•
See E120 and E320 Module Guide, Table 1, Modules and IOAs for detailed module
specifications.
•
See E120 and E320 Module Guide, Appendix A, IOA Protocol Support for information
about the modules that support MLD.
References
For more information about MLD, see the following resources:
•
RFC 3710—Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) for IPv6 (October 1999) on page 578
•
IGMP/MLD-based Multicast Forwarding ('IGMP/MLD
Proxying')—draft-ietf-magma-igmp-proxy-06.txt (October 2004 expiration) on
page 587
•
Multicast Group Membership Discovery MIB—draft-ietf-magma-mgmd-mib-06.txt
(October 2004 expiration) on page 587
Before You Begin
You can configure MLD only on IPv6 interfaces. For information about configuring IPv6
interfaces, see Configuring IPv6 in the JunosE IP, IPv6, and IGP Configuration Guide.
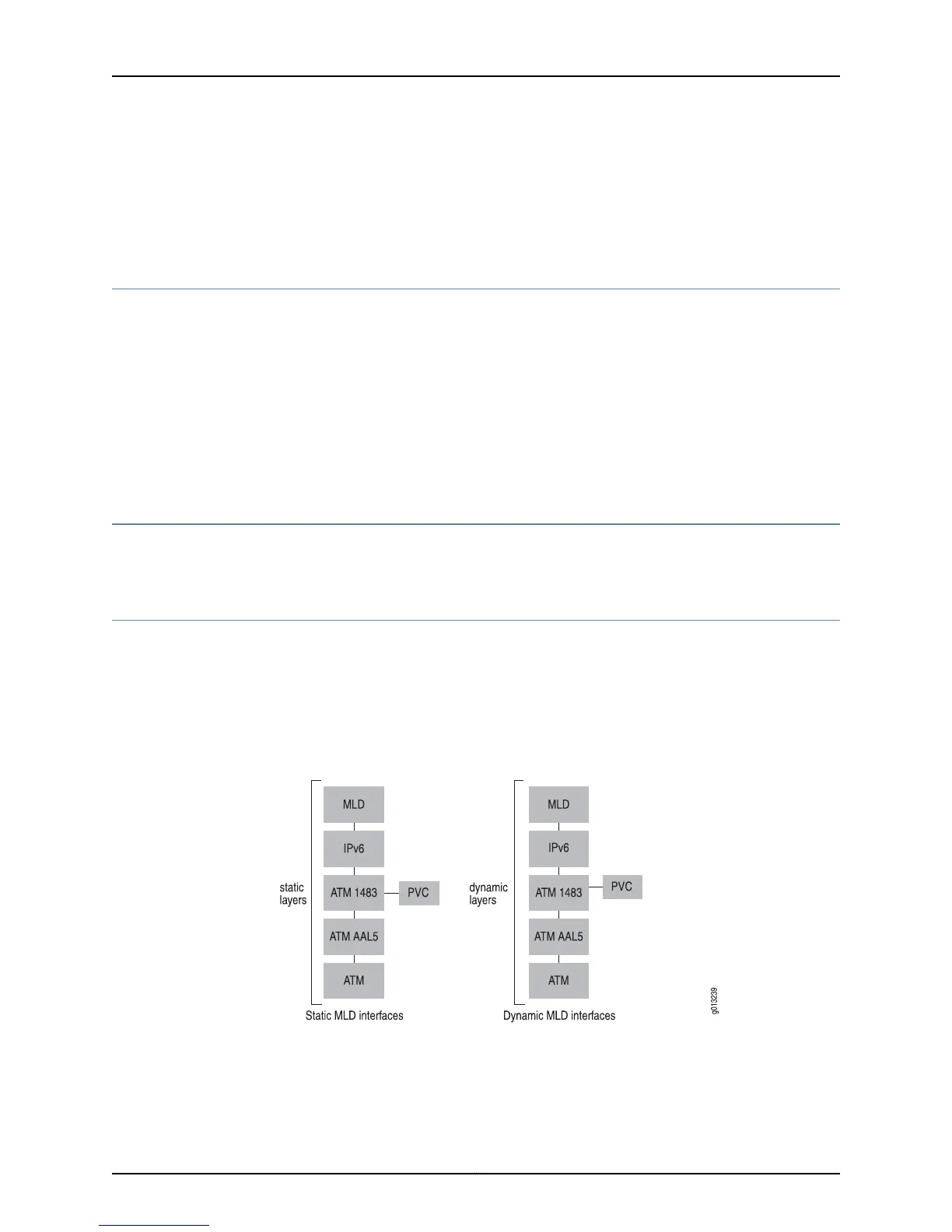
Configuring Static and Dynamic MLD Interfaces
The router supports static and dynamic MLD interfaces. Unlike static interfaces, dynamic
interfaces are not restored when you reboot the router. For some protocols, dynamic
layers can build on static layers in an interface; however, in a dynamic MLD interface, all
the layers are dynamic. See Figure 19 on page 178 for examples of static and dynamic MLD
interfaces.
Figure 19: Static and Dynamic MLD Interfaces
Static MLD interfaces are configured with software such as the CLI or an SNMP
application; dynamic MLD interfaces are configured with a profile. A profile comprises a
set of attributes for an interface; a profile for dynamic MLD interfaces contains attributes
for configuring all the layers in the interface.
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.178
JunosE 11.2.x Multicast Routing Configuration Guide
 Loading...
Loading...