-
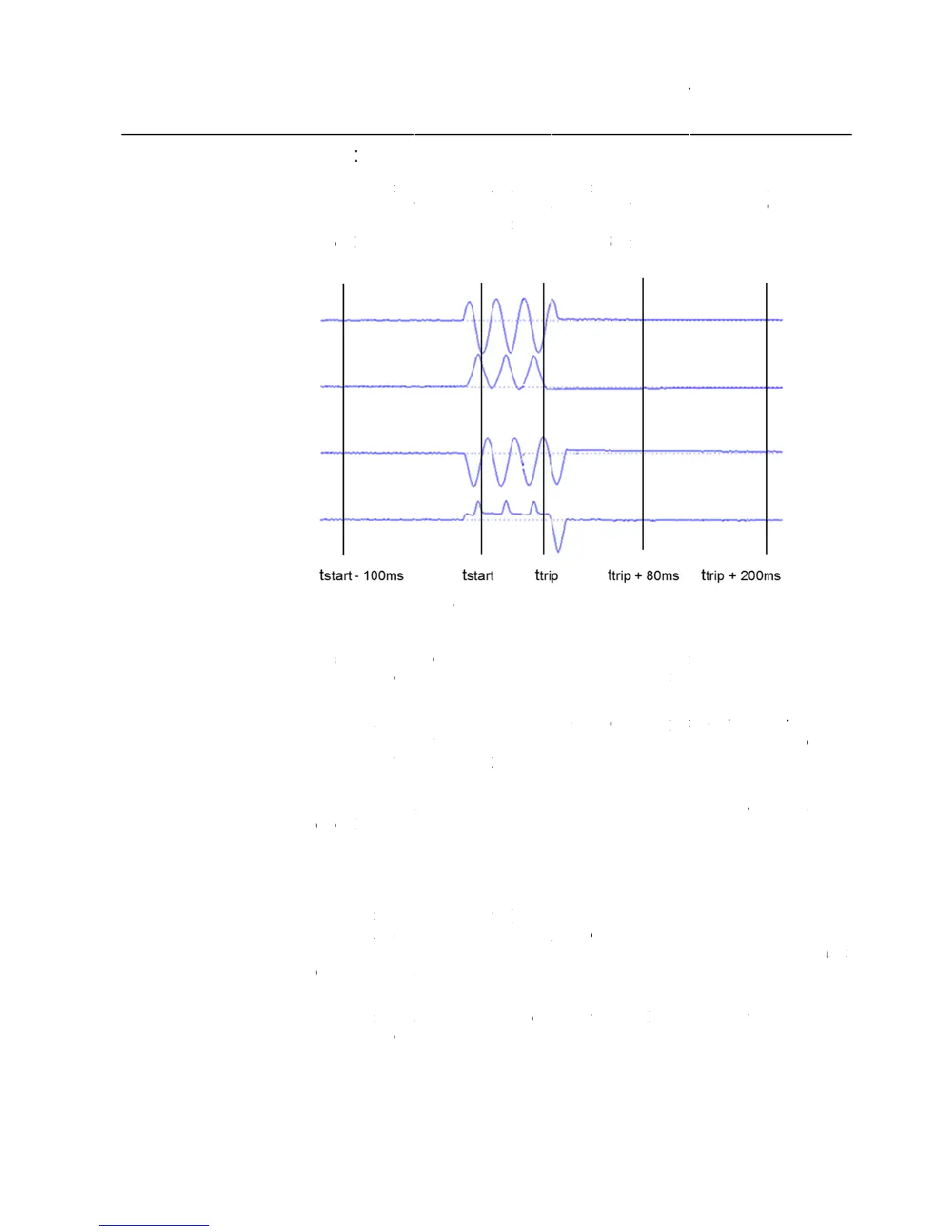
The relay stores records of analog values for last five trip events in non
memory. The fault recording is triggered by the trip signal of a protection function.
Each fault record includes the rms current values of fundamental component for all
These records enable the user to analyze the five most recent power system events.
The oldest recording is lost when a new fault recording is made.
Additional, the relay count the number of phase fault trip and earth fault trip into
dedicated trip counters. These trip counters cannot be reset by the user and are
stored in nonvolatile memory.
The values of fault records and trip counters are accessi
remotely via communication interface of the relay.
volatile memory to store 100 event logs. Each event log includes type of event
recent being first and so on.
