
Do you have a question about the GE MULTILINK ML2400 and is the answer not in the manual?
Instructions on how to set up the GE MultiLink family of switches using the console port.
Details the order codes for the MultiLink ML2400 Ethernet Switch, including module options.
Provides technical, environmental, and physical specifications of the ML2400 switch.
Explains Command Line Firmware and EnerVista Software features and usage.
Covers console connection, setup, IP configuration, privilege levels, and user management.
Guide to logging in, managing privilege levels, and user accounts via the web interface.
Procedure for upgrading the switch firmware via serial/console port or EnerVista software.
Introduces the ML2400 Ethernet Switch, its capabilities, and design aspects.
Details the various port modules available, including four-port, six-port, and eight-port options.
Highlights key features like managed switching, QoS, fiber-built-in design, and modularity.
Describes common applications for the ML2400, such as VLANs and network segmentation.
Outlines essential precautions and steps to take before installing the ML2400 switch.
Provides instructions for connecting various Ethernet media types, including fiber and copper.
Details on how to mount the ML2400 switch, including table-top and rack mounting.
Covers powering the ML2400, UL requirements, and alarm contact connections.
Steps for connecting a console terminal for managing the switch.
Explains the core functions of the ML2400, including switching, filtering, and status LEDs.
Provides guidance on identifying and resolving common issues before seeking support.
Overview of IP addressing, its importance for switch management, and system information.
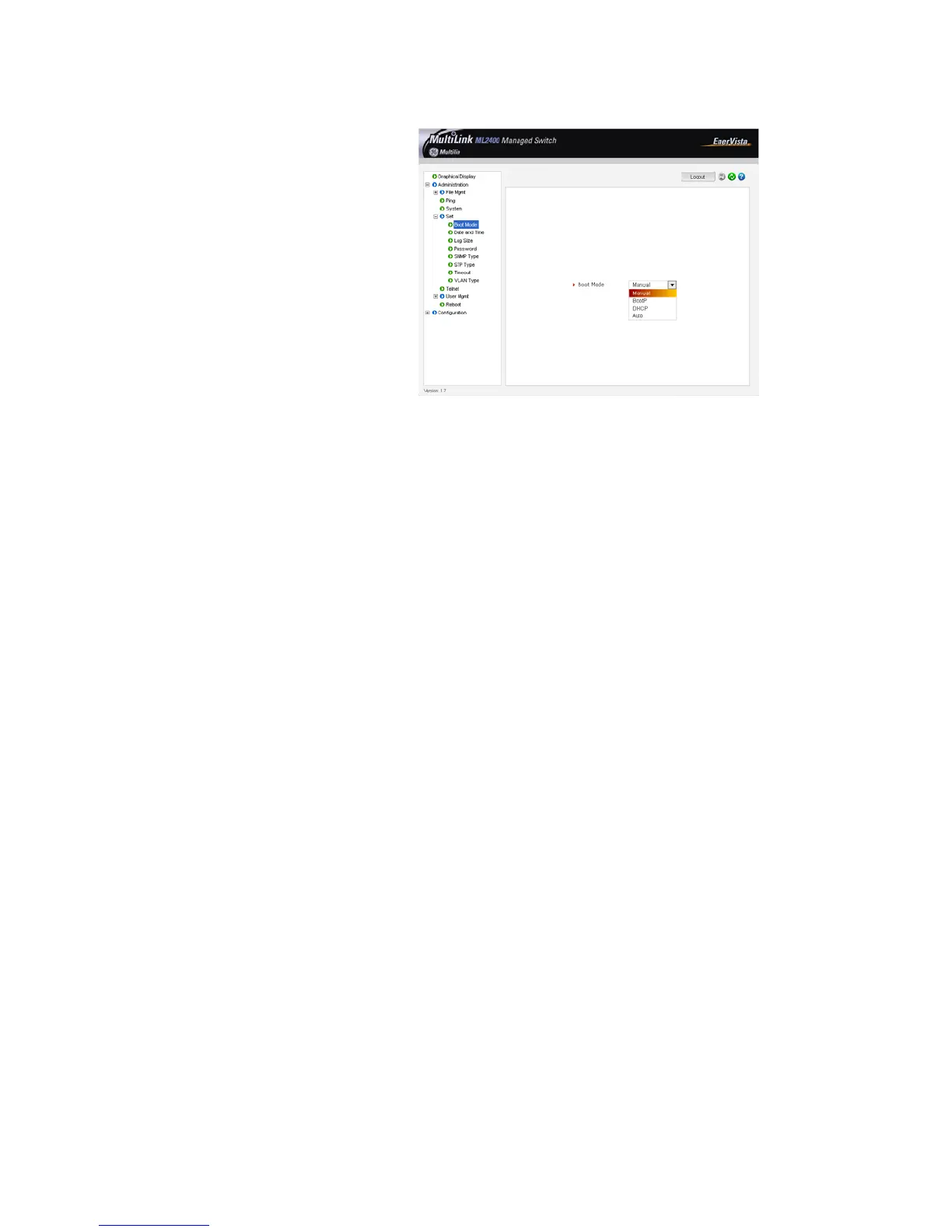
Explains DHCP, bootp, and automatic IP configuration methods for the switch.
