B-18 Electrostatic Classifier Model 3082 and SMPS Spectrometer Model 3938
Penetration is a function of the particle diffusion coefficient D, length of the
tube L, and volumetric flow rate Q. The Diffusion coefficient D is affected
by temperature, gas medium, and particle diameter.
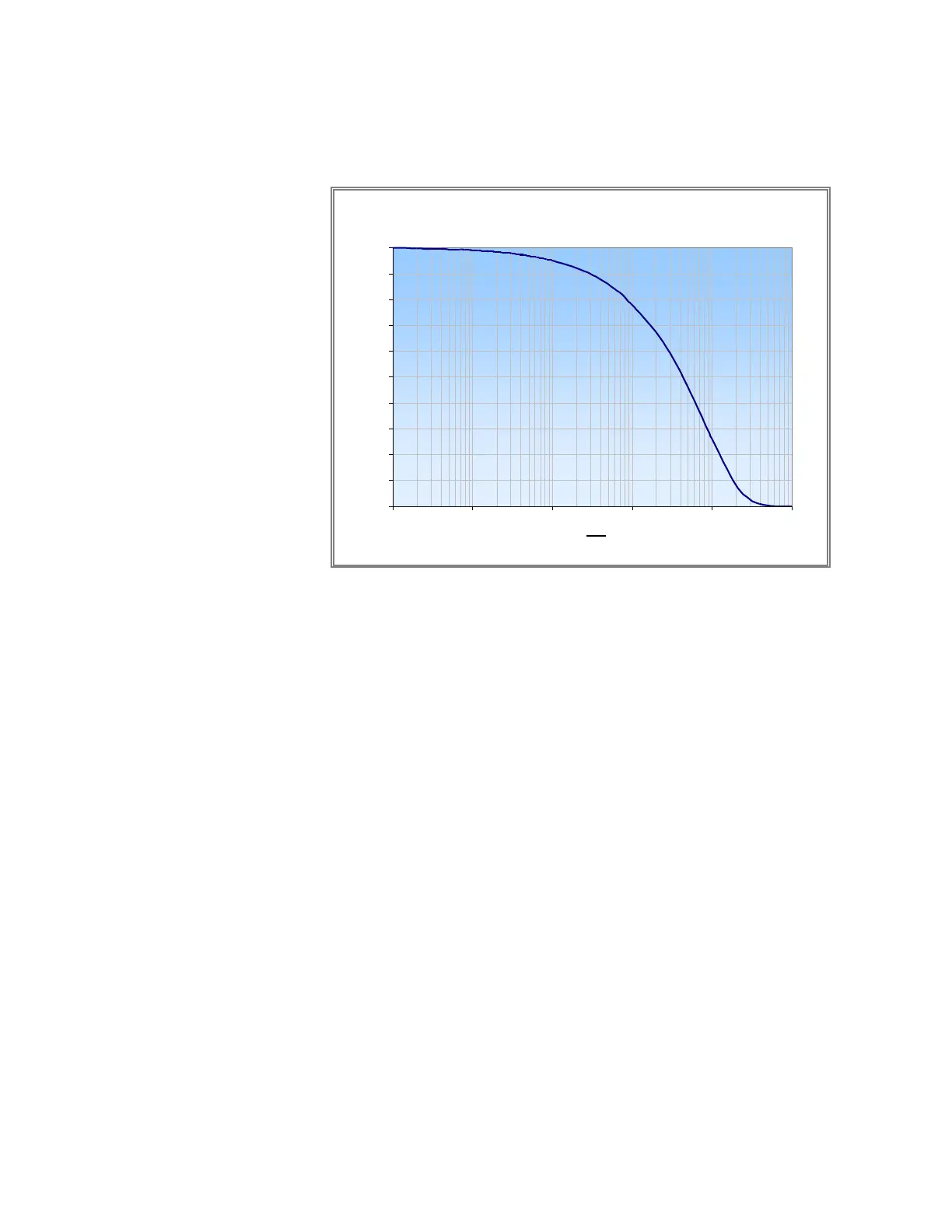
Figure B-7
Circular Tube Penetration Efficiency [Gormley and Kennedy (1949)]
Note that the diffusion loss through a tube (for a fixed volumetric flow rate
and laminar tube flow) is not a function of tubing diameter. The additional
distance the particles must travel to the walls in a wider tube is offset by a
longer residence time.
The Scanning Mobility Particle Sizing™ (SMPS) spectrometer can be
broken down into five different flow paths for which an aerosol penetration
can be calculated.
P
1
= Penetration through the impactor inlet
P
2
= Penetration through the bi-polar neutralizer and internal plumbing
P
3
= Penetration through the tubing to the Differential Mobility Analyzer
(DMA) and CPC
P
4
= Penetration through the DMA
P
5
= Penetration through the CPC
Circular Tube Penetration Efficiency
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
0.00001 0.0001 0.001 0.01 0.1 1

 Loading...
Loading...