Mimosa Client Help Content
Mimosa Clients Dashboard
Copyright © 2014 Mimosa Page 43
Reading MIMO Status Tables
The MIMO Status panel contains two tables: Chains and Streams. Chains represent the physical medium (RF Tx/Rx
values), while Streams represent data. Chains and Streams are not necessarily correlated one to one because the
Rate Adaptation algorithm may periodically increase or decrease the number of data streams sent over the physical
medium when reacting to interference.
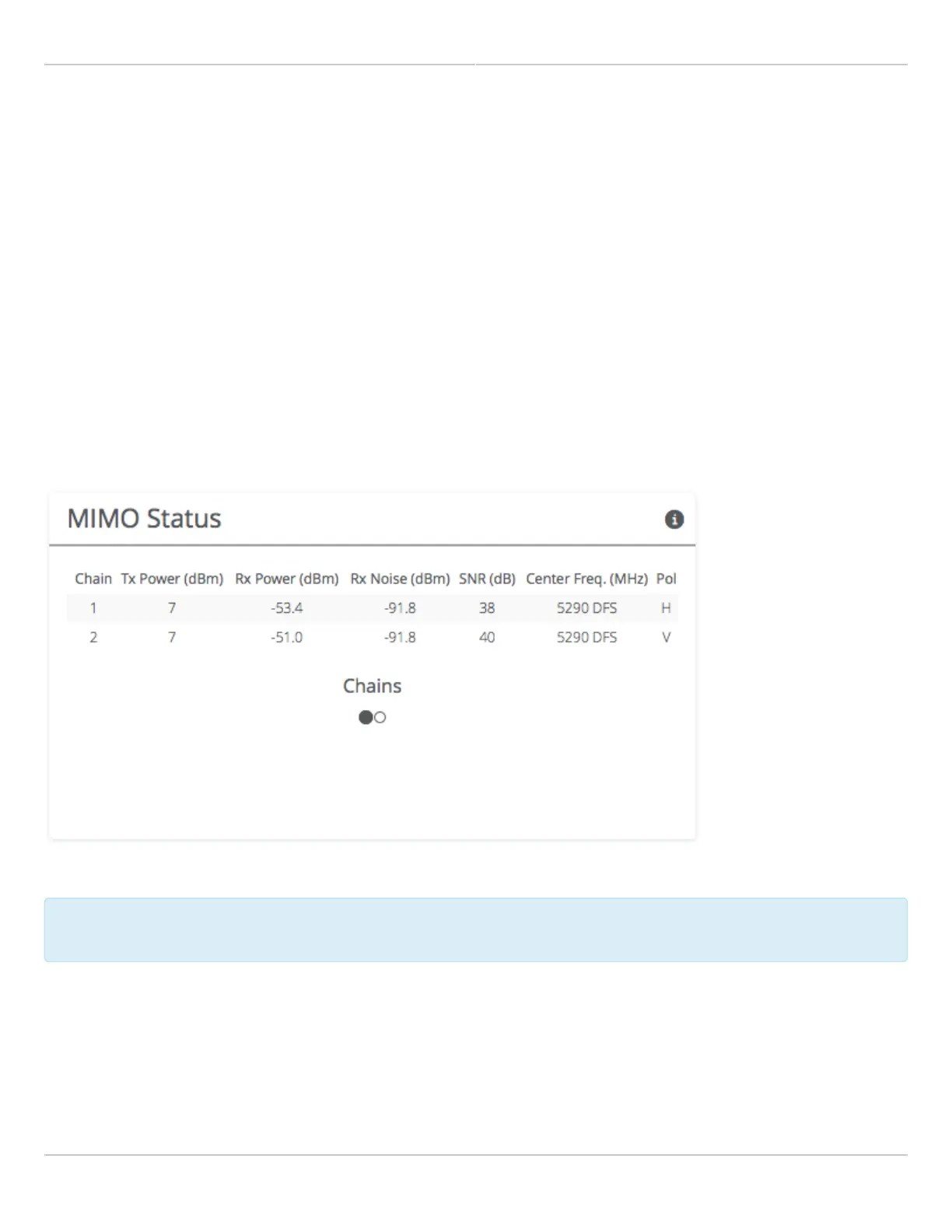
The Chains table describes each chain's power, noise, SNR, frequency and polarization.
The Streams table describes each stream's MCS index, PHY rates and Rx Error Vector Magnitude (EVM).
Each table can be selected by clicking on the navigation circles at the bottom of the panel.
Chains Table
The Chains table contains 6 values: Tx Power, Rx Power, Rx Noise, SNR, Center Frequency and Polarization
(horizontal and vertical).
Tx Power is the amount of power applied to each of the MIMO chains.
Tx power is divided evenly per chain. Example: 15 dBm Tx power for the Channel results in 12 dBm on
Tx power is divided evenly per chain. Example: 15 dBm Tx power for the Channel results in 12 dBm on
each on chain. Since power is expressed in dBm, subtract 3 to divide the total power in half.
each on chain. Since power is expressed in dBm, subtract 3 to divide the total power in half.
Rx Power is the incoming signal level from the remote radio. Larger values are better (e.g. -50 dBm is better than -
60 dBm).
Rx Noise is a combination of the thermal noise floor plus interference detected by the local radio. Smaller values are
better (e.g. -90 dBm is better than -80 dBm). Noise sources can be either in close proximity to the local radio, or
they can be remote transmitters pointed back at the local radio.

 Loading...
Loading...