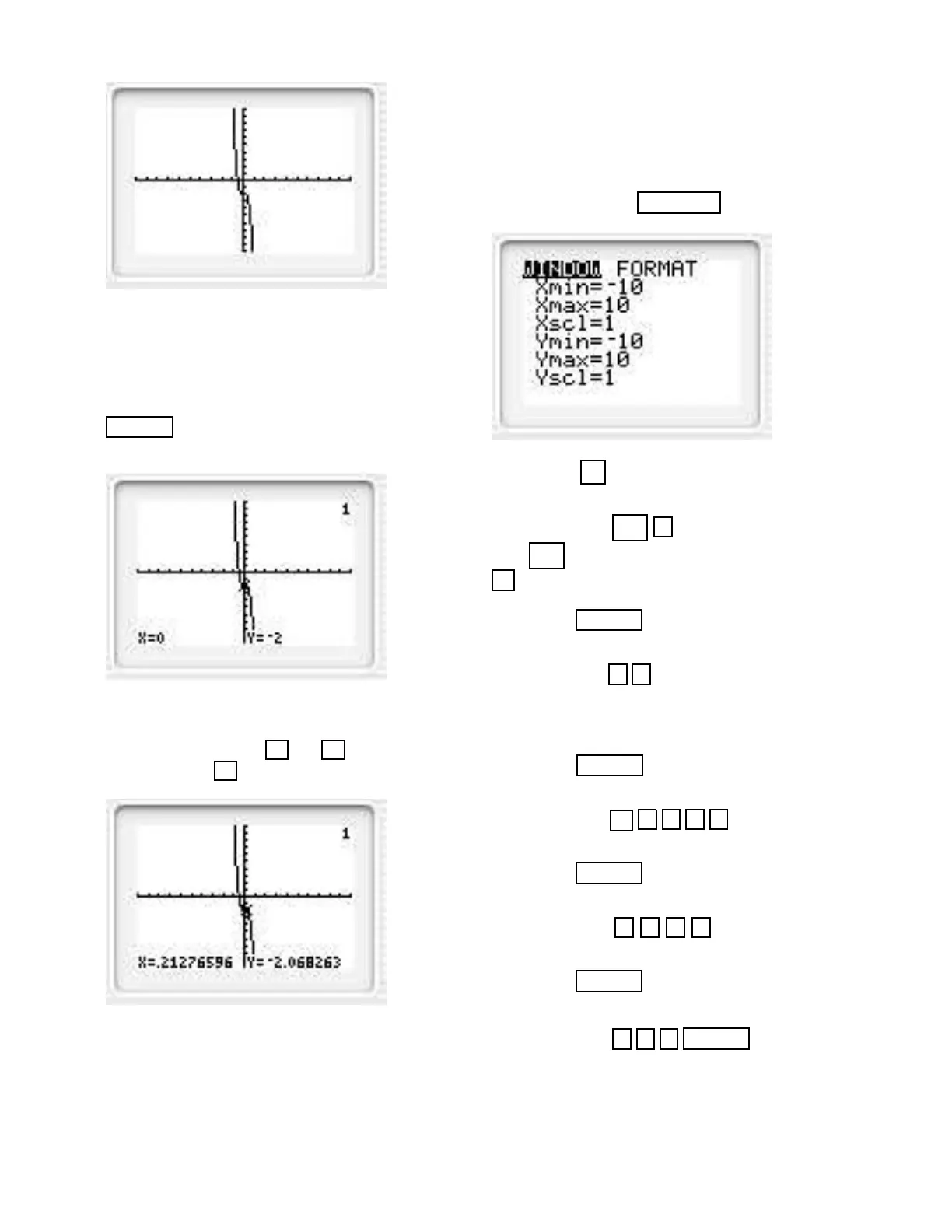
The TRACE Feature
Find points on the graph of the previous example. Re-
call y = x
4
− 12x
3
+ x
2
− 2.
Solution. After graphing the function press the
TRACE key. A blinking star-like cursor will be sitting
on a point of the graph.
At the bottom you see x = 0 and y = −2. This means
that the point (0, 2) lies on the graph. You can move
the cursor by using the and keys. For example,
by pressing the key you obtain
This means that the (approximate) point
(0.21276596, −2.068263) is on the graph.
Change the Dimensions of the Viewing Window
Graph y = x
4
−12x
3
+ x
2
−2 using a window with di-
mensions [−5, 14] by [−2500, 1000]. (This is the second
part of Example 1 in the text).
Solution. Press the WINDOW key and you see
Press the 5 key and the blinking cursor moves
down to the −10 after Xmin.
Press the keys (−) 5 . This changes −10 to −5.
(The
(−) key is used to change the sign, whereas the
− key is used to subtract two quantities.)
Press the ENTER key. The blinking cursor drops
to the 10 after Xmax.
Press the keys 1 4 . This changes 10 to 14
Notice that Xscl is 1. This means the tick marks on
the x-axis are set at 1 unit. We will not change this.
Press the ENTER key twice. The blinking cursor
drops to the −10 after Ymin.
Press the keys − 2 5 0 0 . This changes −10
to −2500.
Press the ENTER key. The blinking cursor drops
to the 10 after Ymax.
Press the keys 1 0 0 0 . This changes 10 to
1000.
Press the ENTER key. The blinking cursor drops
to the 1 after Yscl. We need to set the tick (scale)
marks on the y-axis to a much larger number, say 500.
So press the keys 5 0 0 ENTER .
You should see the following.
35

 Loading...
Loading...











