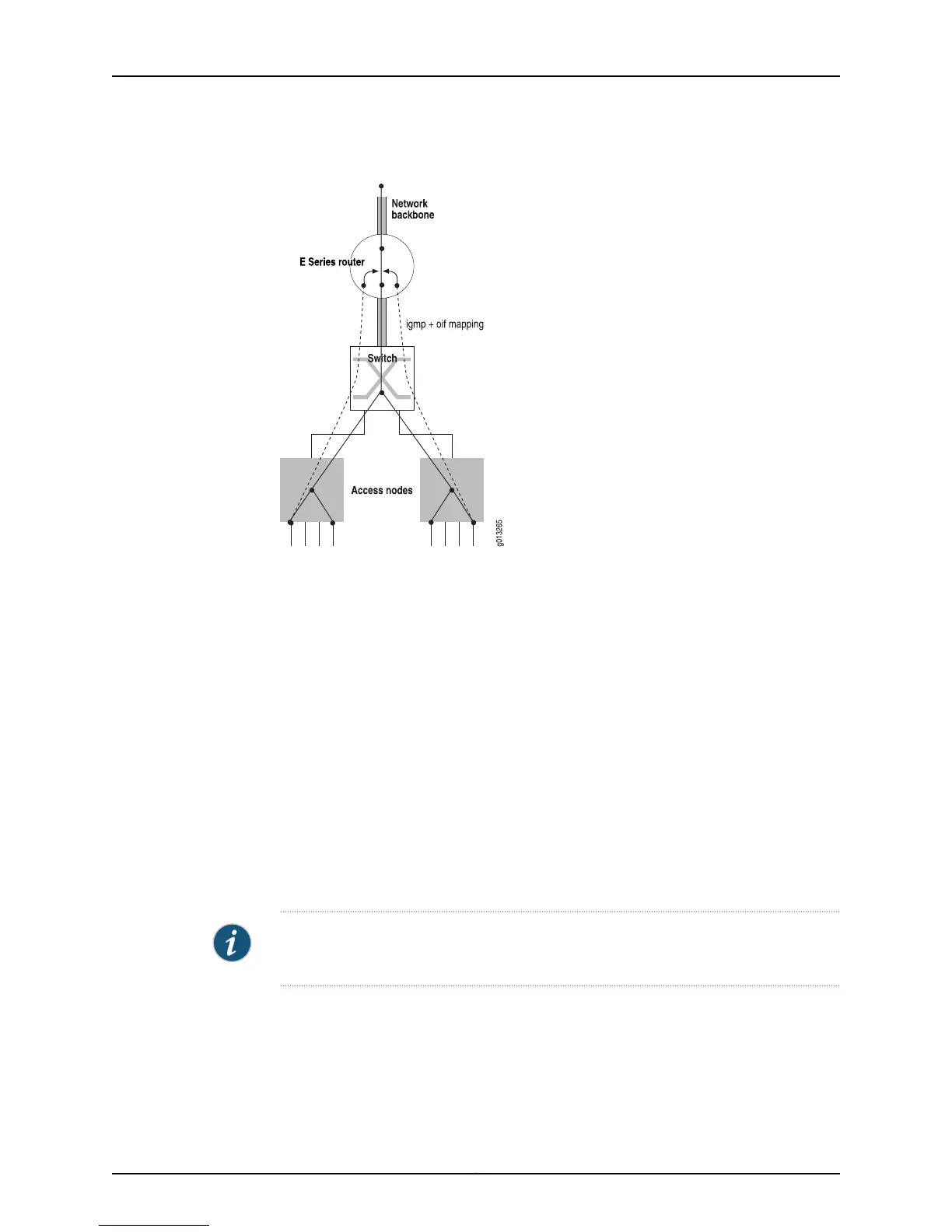
Figure 2: Multicast OIF Mapping
One disadvantage to using multicast OIF mapping is that the multicast traffic bypasses
any QoS treatment that is applied to subscriber interfaces. Configuring QoS adjustment
resolves this problem. (See Parameter Definition Attributes for QoS Administrators
Overview for additional information about configuring QoS adjustment.) With QoS
adjustment configured, when a subscriber requests to receive a multicast stream (or,
more appropriately, when an OIF is added to the mroute), the router reduces the unicast
QoS bandwidth applied to the subscriber interface (that is, the join interface) by the
amount of bandwidth for that multicast stream.
Multicast Traffic Receipt Without Forwarding
In this case, the router is not given the responsibility of forwarding multicast streams.
Instead, the service provider arranges for the router to receive the multicast streams so
the router can detect the flow and perform QoS adjustment. An OIF map is installed that
maps the traffic streams to a loopback interface configured for IGMP version passive.
This means that when the traffic is received, a null mroute is installed (that is, an mroute
with an empty OIF list) and the router applies the QoS adjustment to the join interface.
See Figure 3 on page 17.
NOTE: Ensure that PIM-SM (or any other upstream multicast protocol) is informed of
the group (or source-group) interest.
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.16
JunosE 11.2.x Multicast Routing Configuration Guide
 Loading...
Loading...