The SoE information are accessible locally
communication interface of the relay.
The relay stores records of analog values for last five trip events in non
memory. The fault recording is triggered by the trip signal of a protection function.
Each fault record includes the rms current values of fundamental component for all
ee phases and the neutral current at five different times along the trip event.
These records enable the user to analyze the five most recent power system events.
The oldest recording is lost when a new fault recording is made.
Additional, the relay count the number of phase fault trip and earth fault trip into
dedicated trip counters. These trip counters cannot be reset by the user and are
stored in nonvolatile memory.
The values of fault records and trip counters are accessi
remotely via communication interface of the relay.
volatile memory to store 100 event logs. Each event log includes type of event
recent being first and so on.
The SoE information are accessible locally
communication interface of the relay.
The relay stores records of analog values for last five trip events in non
memory. The fault recording is triggered by the trip signal of a protection function.
Each fault record includes the rms current values of fundamental component for all
ee phases and the neutral current at five different times along the trip event.
These records enable the user to analyze the five most recent power system events.
The oldest recording is lost when a new fault recording is made.
Additional, the relay count the number of phase fault trip and earth fault trip into
dedicated trip counters. These trip counters cannot be reset by the user and are
stored in nonvolatile memory.
The values of fault records and trip counters are accessi
remotely via communication interface of the relay.
volatile memory to store 100 event logs. Each event log includes type of event
recent being first and so on.
The SoE information are accessible locally
communication interface of the relay.
The relay stores records of analog values for last five trip events in non
memory. The fault recording is triggered by the trip signal of a protection function.
Each fault record includes the rms current values of fundamental component for all
ee phases and the neutral current at five different times along the trip event.
These records enable the user to analyze the five most recent power system events.
The oldest recording is lost when a new fault recording is made.
Additional, the relay count the number of phase fault trip and earth fault trip into
dedicated trip counters. These trip counters cannot be reset by the user and are
stored in nonvolatile memory.
The values of fault records and trip counters are accessi
remotely via communication interface of the relay.
volatile memory to store 100 event logs. Each event log includes type of event
recent being first and so on.
The SoE information are accessible locally
communication interface of the relay.
The relay stores records of analog values for last five trip events in non
memory. The fault recording is triggered by the trip signal of a protection function.
Each fault record includes the rms current values of fundamental component for all
ee phases and the neutral current at five different times along the trip event.
These records enable the user to analyze the five most recent power system events.
The oldest recording is lost when a new fault recording is made.
Additional, the relay count the number of phase fault trip and earth fault trip into
dedicated trip counters. These trip counters cannot be reset by the user and are
stored in nonvolatile memory.
The values of fault records and trip counters are accessi
remotely via communication interface of the relay.
volatile memory to store 100 event logs. Each event log includes type of event
recent being first and so on.
The SoE information are accessible locally
communication interface of the relay.
The relay stores records of analog values for last five trip events in non
memory. The fault recording is triggered by the trip signal of a protection function.
Each fault record includes the rms current values of fundamental component for all
ee phases and the neutral current at five different times along the trip event.
These records enable the user to analyze the five most recent power system events.
The oldest recording is lost when a new fault recording is made.
Additional, the relay count the number of phase fault trip and earth fault trip into
dedicated trip counters. These trip counters cannot be reset by the user and are
stored in nonvolatile memory.
The values of fault records and trip counters are accessi
remotely via communication interface of the relay.
volatile memory to store 100 event logs. Each event log includes type of event
recent being first and so on.
The SoE information are accessible locally
communication interface of the relay.
The relay stores records of analog values for last five trip events in non
memory. The fault recording is triggered by the trip signal of a protection function.
Each fault record includes the rms current values of fundamental component for all
ee phases and the neutral current at five different times along the trip event.
These records enable the user to analyze the five most recent power system events.
The oldest recording is lost when a new fault recording is made.
Additional, the relay count the number of phase fault trip and earth fault trip into
dedicated trip counters. These trip counters cannot be reset by the user and are
stored in nonvolatile memory.
The values of fault records and trip counters are accessi
remotely via communication interface of the relay.
volatile memory to store 100 event logs. Each event log includes type of event
recent being first and so on.
The SoE information are accessible locally
communication interface of the relay.
The relay stores records of analog values for last five trip events in non
memory. The fault recording is triggered by the trip signal of a protection function.
