Risks
• For nonclustered nodes with a single HBA, a path failure from the HBA to the SAN switch will
result in a loss of connection with storage devices.
• If a host crashes or experiences a power failure, or if the path is interrupted, data will be lost.
Upon re-establishment of the path, a retransmit can be performed to recover whatever data
may have been lost during the outage. The option to retransmit data after interruption is
application-dependent.
NOTE: For additional risks, see Table 60 (page 165).
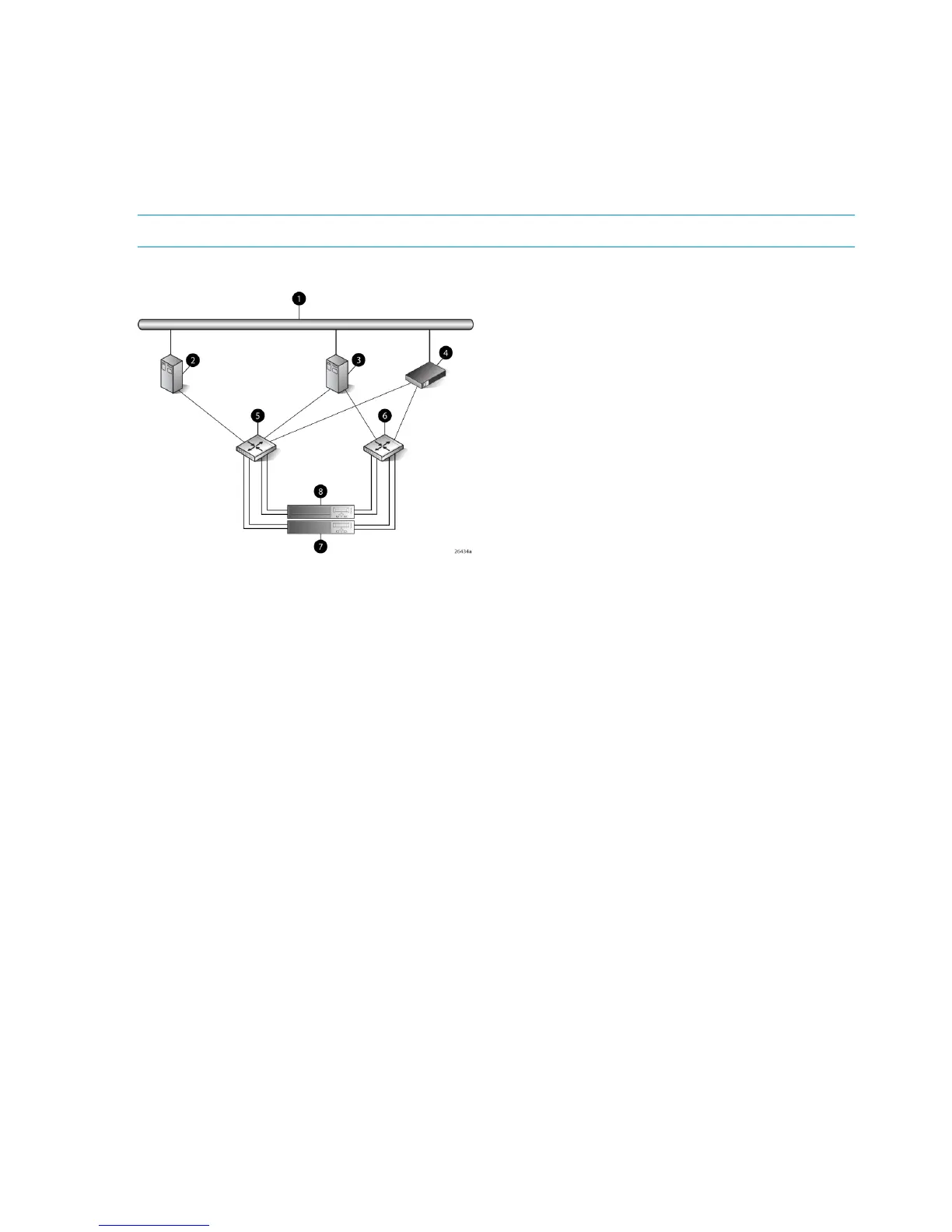
Figure 54 Tru64 UNIX configuration
5 SAN switch 11 Network interconnection
6 SAN switch 22 Host 1
7 Controller A3 Host 2
8 Controller B4 Management server
OpenVMS configuration
Requirements
• Switch zoning or controller level SSP must be used to ensure each single path HBA has an
exclusive path to its LUNs.
• All nodes with direct connection to a disk must have the same access paths available to them.
• Single path HBA server can be in the same fabric as servers with multiple HBAs.
• In the use of snapshots and snapclones, the source virtual disk and all associated snapshots
and snapclones must be presented to the single path hosts that are zoned with the same
controller. In the case of snapclones, after the cloning process has completed and the clone
becomes an ordinary virtual disk, you may present that virtual disk as you would any other
ordinary virtual disk.
HBA configuration
• Host 1 is a single path HBA host.
• Host 2 is a dual HBA host.
See Figure 55 (page 159).
158 Single Path Implementation