Central Processor Units
The cell board can hold up to four CPU modules. Each CPU module can contain up to two CPU
cores on a single die. Modules are populated in increments of one. On a cell board, the processor
modules must be the same family, type, and clock frequencies. Mixing of different processors
on a cell or a partition is not supported. See Table 1-1 for the load order that must be maintained
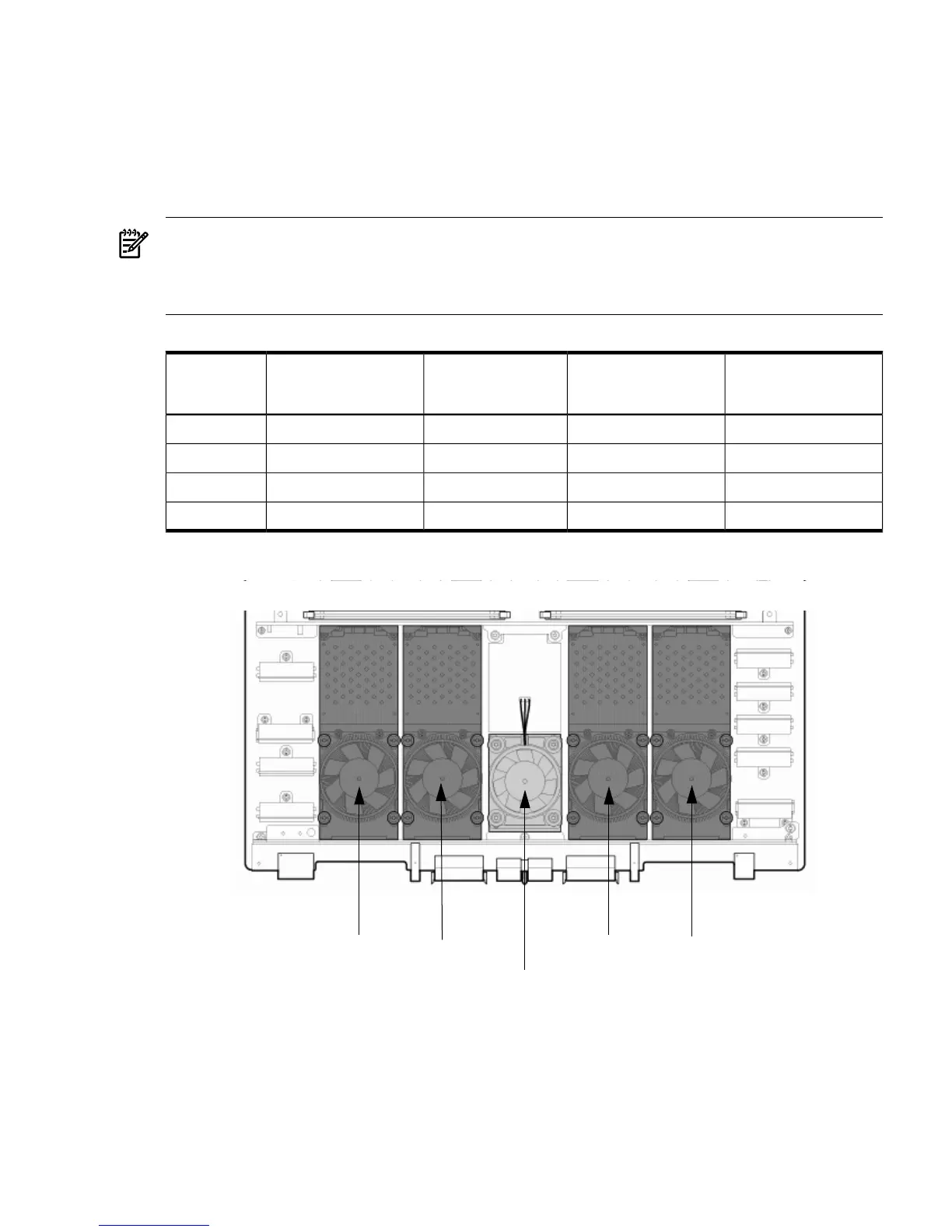
when adding processor modules to the cell board. See Figure 1-7 for the locations on the cell
board for installing processor modules.
NOTE: Unlike previous HP cell based systems, the server cell board does not require that a
termination module be installed at the end of an unused FSB. System firmware is allowed to
disable an unused FSB in the CC. This enables both sockets of the unused bus to remain
unpopulated.
Table 1-1 Cell Board CPU Module Load Order
Socket 0Socket 1Socket 3Socket 2Number of
CPU Modules
Installed
CPU installedEmpty slotEmpty slotEmpty slot1
CPU installedEmpty slotEmpty slotCPU installed2
CPU installedCPU installedEmpty slotCPU installed3
CPU installedCPU installedCPU installedCPU installed4
Figure 1-7 Socket Locations on Cell Board
Memory Subsystem
Figure 1-8 shows a simplified view of the memory subsystem. It consists of four independent
access paths, each path having its own address bus, control bus, data bus, and DIMMs . Address
and control signals are fanned out through register ports to the synchronous dynamic random
access memory (SDRAM) on the DIMMs.
Detailed Server Description 19
 Loading...
Loading...