Chapter 8 Maintenance and Troubleshooting
- 121 -
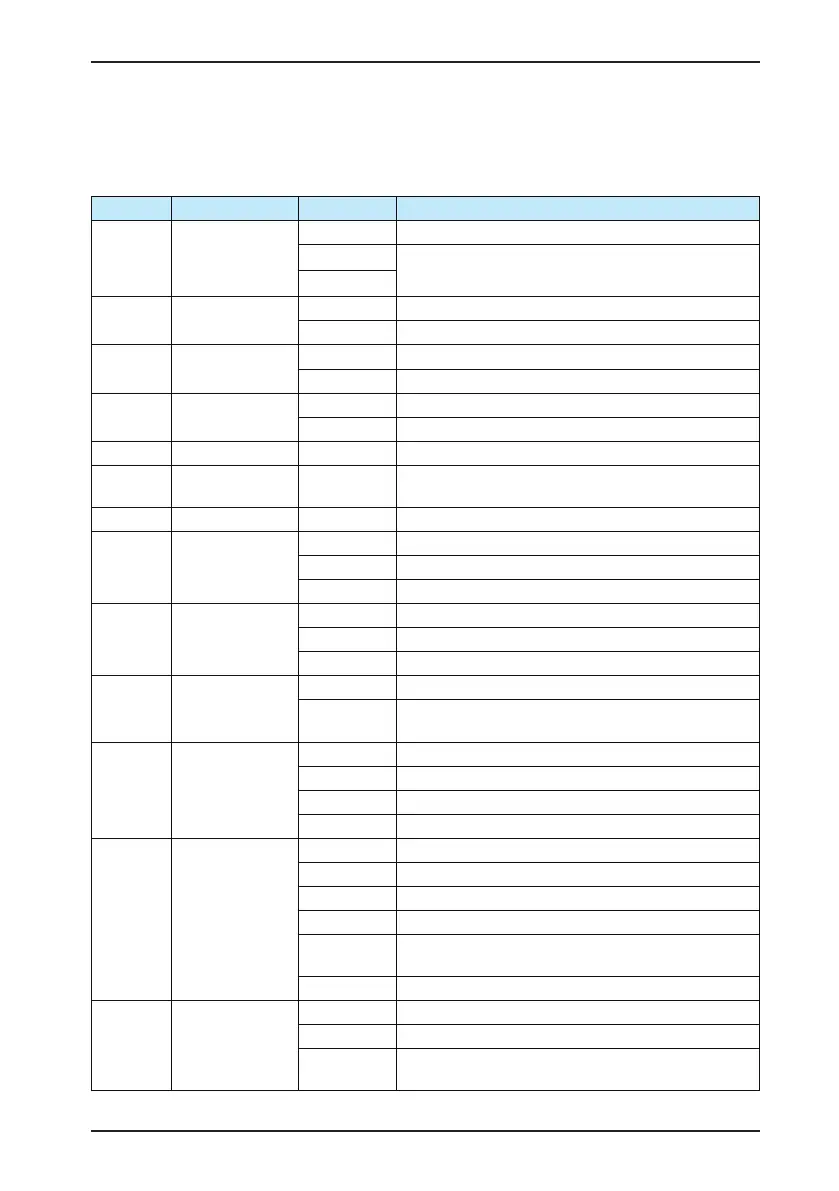
8.5 Introduction to Fault Sub-code
To nd the fault cause quickly, the CS200 provides the fault sub-code. When you view the fault code (E*), the two
digits after the decimal point in E*.00 indicate the fault sub-code.
Fault Code Fault Code Meaning Fault Sub-code Fault Sub-code Meaning
02# to 04# Overcurrent
1 Hardware overcurrent
2
Reserved
3
05# to 07# Overvoltage
1 Interruption detection software overvoltage
2 Timing detection software overvoltage
09# Undervoltage
1 Timing detection software undervoltage
2 Undervoltage occurring during power-on
10# AC drive overload
1 Overload reported according to the overload curve.
2 Overload reported during pulse-by-pulse current limit
11# Motor overload 1 Normal motor overload
15#
Built-in braking unit
overload
1 to 7
Fault sub-code reported according to the brake pipe overload
curve
17# Contactor fault 1 Snubber resistor fault
18#
Current detection
fault
1 Phase U zero drift fault
2 Phase V zero drift fault
3 Phase W zero drift fault
19#
Motor auto-tuning
fault
1 Data overow during motor auto-tuning
2 Bus voltage detection fault
3 The motor auto-tuning times out.
20# Encoder fault
9 The encoder is not connected.
10
PPR of the encoder wroing (reported only during dynamic auto-
tuning)
23#
Short circuit to
ground
1 Hardware overcurrent
2 Hardware overvoltage
3 Software overcurrent
4 Software overvoltage
25#
Power output phase
loss
1 Phase U lost
2 Phase V lost
3 Phase W lost
4 Reserved
5
Phase loss reported during stator resistance auto-tuning while
power-on
6 Phase loss reported during normal stator resistance auto-tuning
48#
RS485
communication fault
1 No data is received from host computer.
2 Wrong data is received continuously.
3
The connection between the communication card and the host
computer is abnormal.

 Loading...
Loading...











