Figure 28 Using Update Manager to Download Certificates
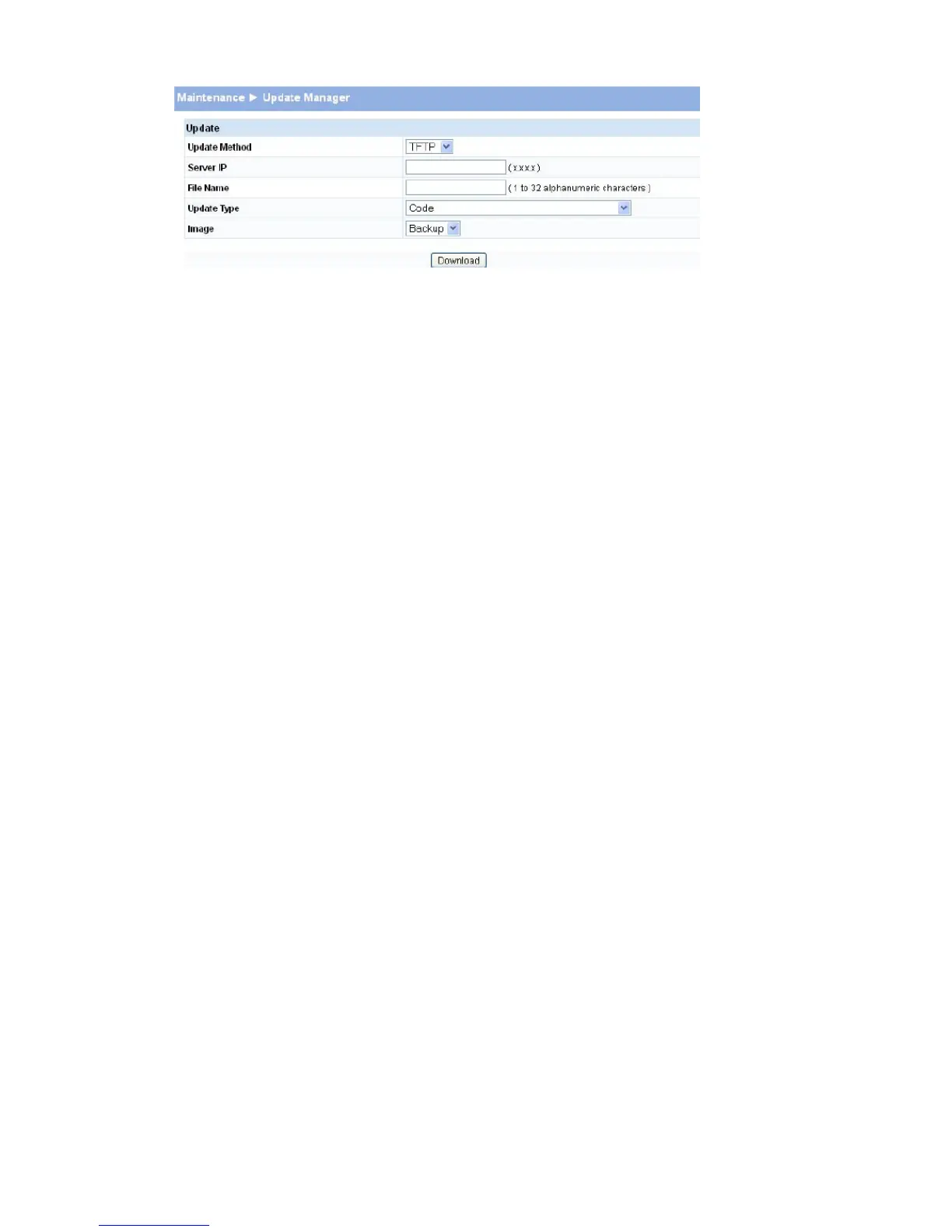
2. Select the protocol to use, based on the server type that the certificate is stored on: TFTP or
HTTP.
3. For an HTTP upload, browse for the file on your local computer or network.
For a TFTP upload, enter the Server IP address, and specify the File Path and File Name.
4. From the Update Type field on the File Download page, select one of the following:
• SSL Trusted Root Certificate PEM File: SSL Trusted Root Certificate File (PEM Encoded)—An
SSL certificate that has been digitally signed by a certificate authority.
• SSL Server Certificate PEM File: SSL Server Certificate File (PEM Encoded)—An SSL
certificate that has been signed by another server.
• SSL DH Weak Encryption Parameter PEM File or SSL DH Strong Encryption Parameter PEM
File—DH certificates provide the algorithms for encrypting key exchanges and are used
independent of the certificate. The weak version uses a cipher strength of 512 bits and
the strong version uses a cypher strength of 1024 bits. Browser settings determine which
DH file parameters are requested at the start of the SSL session.
5. Click Download.
To view that status of the update, you can view the Status > Log page.
6. To return to the Secure HTTP Configuration page, click Security > Secure Connection in the
navigation pane.
7. To enable the HTTPS admin mode, select Enable from the HTTPS Admin Mode field, and then
click Apply.
Generating Certificates
To have the switch generate the certificates:
1. Click Generate Certificates.
The page refreshes with the message “Certificate has been generated.”
2. Click Apply to complete the process.
When the process is complete, the page refreshes with the message “No certificate generation
in progress,” and the Certificate Present field displays as True.
When a certificate is present a Delete button appears to enable deleting the certificate.
42 Security
 Loading...
Loading...