Chapter 1 Safety Information and Precautions
- 9 -
1.2 General Precautions
1. Requirements of a residual current device (RCD)
The AC drive generates high leakage current during running, which ows through the protective earthing (PE)
conductor. Thus install a type-B RCD at primary side of the power supply. When selecting the RCD, consider
the transient and steady-state leakage current to ground that may be generated at startup and during running
of the AC drive. You can select a specialized RCD with the function of suppressing high harmonics or a
general-purpose RCD with relatively large residual current.
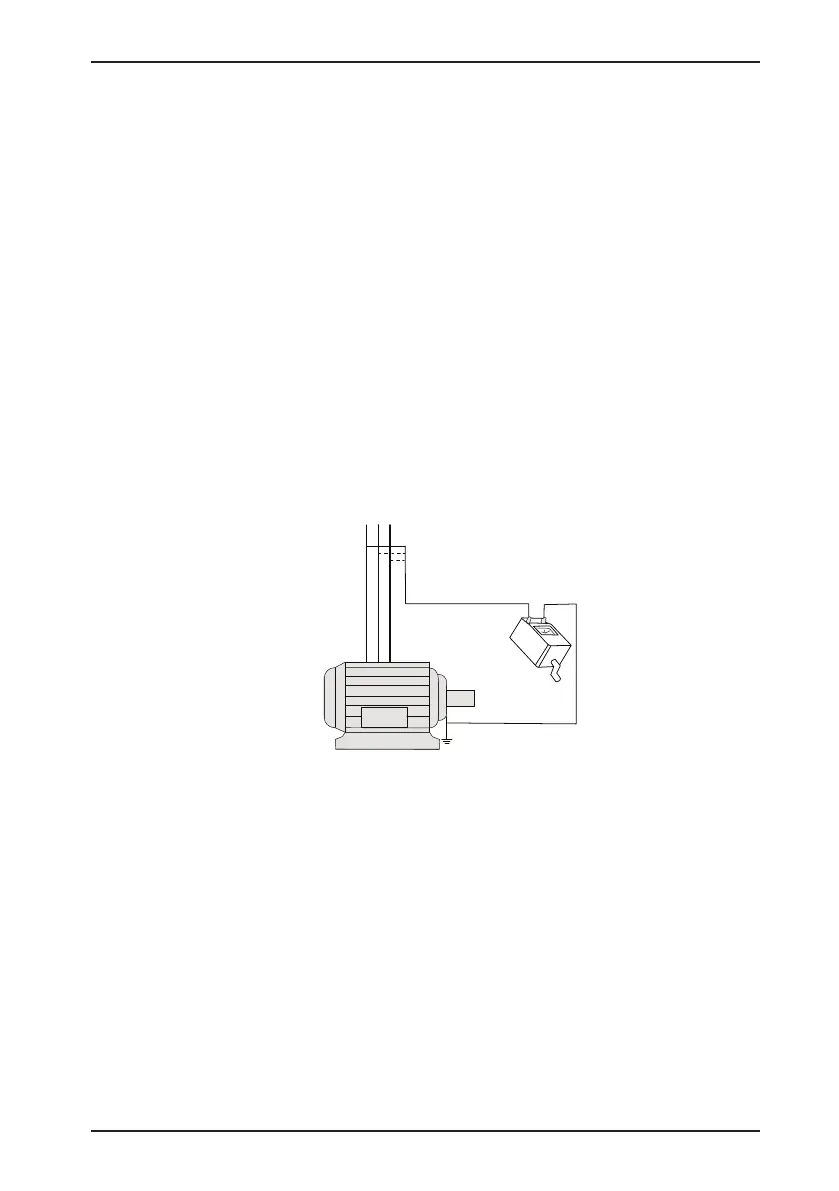
2. Motor insulation test
Arrange for a qualied technician to perform an insulation test on the motor under the following conditions
-
Before the motor is used for the rst time
-
When the motor is reused after being stored for a long time.
-
During regular maintenance check
This precaution detects poor insulation of the motor windings so that early actions can be taken to prevent
damage to the AC drive. The motor must be disconnected from the AC drive during the insulation test. A 500 V
volt insulation tester is recommended for this test, and the insulation resistance must not be less than 5 MΩ.
U V W
Megger
Input terminals
of the motor
Ground
3. Thermal protectin of the motor
If the related capacity of the motor does not match that of the AC drive, adjust the motor protection parameters
on the operation panel or install a thermal relay in the motor circuit for protection. It is especially important to
take this precaution if the AC drive has a higher power rating than the motor.
4. Running at the frequency above 50 Hz
The CS200 AC drive outputs the frequency of 0 to 150 Hz. If it is necessary to operate the CS200 drive at
frequency over 50 Hz, consider the capacity of the machine.
5. Motor heat and noise
The output of the AC drive is pulse width modulation (PWM) wave with certain harmonic frequency, and
therefore, the motor temperature, noise and vibration are slightly greater than those when the AC drive runs
on the line voltage.

 Loading...
Loading...











