CHAPTER 8: APPLICATION OF SETTINGS ENHANCING RELAY PERFORMANCE
B90 LOW IMPEDANCE BUS DIFFERENTIAL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 8-11
8
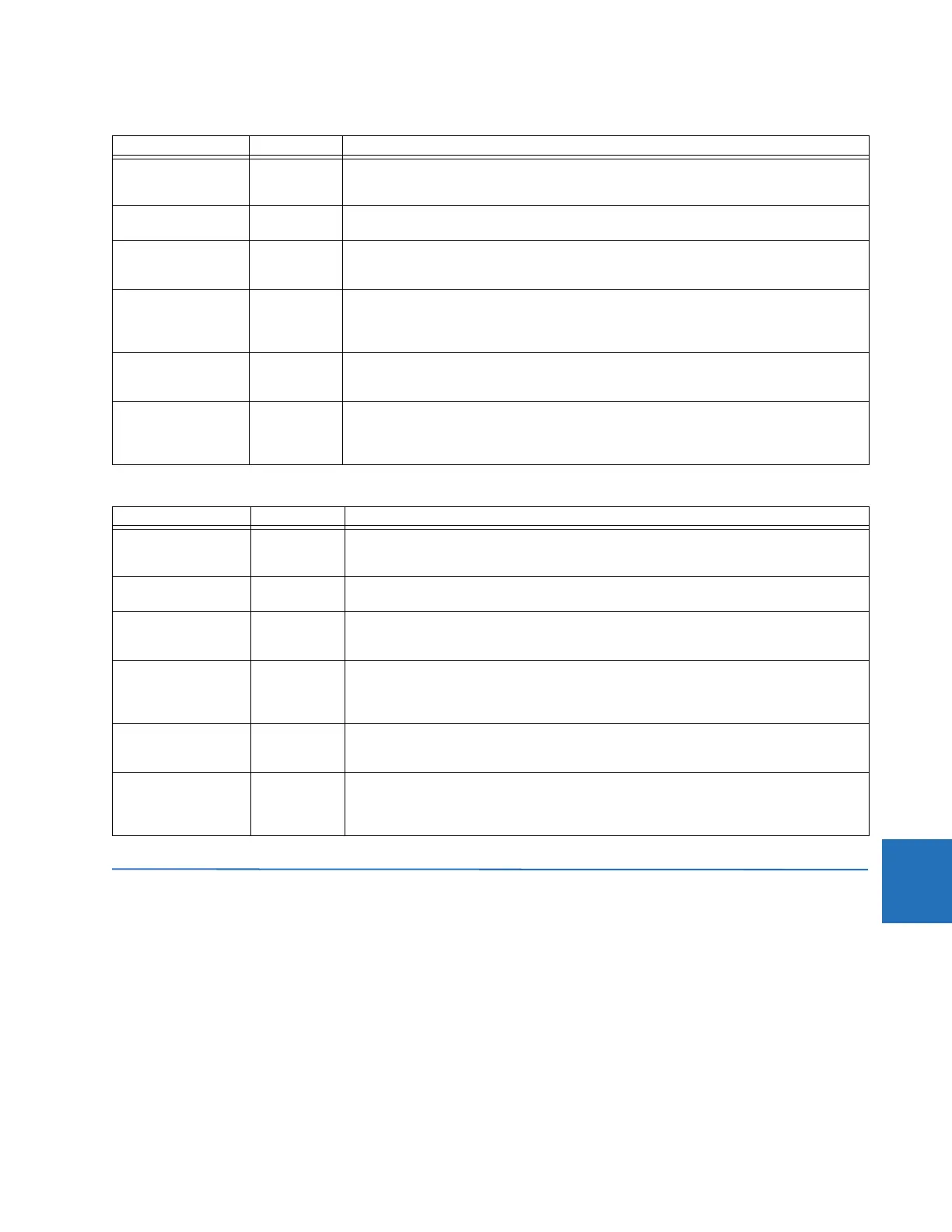
Table 8-9: North bus differential protection settings
Table 8-10: South bus differential protection settings
8.6 Enhancing relay performance
8.6.1 Using setting groups
In the example of the South bus, CT-2 is the weakest (most prone to saturation) CT dictating values of some settings.
However, CT-2 may not be a part of the South bus protection zone if the S-2 switch is opened. As the position of the switch
must be provided for the dynamic bus replica, the status of the switch can be re-used to control the setting groups and
apply more sensitive settings if the weakest CT is not part of the bus zone at a given time. For example, if the S-2 switch is
opened while the S-6 switch is closed, the CT-4 becomes the weakest CT connected to the South bus. The higher
breakpoint (
HIGH BPNT) could be increased to 22.88 pu (fourth column of the Limits of Linear Operations of the CTs table).
Setting Value Comments
PICKUP 0.1 pu Default value. Lower or higher values can be entered upon security/dependability
requirements. The pu value is for the base of 1200A. This means the actual pickup is 120 A
primary.
LOW SLOPE 25% Default value. Lower or higher values can be entered upon security/dependability
requirements.
LOW BPNT 1.79 pu None of the CTs saturate for AC currents below 1.79 pu even with 80% remanence. The DC
component, however, combined with the remanence can saturate some CTs even for currents
below 1.79 pu. The B90 copes with saturation using the current directional principle.
HIGH SLOPE 60% Default value. Lower or higher values can be entered upon security/dependability
requirements. The value of 60% ensures that the differential characteristic alone (without the
directional principle) work correctly under AC saturation of the CTs (26% of spurious
differential during the fault on C-1 saturating CT-1).
HIGH BPNT 8.96 None of the CTs saturate for AC currents below 8.96 pu. The DC component, however, can
saturate some CTs even for currents below 8.96 pu. The B90 copes with saturation using the
current directional principle.
HIGH SET 5.94 The maximum spurious differential current is 2.97 pu. Due to limited accuracy of analysis and
the effect of DC saturation a security factor of 2 has been adopted. The highest internal fault
current is 14kA, or 11.67 pu giving a good chance to clear a number of faults by the unbiased
differential operation.
Setting Value Comments
PICKUP 0.1 pu Default value. Lower or higher values can be entered upon security/dependability
requirements. The pu value is for the base of 1200A. This means the actual pickup is 120 A
primary.
LOW SLOPE 25% Default value. Lower or higher values can be entered upon security/dependability
requirements.
LOW BPNT 1.83 pu None of the CTs saturate for AC currents below 1.83 pu even with 80% remanence. The DC
component, however, combined with the remanence can saturate some CTs even for
currents below 1.83 pu. The B90 copes with saturation using the current directional principle.
HIGH SLOPE 60% Default value. Lower or higher values can be entered upon security/dependability
requirements. The value of 60% ensures that the differential characteristic alone (without the
directional principle) work correctly under AC saturation of the CTs (24% of spurious
differential during the fault on C-2 saturating CT-2).
HIGH BPNT 9.13 pu None of the CTs saturate for AC currents below 9.13 pu. The DC component, however, can
saturate some CTs even for currents below 9.13 pu. The B90 copes with saturation using the
current directional principle.
HIGH SET 5.54 The maximum spurious differential current is 2.77 pu. Due to limited accuracy of analysis and
the effect of DC saturation a security factor of 2 has been adopted. The highest internal fault
current is 14kA, or 11.67 pu giving a good chance to clear a number of faults by the unbiased
differential operation.
 Loading...
Loading...