
 Loading...
Loading...
Do you have a question about the Tektronix TDS 784D and is the answer not in the manual?
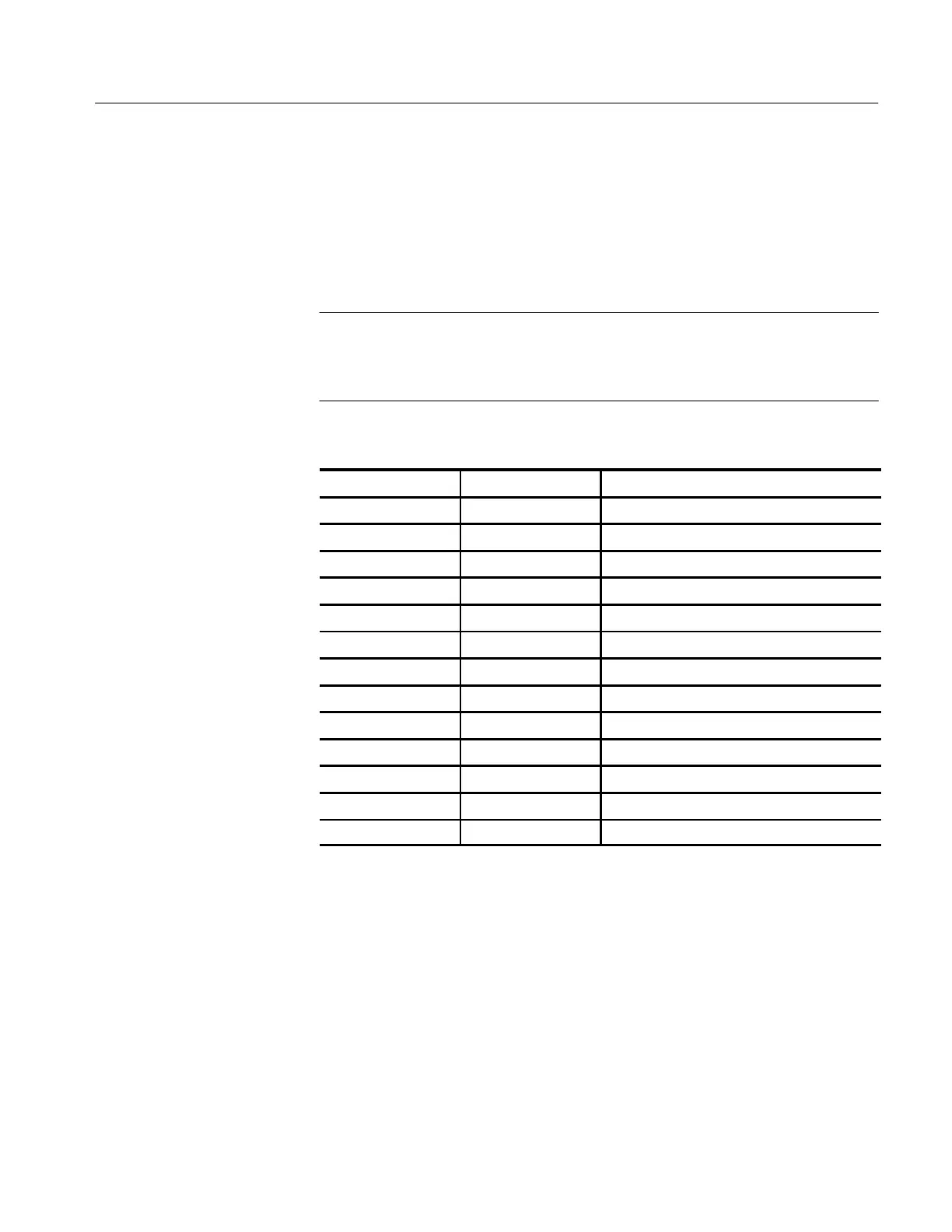
| Bandwidth | 1 GHz |
|---|---|
| Channels | 4 |
| Sample Rate | 4 GS/s |
| Vertical Sensitivity | 1 mV/div to 10 V/div |
| Vertical Resolution | 8 bits |
| Input Coupling | AC, DC, GND |
| Input Impedance | 1 MΩ ± 1% |
| Display | color LCD |
| Timebase Accuracy | 50 ppm |
| Trigger Modes | Edge, Pulse, Video |
| Power Requirements | 100-240 VAC |
| Dimensions | 508 mm |
Safety precautions to avoid injury and damage to the product and connected equipment.
Precautions to prevent damage from electrostatic discharge to circuitry.
Ensures oscilloscope is properly installed and powered on before use.
How to acquire, select, and display waveforms properly for measurement.
Explains how to trigger for a stable display, covering basic principles and types.
Details how to use the oscilloscope's five classes of measurements for accurate results.
How to save and recall waveforms, setups, and displays, and manage files.
How to prepare and set up the oscilloscope for control and operation over the GPIB interface.
How to display status of internal systems and access on-line help.
Explains powerful features for testing and digitally processing acquired waveforms.
Defines and calculates automated measurements such as Amplitude, Area, and Cycle Area.
Explains the algorithm used by the oscilloscope for integrating waveforms.
Probes using active circuit elements like transistors, requiring a power source.
Enable direct observation and measurement of current waveforms from DC to 1 GHz.
Blend optical power meter functions with high-speed analog waveform analysis.
Triggers when data source changes state within setup or hold time relative to a clock source.