Each fault record includes the rms current values of fundamental component for all
ee phases and the neutral current at five different times along the trip event.
These records enable the user to analyze the five most recent power system events.
The oldest recording is lost when a new fault recording is made.
Additional, the relay count the number of phase fault trip and earth fault trip into
dedicated trip counters. These trip counters cannot be reset by the user and are
stored in nonvolatile memory.
The values of fault records and trip counters are accessi
remotely via communication interface of the relay.
-
volatile memory to store 100 event logs. Each event log includes type of event
recent being first and so on.
The SoE information are accessible locally
communication interface of the relay.
The relay stores records of analog values for last five trip events in non
memory. The fault recording is triggered by the trip signal of a protection function.
Each fault record includes the rms current values of fundamental component for all
ee phases and the neutral current at five different times along the trip event.
These records enable the user to analyze the five most recent power system events.
The oldest recording is lost when a new fault recording is made.
Additional, the relay count the number of phase fault trip and earth fault trip into
dedicated trip counters. These trip counters cannot be reset by the user and are
stored in nonvolatile memory.
The values of fault records and trip counters are accessi
remotely via communication interface of the relay.
-
events (SoE) information, the relay incorporates a non
volatile memory to store 100 event logs. Each event log includes type of event
recent being first and so on.
The SoE information are accessible locally
communication interface of the relay.
The relay stores records of analog values for last five trip events in non
memory. The fault recording is triggered by the trip signal of a protection function.
Each fault record includes the rms current values of fundamental component for all
ee phases and the neutral current at five different times along the trip event.
These records enable the user to analyze the five most recent power system events.
The oldest recording is lost when a new fault recording is made.
Additional, the relay count the number of phase fault trip and earth fault trip into
dedicated trip counters. These trip counters cannot be reset by the user and are
stored in nonvolatile memory.
The values of fault records and trip counters are accessi
remotely via communication interface of the relay.
events (SoE) information, the relay incorporates a non
volatile memory to store 100 event logs. Each event log includes type of event
recent being first and so on.
The SoE information are accessible locally
communication interface of the relay.
The relay stores records of analog values for last five trip events in non
memory. The fault recording is triggered by the trip signal of a protection function.
Each fault record includes the rms current values of fundamental component for all
ee phases and the neutral current at five different times along the trip event.
These records enable the user to analyze the five most recent power system events.
The oldest recording is lost when a new fault recording is made.
Additional, the relay count the number of phase fault trip and earth fault trip into
dedicated trip counters. These trip counters cannot be reset by the user and are
stored in nonvolatile memory.
The values of fault records and trip counters are accessi
remotely via communication interface of the relay.
events (SoE) information, the relay incorporates a non
volatile memory to store 100 event logs. Each event log includes type of event
The SoE information are accessible locally
communication interface of the relay.
The relay stores records of analog values for last five trip events in non
memory. The fault recording is triggered by the trip signal of a protection function.
Each fault record includes the rms current values of fundamental component for all
ee phases and the neutral current at five different times along the trip event.
These records enable the user to analyze the five most recent power system events.
The oldest recording is lost when a new fault recording is made.
Additional, the relay count the number of phase fault trip and earth fault trip into
dedicated trip counters. These trip counters cannot be reset by the user and are
The values of fault records and trip counters are accessi
remotely via communication interface of the relay.
events (SoE) information, the relay incorporates a non
volatile memory to store 100 event logs. Each event log includes type of event
The SoE information are accessible locally
communication interface of the relay.
The relay stores records of analog values for last five trip events in non
memory. The fault recording is triggered by the trip signal of a protection function.
Each fault record includes the rms current values of fundamental component for all
ee phases and the neutral current at five different times along the trip event.
These records enable the user to analyze the five most recent power system events.
The oldest recording is lost when a new fault recording is made.
Additional, the relay count the number of phase fault trip and earth fault trip into
dedicated trip counters. These trip counters cannot be reset by the user and are
The values of fault records and trip counters are accessi
remotely via communication interface of the relay.
events (SoE) information, the relay incorporates a non
volatile memory to store 100 event logs. Each event log includes type of event
.
The event logs are stored sequentially, the most
The SoE information are accessible locally
communication interface of the relay.
The relay stores records of analog values for last five trip events in non
memory. The fault recording is triggered by the trip signal of a protection function.
Each fault record includes the rms current values of fundamental component for all
ee phases and the neutral current at five different times along the trip event.
