148 Agilent N518xA, E8663B, E44x8C, and E82x7D Signal Generators Programming Guide
Programming the Status Register System
Status Register Bit Values
Status Register Bit Values
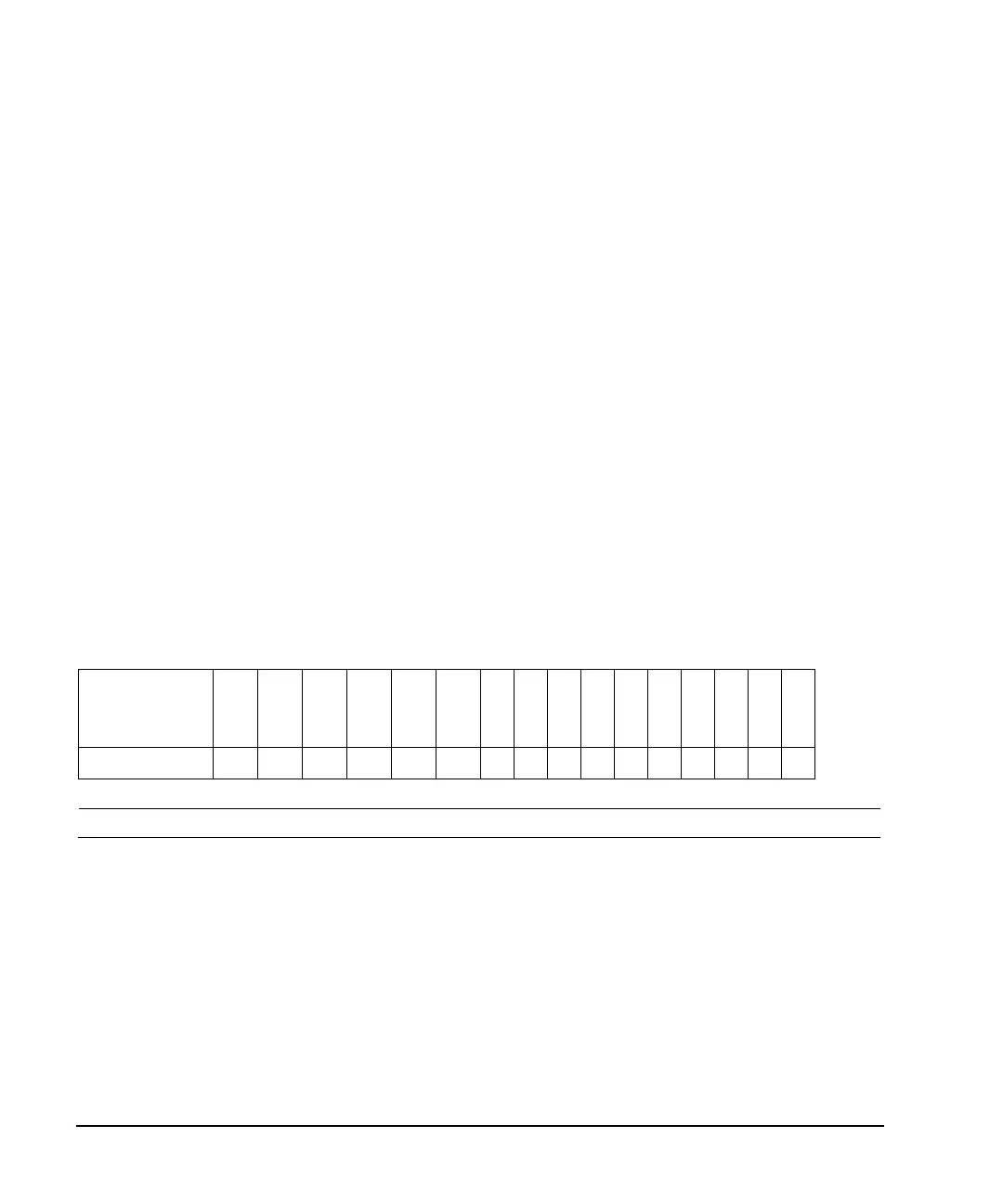
Each bit in a register is represented by a decimal value based on its location in the register (see
Table 4- 1).
• To enable a particular bit in a register, send its value with the SCPI command. Refer to the signal
generator’s SCPI command listing for more information.
• To enable more than one bit, send the sum of all the bits that you want to enable.
• To verify the bits set in a register, query the register.
Example: Enable a Register
To enable bit 0 and bit 6 of the Standard Event Status Group’s Event Register:
1. Add the decimal value of bit 0 (1) and the decimal value of bit 6 (64) to give a decimal value of
65.
2. Send the sum with the command: *ESE 65.
Example: Query a Register
To query a register for a condition, send a SCPI query command. For example, if you want to query
the Standard Operation Status Group’s Condition Register, send the command:
STATus:OPERation:CONDition?
If bit 7, bit 3 and bit 2 in this register are set (bits = 1) then the query will return the decimal value
140. The value represents the decimal values of bit 7, bit 3 and bit 2: 128 + 8 + 4 = 140.
NOTE Bit 15 is not used and is always set to zero.
Table 4-1 Status Register Bit Decimal Values
Decimal
Value
Always 0
16384
8192
4096
2048
1024
512
256
128
64
32
16
8
4
2
1
Bit Number 15 14 13 12 11 10 9876543210

 Loading...
Loading...