one of the PPPoA, PPPoE or MER
enabled PVC(s) during the connection establishment.
Select it, enter the IP addresses of the primary and
secondary DNS server.
IPv6 DNS
Choose ADVANCED > DNS > IPv6 DNS. The DNS in this page is based on IPv6
protocol. For the parameter description in this page, please refer to ADVANCED >

 Loading...
Loading...