These records enable the user to analyze the five most recent power system events.
The oldest recording is lost when a new fault recording is made.
Additional, the relay count the number of phase fault trip and earth fault trip into
dedicated trip counters. These trip counters cannot be reset by the user and are
The values of fault records and trip counters are accessi
remotely via communication interface of the relay.
events (SoE) information, the relay incorporates a non
volatile memory to store 100 event logs. Each event log includes type of event
The event logs are stored sequentially, the most
The SoE information are accessible locally
communication interface of the relay.
The relay stores records of analog values for last five trip events in non
memory. The fault recording is triggered by the trip signal of a protection function.
Each fault record includes the rms current values of fundamental component for all
ee phases and the neutral current at five different times along the trip event.
These records enable the user to analyze the five most recent power system events.
The oldest recording is lost when a new fault recording is made.
Additional, the relay count the number of phase fault trip and earth fault trip into
dedicated trip counters. These trip counters cannot be reset by the user and are
The values of fault records and trip counters are accessi
remotely via communication interface of the relay.
events (SoE) information, the relay incorporates a non
volatile memory to store 100 event logs. Each event log includes type of event
The event logs are stored sequentially, the most
The SoE information are accessible locally
The relay stores records of analog values for last five trip events in non
memory. The fault recording is triggered by the trip signal of a protection function.
Each fault record includes the rms current values of fundamental component for all
ee phases and the neutral current at five different times along the trip event.
These records enable the user to analyze the five most recent power system events.
The oldest recording is lost when a new fault recording is made.
Additional, the relay count the number of phase fault trip and earth fault trip into
dedicated trip counters. These trip counters cannot be reset by the user and are
The values of fault records and trip counters are accessi
remotely via communication interface of the relay.
events (SoE) information, the relay incorporates a non
volatile memory to store 100 event logs. Each event log includes type of event
The event logs are stored sequentially, the most
The relay stores records of analog values for last five trip events in non
memory. The fault recording is triggered by the trip signal of a protection function.
Each fault record includes the rms current values of fundamental component for all
ee phases and the neutral current at five different times along the trip event.
These records enable the user to analyze the five most recent power system events.
The oldest recording is lost when a new fault recording is made.
Additional, the relay count the number of phase fault trip and earth fault trip into
dedicated trip counters. These trip counters cannot be reset by the user and are
The values of fault records and trip counters are accessi
remotely via communication interface of the relay.
events (SoE) information, the relay incorporates a non
volatile memory to store 100 event logs. Each event log includes type of event
The event logs are stored sequentially, the most
The relay stores records of analog values for last five trip events in non
memory. The fault recording is triggered by the trip signal of a protection function.
Each fault record includes the rms current values of fundamental component for all
ee phases and the neutral current at five different times along the trip event.
These records enable the user to analyze the five most recent power system events.
The oldest recording is lost when a new fault recording is made.
Additional, the relay count the number of phase fault trip and earth fault trip into
dedicated trip counters. These trip counters cannot be reset by the user and are
The values of fault records and trip counters are accessi
remotely via communication interface of the relay.
events (SoE) information, the relay incorporates a non
volatile memory to store 100 event logs. Each event log includes type of event
The event logs are stored sequentially, the most
The relay stores records of analog values for last five trip events in non
memory. The fault recording is triggered by the trip signal of a protection function.
Each fault record includes the rms current values of fundamental component for all
ee phases and the neutral current at five different times along the trip event.
These records enable the user to analyze the five most recent power system events.
The oldest recording is lost when a new fault recording is made.
Additional, the relay count the number of phase fault trip and earth fault trip into
dedicated trip counters. These trip counters cannot be reset by the user and are
The values of fault records and trip counters are accessi
events (SoE) information, the relay incorporates a non
volatile memory to store 100 event logs. Each event log includes type of event
The event logs are stored sequentially, the most
The relay stores records of analog values for last five trip events in non
memory. The fault recording is triggered by the trip signal of a protection function.
Each fault record includes the rms current values of fundamental component for all
ee phases and the neutral current at five different times along the trip event.
These records enable the user to analyze the five most recent power system events.
The oldest recording is lost when a new fault recording is made.
Additional, the relay count the number of phase fault trip and earth fault trip into
dedicated trip counters. These trip counters cannot be reset by the user and are
events (SoE) information, the relay incorporates a non
volatile memory to store 100 event logs. Each event log includes type of event
The event logs are stored sequentially, the most
The relay stores records of analog values for last five trip events in non
memory. The fault recording is triggered by the trip signal of a protection function.
