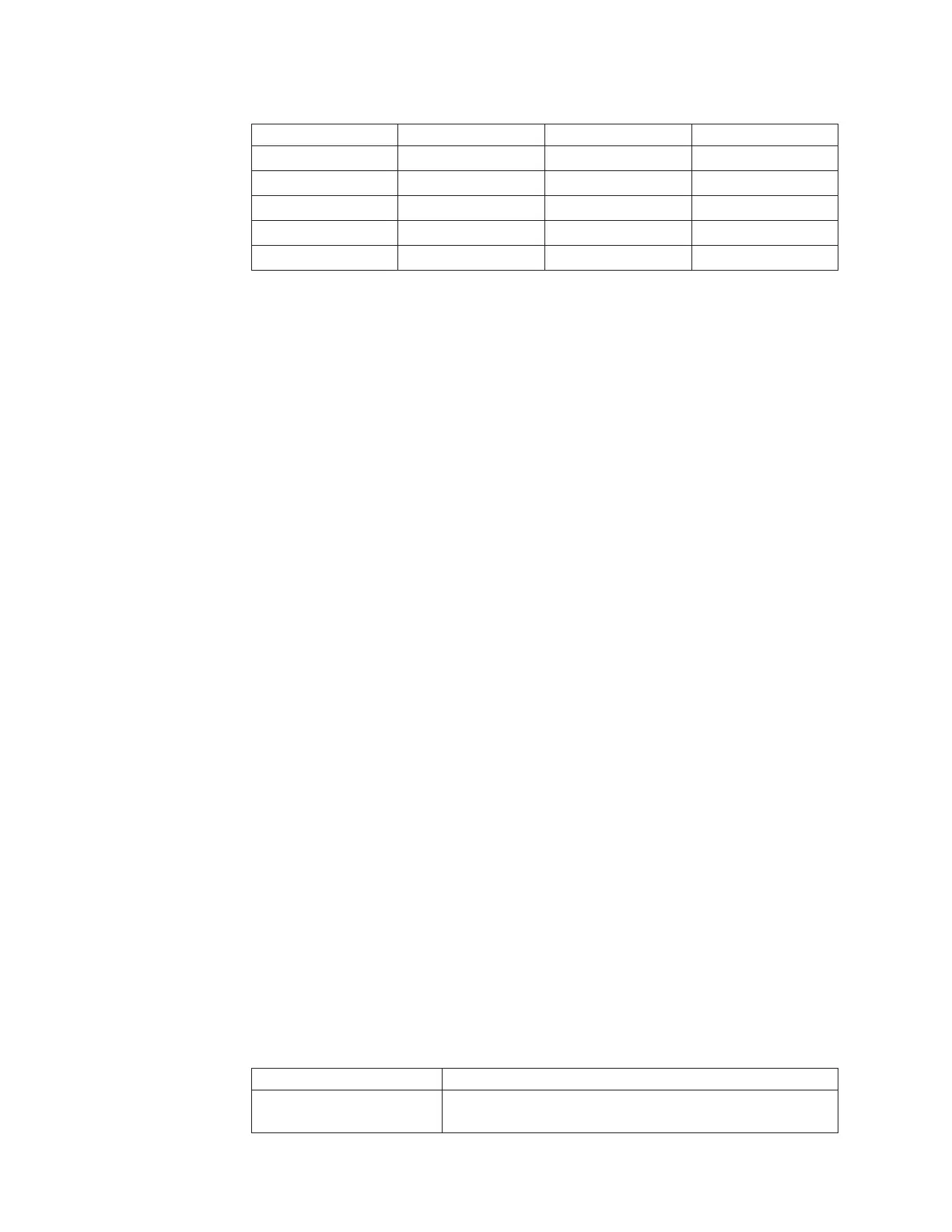
Table 9. Maximum memory installation using ranked DIMMs (continued)
Number of DIMMs DIMM type DIMM size Total memory
18 Dual-rank RDIMMs 2 GB 36 GB
18 Dual-rank RDIMMs 4 GB 72 GB
18 Dual-rank RDIMMs 8 GB 144 GB
12 Quad-rank RDIMMs 16 GB 192 GB
18 Dual-rank RDIMMs 16 GB 288 GB
v The RDIMM options that are available for the server are 2 GB, 4 GB, 8 GB, and
16 GB. The server supports a minimum of 2 GB and a maximum of 288 GB of
system memory using RDIMMs.
For 32-bit operating systems only: Some memory is reserved for various system
resources and is unavailable to the operating system. The amount of memory
that is reserved for system resources depends on the operating system, the
configuration of the server, and the configured PCI devices.
v The UDIMM options that are available for the server are 2 GB and 4 GB. The
server supports a minimum of 2 GB and a maximum of 48 GB of system
memory using UDIMMs.
Note: The amount of usable memory is reduced depending on the system
configuration. A certain amount of memory must be reserved for system
resources. To view the total amount of installed memory and the amount of
configured memory, run the Setup utility. For additional information, see
Chapter 3, “Configuring the server,” on page 157.
v A minimum of one DIMM must be installed for each microprocessor. For
example, you must install a minimum of two DIMMs if the server has two
microprocessors installed. However, to improve system performance, install a
minimum of three DIMMs for each microprocessor.
v DIMMs in the same system must be the same type (UDIMM or RDIMM) to
ensure that the server will operate correctly.
v When you install one quad-rank RDIMM in a channel, install it in the DIMM
connector furthest away from the microprocessor.
v Do not install one quad-rank RDIMM in one channel and three RDIMMs in
another channel.
DIMM installation sequence
The server comes with a minimum of one 2 GB DIMM installed in slot 3. When
you install additional DIMMs, install them in the order shown in the following
table to optimize system performance. In non-mirroring mode, all three channels
on the memory interface for each microprocessor can be populated in any order
and have no matching requirements.When you install additional DIMMs, install
them in the order shown in Table 10, to maintain performance.
Important: If you have configured the server to use memory mirroring, do not use
the order in Table 10; go to “Memory mirroring” on page 119 and use the
installation order shown there.
Table 10. DIMM installation sequence for non-mirroring (normal) mode
Installed microprocessors DIMM connector population sequence
Microprocessor socket 1 Install the DIMMs in the following sequence: 3, 6, 9, 2, 5, 8,
1, 4, 7
118 System x3650 M3 Types 4255, 7945, and 7949: Installation and User’s Guide
 Loading...
Loading...











