Hybrid electric water heater (WiFi model) – GENERAL INFORMATION
107
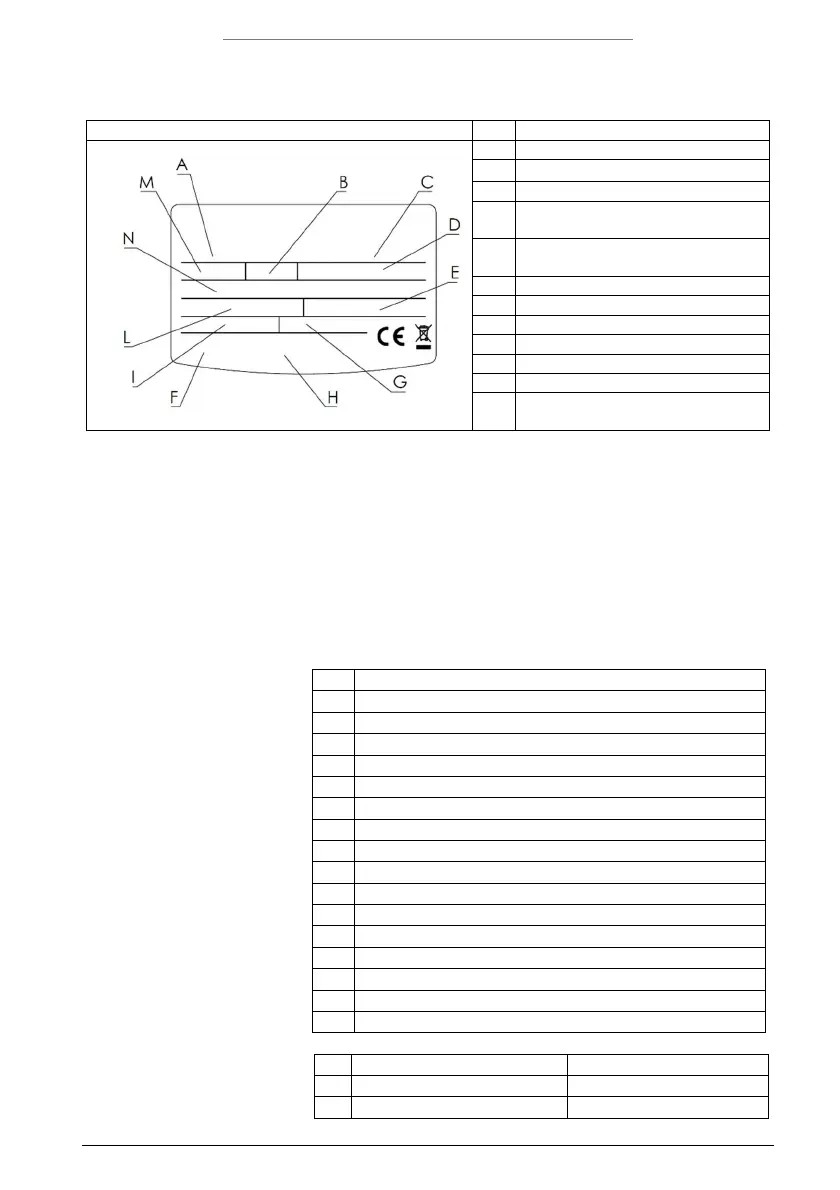
1.7 Identification of the appliance
The main information for identifying the appliance is contained on the adhesive data plate located on the water heater
casing.
B tank capacity
D
power supply voltage. frequency.
maximum absorbed power
E
max./min. pressure of the refrigeration
circuit
max./min. power in heat pump mode
N
Global warming potential GWP / Quantity
of fluorinated gases
2 TECHNICAL FEATURES
2.1 Operating principle
The electric hybrid water heater uses electrical energy rationally, achieving the same result as an electric water heater
much more efficiently. This is possible due to the heat pump unit which allows an electrical energy savings of
approximately 50% compared to an electrical water heater.
The efficiency of a heat pump cycle is measured by the Coefficient of Performance (COP), i.e. the ratio between the
energy supplied to the appliance (in this case, the heat transferred to the water to be heated) and the electrical energy
used (by the compressor and the appliance's auxiliary devices). The COP varies according to the type of heat pump
and to its relative conditions of operation. For example, a COP value equal to 3 indicates that for every 1 kWh of electrical
energy used, the heat pump supplies 3 kWh of heat to the medium to be heated, of which 2 kWh are extracted from the
free source.
2.2 Construction features
(See Fig. 2)
A Compressor
B Compressor start capacitor
C Fan
D NTC air sensor
E Evaporator
F Capillary tube
G Main P.C.B.
H NTC evaporator sensor
I NTC hot water sensor housing
J Capacitor
K Flange heating element
L NTC hot water sensor
M Heating element connections
N 1200 W electrical heating element
O Magnesium anodes
P Impressed current anode
Q WiFi electronic board
2.3 Overall dimensions
(See Fig. 3a and 3b)
80 LITRE MODEL 100 LITRE MODEL
A 784 934
B 1009 1153
 Loading...
Loading...











