10.99 Faults and Alarms
Siemens AG 6SE7087-6KP50
SIMOVERT MASTERDRIVES Operating Instructions 12-1
12 Faults and Alarms
12.1 Faults
General information regarding faults
For each fault, the following information is available:
Parameter r947 Fault number
r949 Fault value
r951 Fault list
P952 Number of faults
r782 Fault time
If a fault message is not reset before the electronic supply voltage is
switched off, then the fault message will be present again when the
electronic supply is switched on again. The unit cannot be operated
without resetting the fault message. (Exception: Automatic restart has
been selected, see P373).
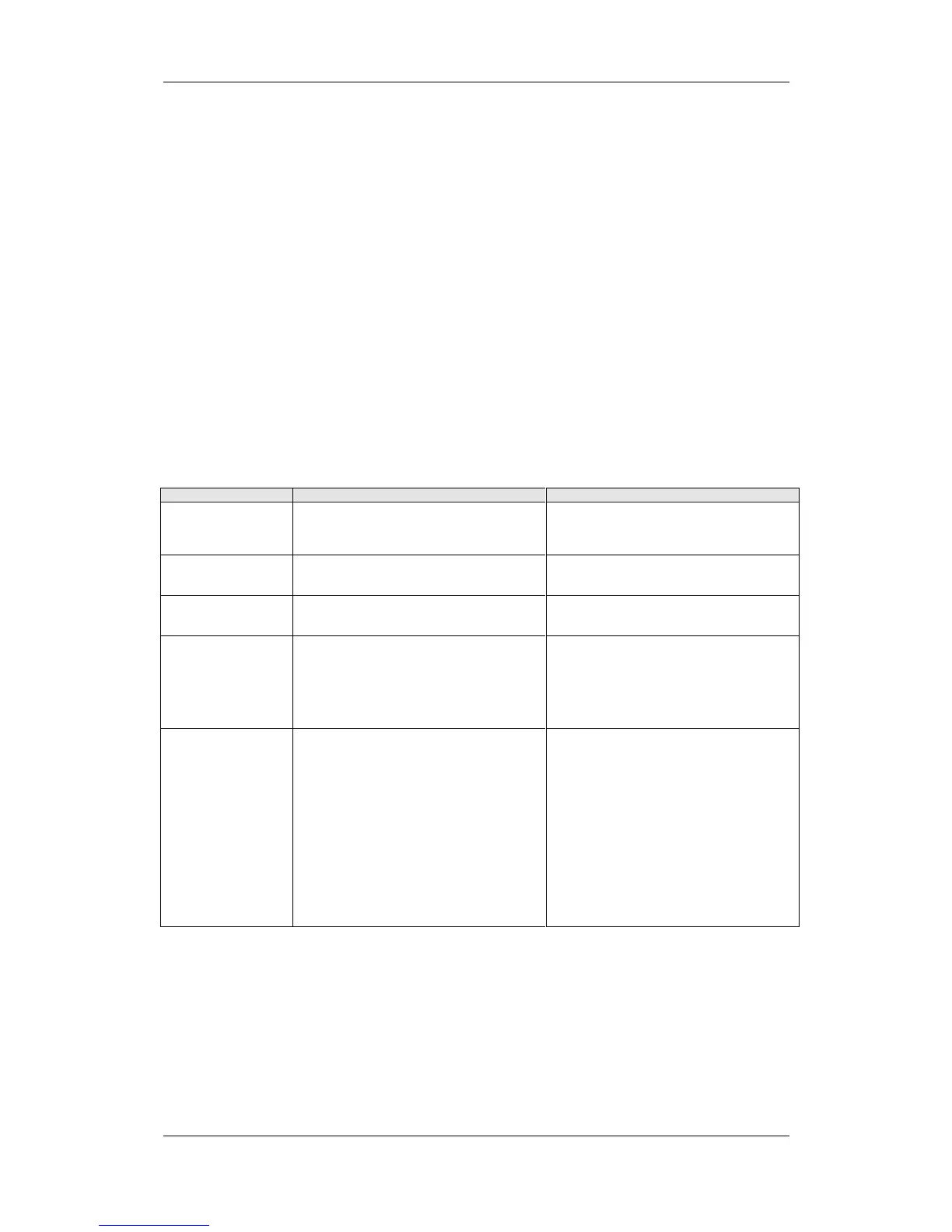
Number / Fault Cause Counter-measure
F001
Main contactor
checkback
The monitoring time of the main contactor
checkback (P600) has expired.
- Check main contactor checkback
- Clear main contactor checkback (P591.B =
0)
- Increase monitoring time (P600)
F002
Pre-charging fault
The monitoring time of pre-charging has
expired, i.e. the DC link voltage has not
reached the setpoint within 3 secs.
- Check voltage connection (AC or DC)
- Compare value in P070 and unit MLFB
F006
DC link overvoltage
Due to excessive DC link voltage, shutdown
has occurred (shutdown threshold approx.
820 V)
Check the line voltage (AC-AC) or the input
direct voltage (DC-AC). Compare value with
P071 (Line Volts)
F008
DC link undervoltage
The lower limit value of 76% of the DC link
voltage has been fallen short of.
- check the line voltage (AC-AC) or the input
direct voltage (DC-AC). Compare value with
P071 (Line Volts)
- check input rectifier (AC-AC)
- check DC link
F011
Overcurrent
Overcurrent shutdown has occurred.
The shutdown threshold has been exceeded.
The phase in which an overcurrent has
occurred is indicated in a bit-coded manner in
the fault value (see P949).
Phase U --> Bit 0 = 1--> fault value = 1
Phase V --> Bit 1 = 1--> fault value = 2
Phase W--> Bit 2 = 1--> fault value = 4
If an overcurrent occurs simultaneously in
several phases, the total of the fault values of
the phases concerned is the resulting fault
value.
- Check the converter output for short-circuit or
earth fault
- Check the load for an overload condition
- Check whether motor and converter are
correctly matched
- Check whether the dynamic requirements
are too high
 Loading...
Loading...











