3
Energy Recovery Ventilation System
DANGER
This product cannot be used for air exchange of the burner. When a gas heater is used in the room,
special ventilation equipment must be used.
1 General introduction
The energy recovery ventilation system (ERV) has the total heat recovery device as its core to achieve
air-to-air total heat exchange and fresh air ltration.
1.1 Working principle
The unit takes fresh air in and discharge the indoor stagnant air to the outdoor. These ows go on to
have a heat exchange through the heat recovery system.
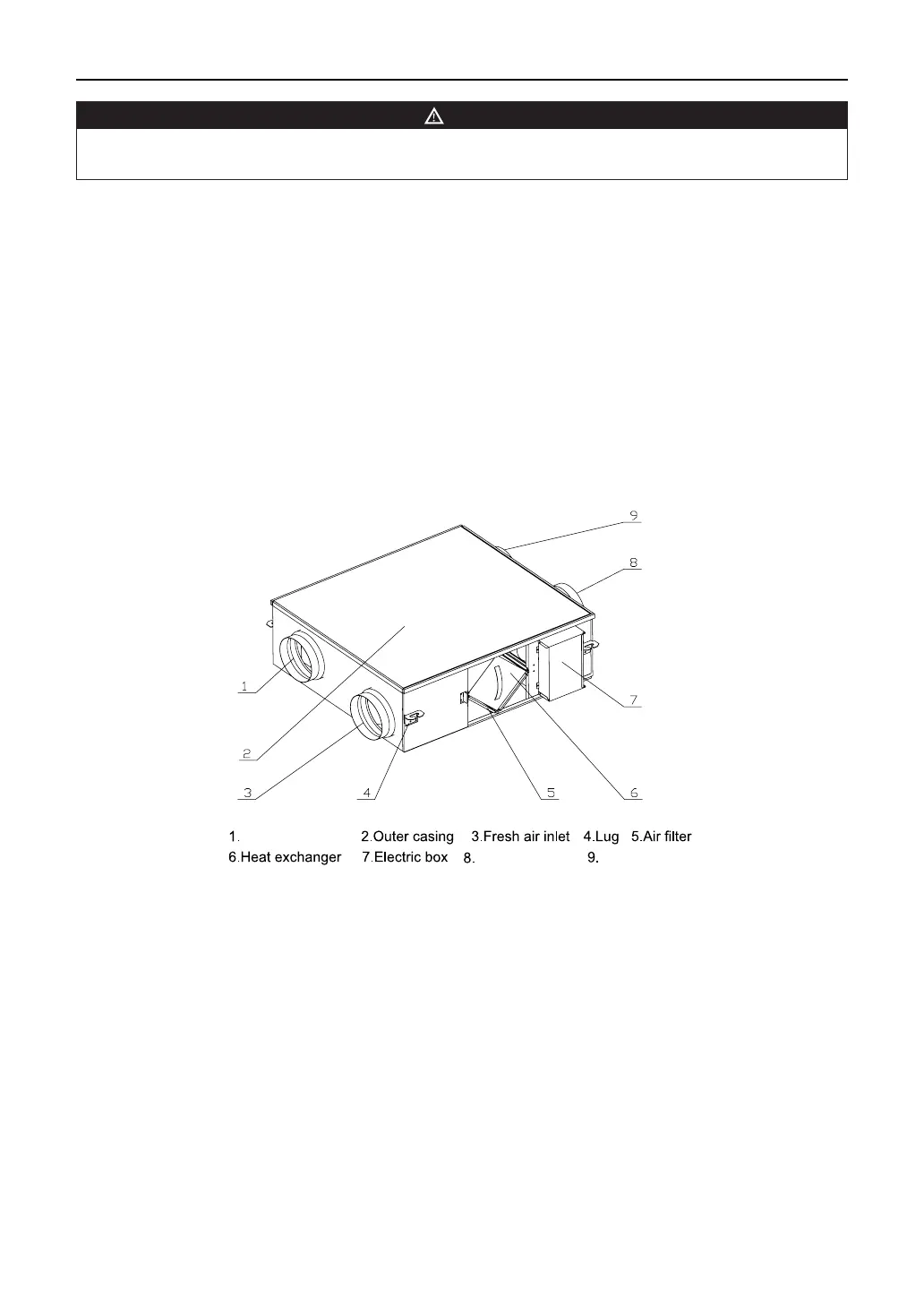
1.2 Components
The key components are low-noise centrifugal fans, lters and heat exchangers. Before the take-in air
ows to the heat exchanger, the lter removes dust particles, bers and other impurities from the air. The
access door is provided to pull out the lter. Durable seals are used to join the casing and access door to
prevent air leakage.
Return air inlet
Return air outlet
Fresh air outlet
Figure 1 Main structure of the ERV
Note: The actual design of the ERV always prevails.
1.3 Operation conditions
It is recommended that the unit is operating in the conditions below, otherwise, condensate will be
produced and damage to electric elements caused.
(1) Indoor—operation temperature: 0~40°C, relative humidity: 20~80%
(2) Outdoor—operation temperature: -10~48°C, relative humidity: 20~85%
The unit only serves locations that have to meet the need of comfort. It should be away from corrosives,
explosives, oil mist and other hazardous substance, to ensure normal operation and expectation of life
and to prevent re hazard and any damage. Special locations require that the equipment have corrosion
and explosion protection.
 Loading...
Loading...