Covers configuring serial port and system parameters like date, time, and IP settings.
Details on saving and loading configurations via CLI and EnerVista software.
Introduction to IPv6 addressing and its differences from IPv4.
Explains methods for securing switch access, including passwords and port security.
CLI commands for managing port security, MAC addresses, and logging.
GUI steps for configuring port security, managing MAC addresses, and reviewing logs.
Overview of the 802.1x protocol and its role in network authentication.
CLI commands for setting up 802.1x, including port control and RADIUS server configuration.
GUI steps for configuring RADIUS server and port settings for 802.1x authentication.
Explains the TACACS+ protocol for access control, authentication, and authorization.
CLI commands for configuring TACACS+ servers and managing authentication.
GUI steps for configuring TACACS+ servers and enabling services.
Explains port mirroring for traffic analysis, intrusion detection, and troubleshooting.
CLI commands for configuring and managing port mirroring functionality.
Configuration of port characteristics like speed, duplex, flow control, and back pressure.
GUI steps for configuring port mirroring and individual port settings.
Overview of VLANs, their role in creating separate collision domains and broadcast domains.
CLI commands for configuring port VLANs, including adding, starting, and saving configurations.
GUI steps for configuring port VLANs, including adding and activating VLANs.
CLI commands for configuring tag VLANs, including filtering and port tagging.
GUI steps for configuring tag VLANs, enabling tagging, and managing port settings.
Introduction to GARP and GVRP for automatic VLAN propagation across switches.
CLI commands for configuring GVRP operations, port states, and forbidding.
GUI steps for configuring GVRP, enabling/disabling, and setting port states.
Explains STP's function in preventing network loops and its features and operation.
CLI commands for enabling STP, viewing configurations, and setting bridge parameters.
Introduction to RSTP (IEEE 802.1w) as an evolution of STP for faster convergence.
CLI commands for configuring Normal RSTP, Smart RSTP, and port parameters.
GUI steps for configuring RSTP, including bridge configuration and port settings.
Explanation of Quality of Service (QoS), its importance, and concepts like preemptive queuing.
CLI commands for configuring Port, Tag, and ToS based QoS, including weights and priorities.
GUI steps for configuring Port, Tag, and ToS based QoS settings.
Introduction to IGMP for IP multicasting, host group management, and its role in networks.
CLI commands for configuring IGMP, including enabling/disabling, querier settings, and port modes.
GUI steps for configuring IGMP parameters and viewing IGMP groups and routers.
Introduction to SNMP for network management, MIBs, and SNMP versions.
CLI commands for configuring SNMP v1, v2c, and v3, including traps and security.
GUI steps for configuring SNMP parameters, community strings, managers, and trap receivers.
CLI commands for configuring RMON groups, including statistics, history, alarm, and event actions.
Configuration of alarm relays for reporting faults and events via software control.
Configuration of SMTP alerts for sending e-mail notifications of traps and events.
Viewing port statistics and log statistics through the EnerVista Secure Web Management Software.
Optimizing serial connection parameters in applications like HyperTerminal for performance.
Using commands to view command history and software version information.
Using ping commands to test network connectivity and IP address setup.
Customizing the command line prompt for improved usability and identification.
Viewing and exporting the system event log for troubleshooting and monitoring.
A comprehensive list of main commands categorized as show, set, and context-less.
Overview of the Modbus protocol and command-line interface settings for configuration.
Modbus memory map detailing addresses, descriptions, ranges, formats, and default values.
Details manual revisions, part numbers, release dates, and ECOs for tracking changes.
GE Multilin's warranty statement for manufactured switches, covering defects and limitations.