3-10 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM
SENSOR AND SWITCH
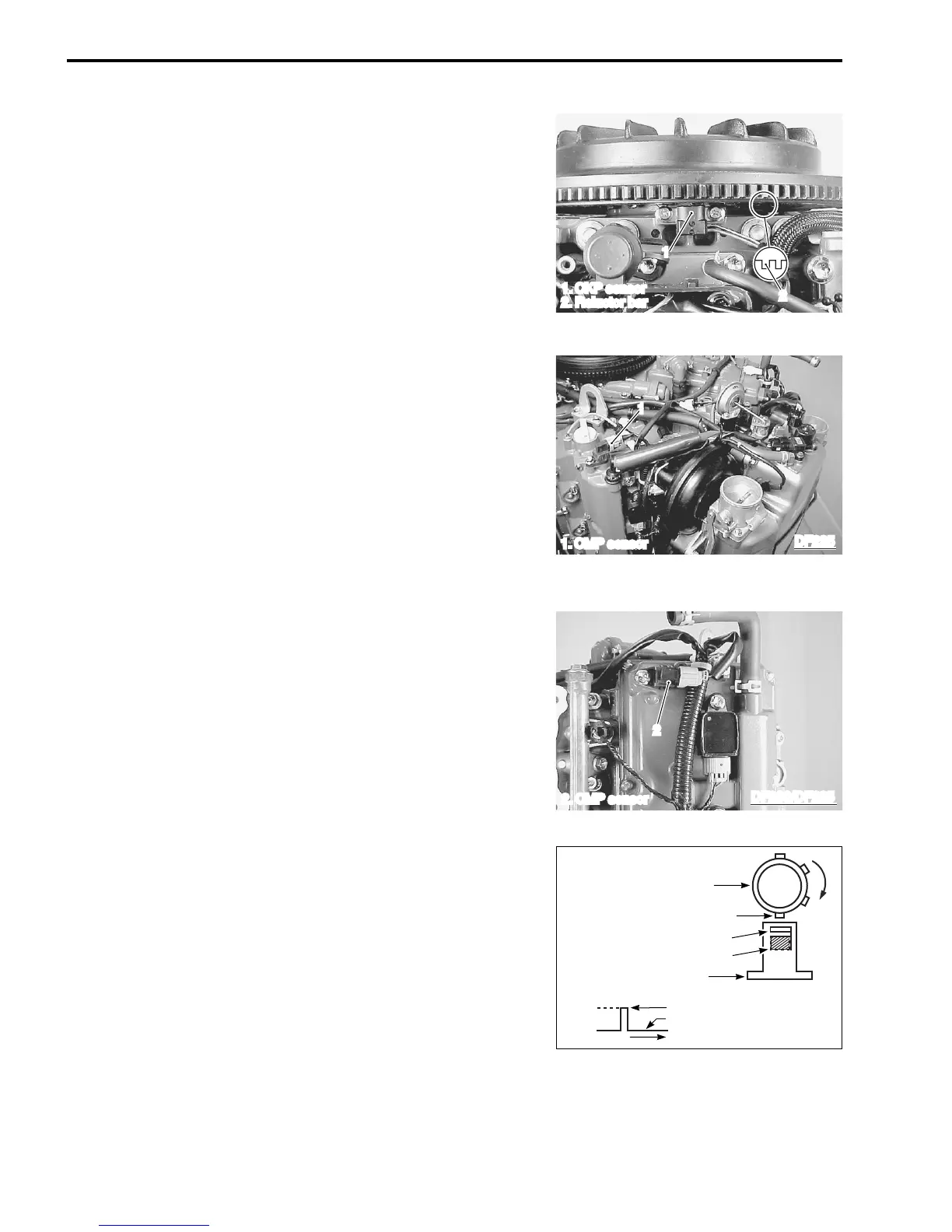
CKP (Crankshaft Position) SENSOR
There is one (1) CKP sensor installed below the flywheel rotor.
When the reluctor bars on the flywheel pass the sensor, a signal
(voltage pulse) is generated and sent to the ECM.
This is the fundamental signal used to judge engine speed and
crankshaft angle.
There are 34 reluctor bars, spaced 10 degrees apart, followed
by a 20 degree index space. During one crankshaft rotation, 34
signals are input to the ECM.
CMP (Camshaft Position) SENSOR #1
• For DF250 model:
CMP sensor #1 is mounted on the PORT cylinder head cover
with trigger vanes pressed onto the end of the PORT exhaust
camshaft. This sensor detects piston position.
• For DF200/225 models:
CMP sensor #1 is mounted on the STBD cylinder head cover
with trigger vanes pressed onto the end of the Intake cam-
shaft. This sensor detects piston position.
• Signals received from this sensor are also used by the ECM
to determine sequential fuel injection control.
The CMP sensor contains a “Hall Effect” semiconductor and a
magnet. The semiconductor generates a voltage in proportion to
the line of magnetic force passed through it. When a trigger
vane on the camshaft reluctor aligns with the sensor’ internal
magnet, a large amount of magnetic force is generated allowing
a high voltage to pass through the semiconductor. When the
trigger vane moves away from the sensor, no magnetic force is
generated and low voltage passes through the semiconductor.
These generated voltages are rectified to create “ON” (high volt-
age) & “OFF” (low voltage) signals to the ECM.
The four camshaft trigger vanes provid four high voltage signals
from CMP sensor to ECM during one rotation of camshaft (two
rotations of crankshaft).
1
1. CKP sensor
2. Reluctor bar
2
1
1. CMP sensor
DF225
2. CMP sensor
DF200/DF225
2
Camshaft
Trigger vane
“Hall Effect” semiconductor
Magnet
CMP sensor
High voltage
Low voltage

 Loading...
Loading...