Planning the electrical installation
38
3. Check that the motor voltage rating meets the application requirements:
See notes 6 and 7 below the Requirements table.
4. Consult the motor manufacturer before using a motor in a drive system where the
motor nominal voltage differs from the AC power source voltage.
5. Ensure that the motor insulation system withstands the maximum peak voltage in
the motor terminals. See the Requirements table below for the required motor
insulation system and drive filtering.
Example 1: When the supply voltage is 440 V and a drive with a diode supply is
operating in motor mode only, the maximum peak voltage in the motor terminals
can be approximated as follows: 440 V · 1.35 · 2 = 1190 V. Check that the motor
insulation system withstands this voltage.
Example 2: When the supply voltage is 440 V and the drive is equipped with an
IGBT supply, the maximum peak voltage in the motor terminals can be
approximated as follows: 440 V · 1.41 · 2 = 1241 V. Check that the motor
insulation system withstands this voltage.
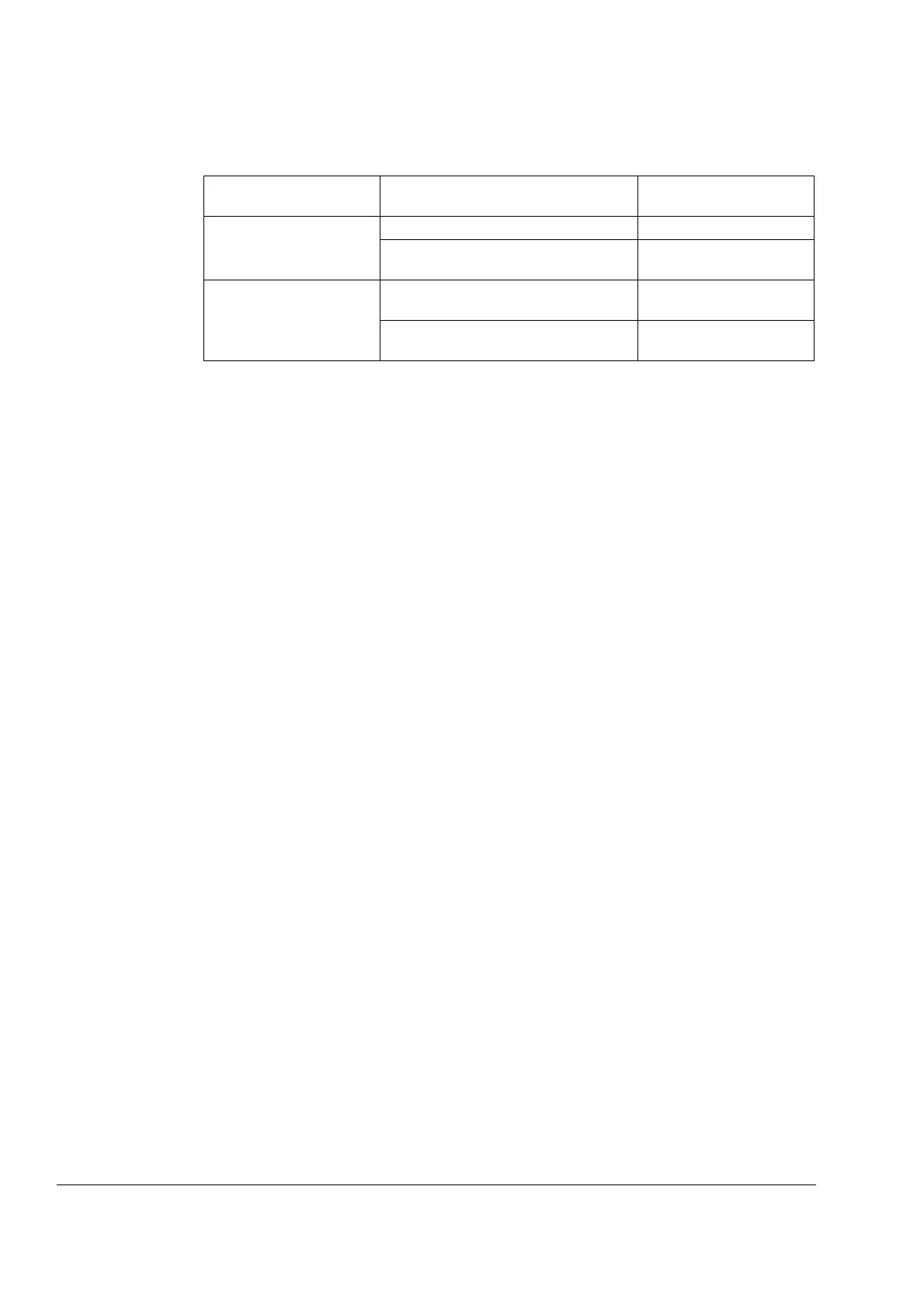
If the drive is equipped
with …
… and … … then the motor voltage
rating should be …
diode supply
ACS800-01, -U1, -02, -U2,
-04, -04M, -U4 -07, -U7
no resistor braking is in use U
N
frequent or long term brake cycles will
be used
U
ACeq1
IGBT supply
ACS800-11, -U11, -17
DC link voltage will not be increased
from nominal (parameter setting)
U
N
DC link voltage will be increased from
nominal (parameter setting)
U
ACeq2
U
N
= Rated input voltage of the drive
U
ACeq1
= U
DC
/1.35
U
ACeq2
= U
DC
/1.41
U
ACeq
is the equivalent AC power source voltage of the drive in VAC.
U
DC
is the maximum DC link voltage of the drive in VDC.
For resistor braking: U
DC
= 1.21 × nominal DC link voltage.
For units with IGBT supply: See the parameter value.
(Note: Nominal DC link voltage is U
N
× 1.35 or U
N
× 1.41 in VDC.)

 Loading...
Loading...











