Chapter 12 Description of Parameter SettingsME300
12.1-08-2
small. It gradually increases the controller output to eliminate the error until it is zero. This
stabilizes the system without a steady-state error by using proportional gain control and integral
time control.
Differential control (D):
The controller output is proportional to the differential of the controller input. During elimination of
the error, oscillation or instability may occur. Use the differential control to suppress these effects
by acting before the error. That is, when the error is near 0, the differential control should be 0.
Use proportional gain (P) and differential control (D) to improve the system state during PID
adjustment.
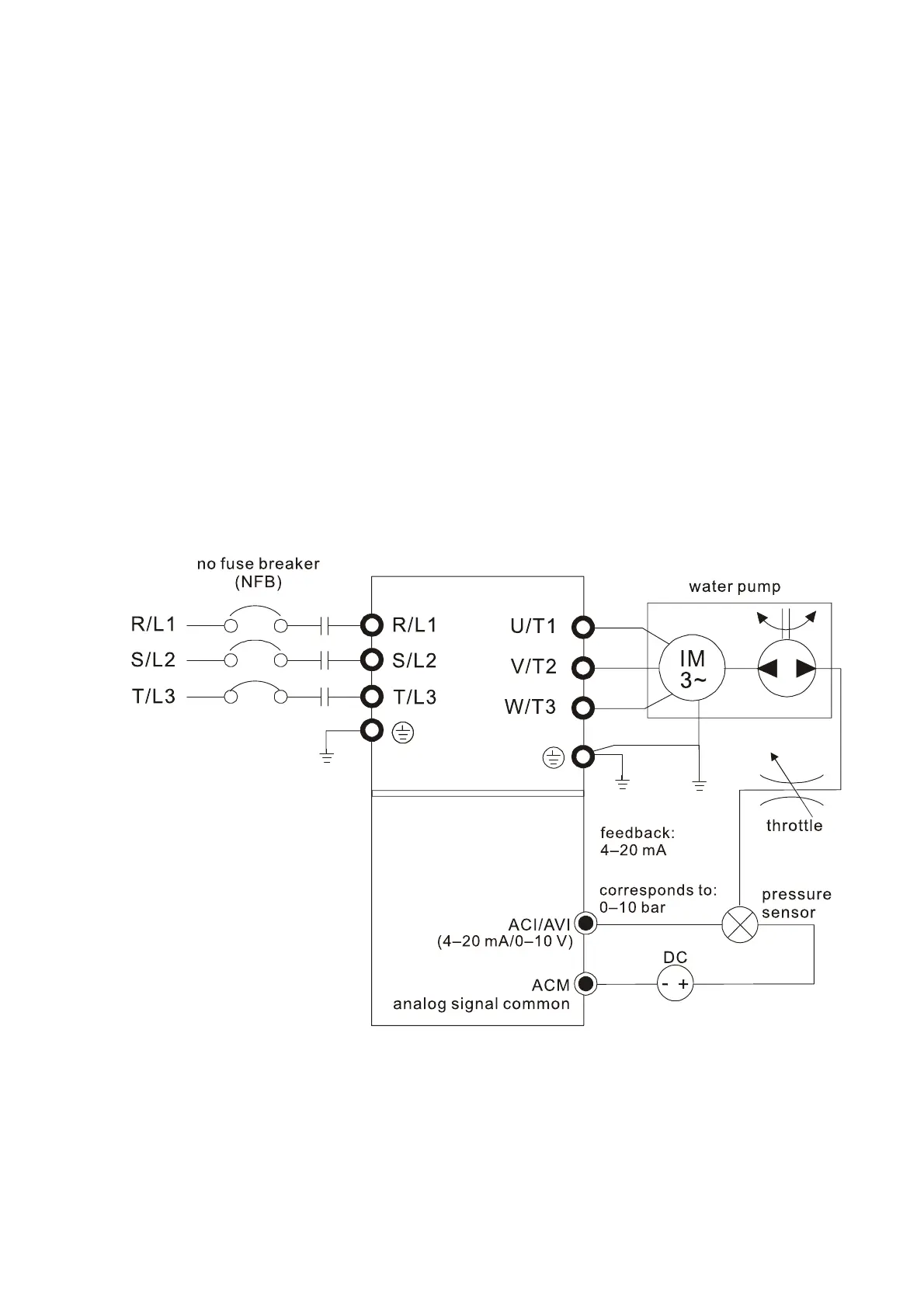
4. Using PID control in a constant pressure pump feedback application:
Set the application’s constant pressure value (bar) to be the set point of PID control. The
pressure sensor sends the actual value as the PID feedback value. After comparing the PID set
point and PID feedback, an error displays. The PID controller calculates the output by using
proportional gain (P), integral time (I) and differential time (D) to control the pump. It controls the
drive to use a different pump speed and achieves constant pressure control by using a 4
–20 mA
signal corresponding to 0–10 bar as feedback to the drive. A–b
Pr.00-04 = 10 (display PID feedback (b) (%))
Pr.01-12 Acceleration Time is set according to actual conditions.
Pr.01-13 Deceleration Time is set according to actual conditions.
Pr.00-21 = 0 to operate through the digital keypad
Pr.00-20 = 0, the digital keypad controls the set point.
Pr.08-00 = 1 (negative PID feedback from analog input)
 Loading...
Loading...