Each fault record includes the rms current values of fundamental component for all
ee phases and the neutral current at five different times along the trip event.
These records enable the user to analyze the five most recent power system events.
The oldest recording is lost when a new fault recording is made.
Additional, the relay count the number of phase fault trip and earth fault trip into
dedicated trip counters. These trip counters cannot be reset by the user and are
events (SoE) information, the relay incorporates a non
volatile memory to store 100 event logs. Each event log includes type of event
The event logs are stored sequentially, the most
The relay stores records of analog values for last five trip events in non
memory. The fault recording is triggered by the trip signal of a protection function.
Each fault record includes the rms current values of fundamental component for all
ee phases and the neutral current at five different times along the trip event.
These records enable the user to analyze the five most recent power system events.
The oldest recording is lost when a new fault recording is made.
Additional, the relay count the number of phase fault trip and earth fault trip into
dedicated trip counters. These trip counters cannot be reset by the user and are
events (SoE) information, the relay incorporates a non
volatile memory to store 100 event logs. Each event log includes type of event
The event logs are stored sequentially, the most
The relay stores records of analog values for last five trip events in non
memory. The fault recording is triggered by the trip signal of a protection function.
Each fault record includes the rms current values of fundamental component for all
ee phases and the neutral current at five different times along the trip event.
These records enable the user to analyze the five most recent power system events.
Additional, the relay count the number of phase fault trip and earth fault trip into
dedicated trip counters. These trip counters cannot be reset by the user and are
events (SoE) information, the relay incorporates a non
volatile memory to store 100 event logs. Each event log includes type of event
The event logs are stored sequentially, the most
The relay stores records of analog values for last five trip events in non
memory. The fault recording is triggered by the trip signal of a protection function.
Each fault record includes the rms current values of fundamental component for all
ee phases and the neutral current at five different times along the trip event.
These records enable the user to analyze the five most recent power system events.
Additional, the relay count the number of phase fault trip and earth fault trip into
dedicated trip counters. These trip counters cannot be reset by the user and are
events (SoE) information, the relay incorporates a non
volatile memory to store 100 event logs. Each event log includes type of event
The event logs are stored sequentially, the most
The relay stores records of analog values for last five trip events in non
-
memory. The fault recording is triggered by the trip signal of a protection function.
Each fault record includes the rms current values of fundamental component for all
ee phases and the neutral current at five different times along the trip event.
These records enable the user to analyze the five most recent power system events.
Additional, the relay count the number of phase fault trip and earth fault trip into
dedicated trip counters. These trip counters cannot be reset by the user and are
events (SoE) information, the relay incorporates a non
volatile memory to store 100 event logs. Each event log includes type of event
The event logs are stored sequentially, the most
memory. The fault recording is triggered by the trip signal of a protection function.
Each fault record includes the rms current values of fundamental component for all
ee phases and the neutral current at five different times along the trip event.
These records enable the user to analyze the five most recent power system events.
Additional, the relay count the number of phase fault trip and earth fault trip into
dedicated trip counters. These trip counters cannot be reset by the user and are
events (SoE) information, the relay incorporates a non
volatile memory to store 100 event logs. Each event log includes type of event
The event logs are stored sequentially, the most
memory. The fault recording is triggered by the trip signal of a protection function.
Each fault record includes the rms current values of fundamental component for all
ee phases and the neutral current at five different times along the trip event.
These records enable the user to analyze the five most recent power system events.
Additional, the relay count the number of phase fault trip and earth fault trip into
dedicated trip counters. These trip counters cannot be reset by the user and are
events (SoE) information, the relay incorporates a non
-
volatile memory to store 100 event logs. Each event log includes type of event
The event logs are stored sequentially, the most
memory. The fault recording is triggered by the trip signal of a protection function.
Each fault record includes the rms current values of fundamental component for all
These records enable the user to analyze the five most recent power system events.
Additional, the relay count the number of phase fault trip and earth fault trip into
The event logs are stored sequentially, the most
memory. The fault recording is triggered by the trip signal of a protection function.
Each fault record includes the rms current values of fundamental component for all
These records enable the user to analyze the five most recent power system events.
The event logs are stored sequentially, the most

 Loading...
Loading...