42 HPFF8(E)/HPFF8CM(E) NAC Expander — P/N 53499:B4 10/1/2018
Section 6: Power Supply Requirements
6.1 Overview
This section contains instructions and tables for calculating power supply currents in standby and alarm conditions. This is a four step
process, consisting of the following:
1. Calculating the total amount of AC branch circuit current required to operate the system
2. Calculating the power supply load current for non-alarm and alarm conditions and calculating the secondary (battery) load
3. Calculating the size of the batteries required to support the system if an AC loss occurs
4. Selecting the proper batteries for your system.
This section also contains related calculations for NAC circuits; see Section 6.5, “NAC Circuit Loop Wiring Requirements”.
6.2 Calculating the AC Branch Circuit Current
The power supply requires connection to a separate, dedicated AC branch circuit, which must be labeled FIRE ALARM. This branch cir-
cuit must be connected to the line side of the main power feed of the protected premises. No other non-fire alarm equipment may be
powered from the fire alarm branch circuit. The branch circuit wire must run continuously, without any disconnect devices, from the
power source to the power supply. Overcurrent protection for this circuit must comply with Article 760 of the National Electrical codes
as well as local codes. Use 14 AWG (2.08 mm²) wire with 600 volt insulation for this branch circuit.
Use Table 6.1 to determine the total amount of current, in AC amperes, that must be supplied to the system.
6.3 Calculating the System Current Draw
6.3.1 Overview
The power supply must be able to power all internal and external devices continuously during the non-alarm condition. To calculate the
non-alarm condition load on the power supply when primary power is applied, use the Calculation Column 1 in Table 6.4. The power
supply must support a larger load current during an alarm condition. To calculate the fire alarm load on the power supply, use the Calcu-
lation Column 2 in Table 6.4. The secondary power source (batteries) must be able to power the system during primary power loss. To
calculate the non-alarm condition load on the power supply when primary power is applied, use the Calculation Column 3 in Table 6.4.
When calculating current draw and the battery size, note the following:
• Primary refers to the main AC power source for the power supply.
• Secondary refers to the Power supply's backup batteries.
• All currents are given in amperes (A). Table 6.2 shows how to convert milliamperes and microamperes to full amperes.
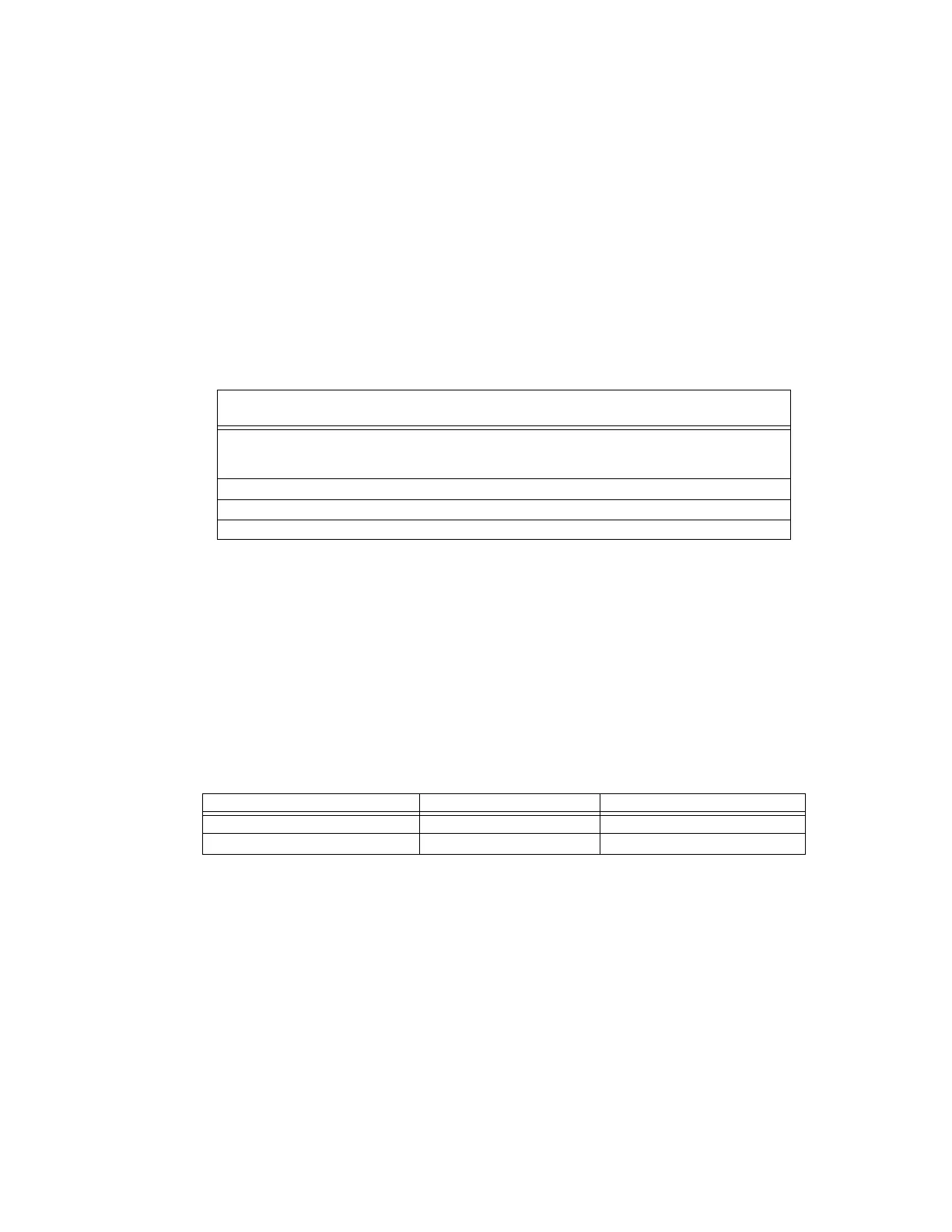
Device Type
Number
of Devices
Current Draw
(AC Amps)
Total Current
per Device
HPFF8/HPFF8CM
or
HPFF8E/HPFF8CME
#X
3.6 A
or
2.1
=
( ) ( ) X ( ) =
( ) ( ) X ( ) =
Sum Column for AC Branch Current Required =
Table 6.1 120/240 VAC Branch Circuit Requirements
To convert... Multiply Example
Milliamperes (mA) to amperes (A) mA x 0.001 3 mA x 0.001 = 0.003 A
Microamperes (µA) to amperes (A) µA x 0.000001 300 µA x 0.000001 = 0.0003 A
Table 6.2 Converting to Full Amperes
 Loading...
Loading...