Page 14-6
and you will notice that the CAS default variable X in the equation writer
screen replaces the variable s in this definition. Therefore, when using the
function LAP you get back a function of X, which is the Laplace transform of
f(X).
Example 2
– Determine the inverse Laplace transform of F(s) = sin(s). Use:
‘1/(X+1)^2’
`
ILAP
The calculator returns the result: ‘X/EXP(X)’, meaning that L
-1
{1/(s+1)
2
} = x⋅e
-x
.
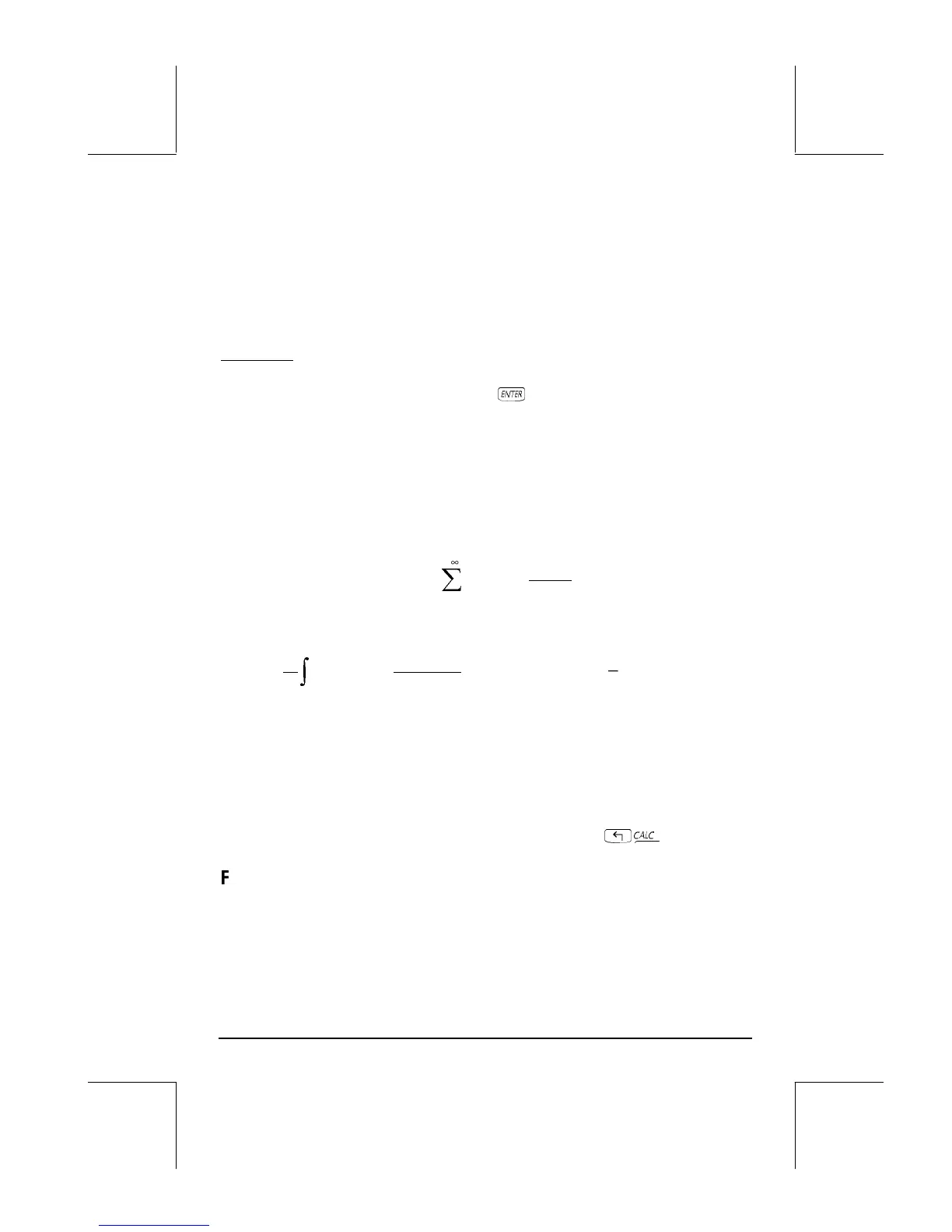
Fourier series
A complex Fourier series is defined by the following expression
∑
+∞
−∞=
⋅=
n
n
T
tin
ctf ),
2
exp()(
π
where
∫
∞−−−∞=⋅⋅
⋅⋅⋅
⋅=
T
n
ndtt
ni
tf
T
c
0
.,...2,1,0,1,2,...,,)
2
exp()(
1
Function FOURIER
Function FOURIER provides the coefficient c
n
of the complex-form of the
Fourier series given the function f(t) and the value of n. The function FOURIER
requires you to store the value of the period (T) of a T-periodic function into
the CAS variable PERIOD before calling the function. The function FOURIER is
available in the DERIV sub-menu within the CALC menu (
„Ö
).
Fourier series for a quadratic function
Determine the coefficients c
0
, c
1
, and c
2
for the function g(t) = (t-1)
2
+(t-1), with
period T = 2.

 Loading...
Loading...