ITU-T G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection Switching Functionality
The Ethernet ring protection functionality includes the following:
•
Loop avoidance
•
The use of learning, forwarding, and Filtering Database (FDB) mechanisms
Loop avoidance in an Ethernet ring is achieved by ensuring that, at any time, traffic flows on all but the Ring
Protection Link (RPL).
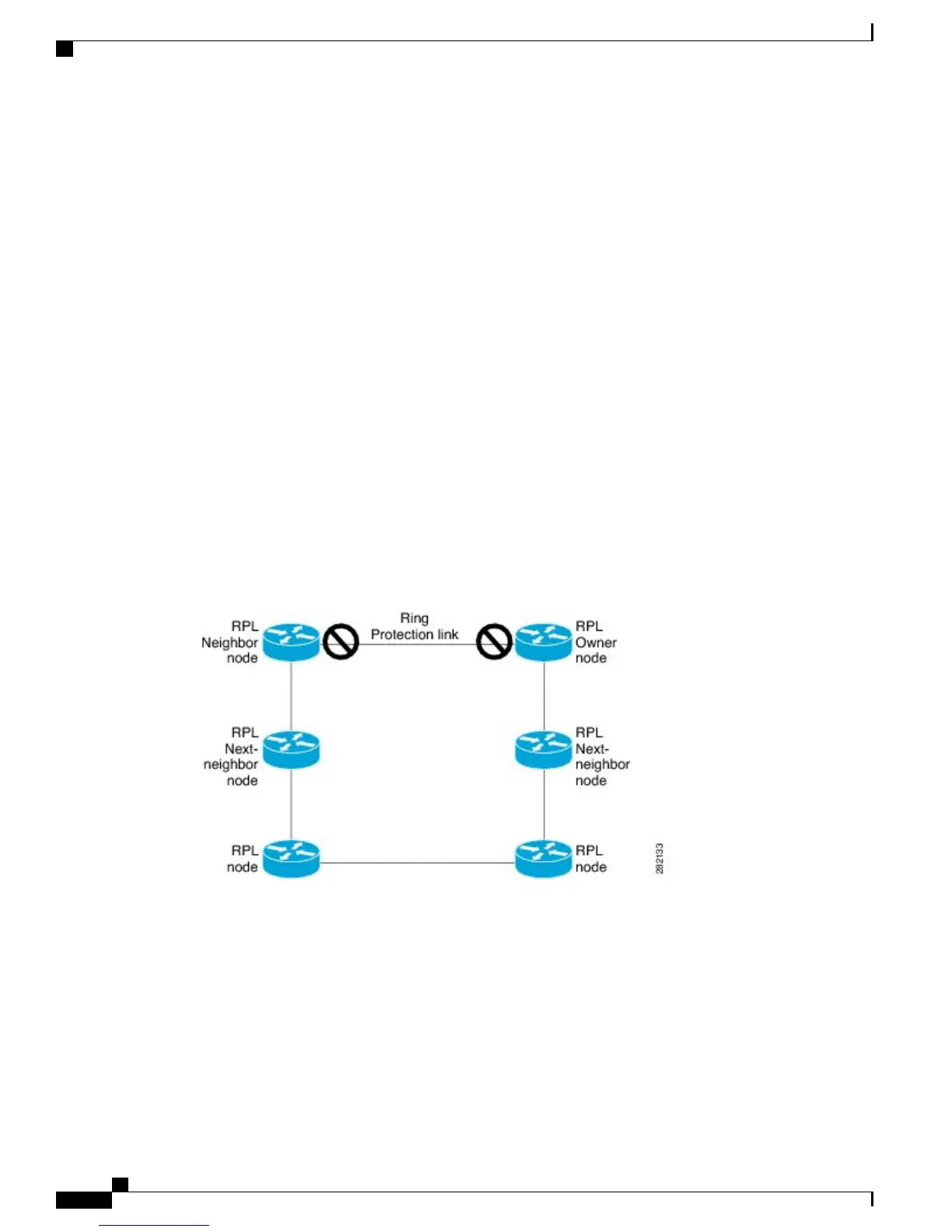
The following is a list of RPL types (or RPL nodes) and their functions:
• RPL owner—Responsible for blocking traffic over the RPL so that no loops are formed in the Ethernet
traffic. There can be only one RPL owner in a ring.
• RPL neighbor node—An Ethernet ring node adjacent to the RPL. It is responsible for blocking its end
of the RPL under normal conditions. This node type is optional and prevents RPL usage when protected.
• RPL next-neighbor node—Next-neighbor node is an Ethernet ring node adjacent to an RPL owner node
or RPL neighbor node. It is mainly used for FDB flush optimization on the ring. This node is also
optional.
The following figure illustrates the G.8032 Ethernet ring topology.
Figure 8: G.8032 Ethernet Ring Topology
R-APS Control Messages
Nodes on the ring use control messages called Ring Automatic Protection Switching (R-APS) messages to
coordinate the activities of switching the ring protection link (RPL) on and off. Any failure along the ring
triggers a R-APS Signal Failure (R-APS SF) message in both directions of the nodes adjacent to the failed
link, after the nodes have blocked the port facing the failed link. On obtaining this message, the RPL owner
unblocks the RPL port.
LAN Switching Configuration Guide Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.5.1 (Cisco ASR 900 Series)
48
ITU-T G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection Switching
ITU-T G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection Switching Functionality

 Loading...
Loading...











